Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Biodegradable Piezoelectric Micro- and Nanomaterials for Regenerative Medicine, Targeted Therapy, and Microrobotics
- First Published: 28 January 2025
This article outlines the key efforts in the state-of-the-art of biodegradable piezoelectric nanomaterials and their possible impact in the biomedical field. Material types and compositions, fabrication techniques, methods to enhance piezoelectric properties, and characterization approaches are described. Specific applications of these materials in regenerative medicine, targeted therapy, and microrobotics are discussed, highlighting current challenges and future directions.
Self-Assembled Peptide-Gold Nanoclusters with SiRNA Targeting Telomeric Response to Enhance Radiosensitivity in Lung Cancer Cells
- First Published: 16 December 2024
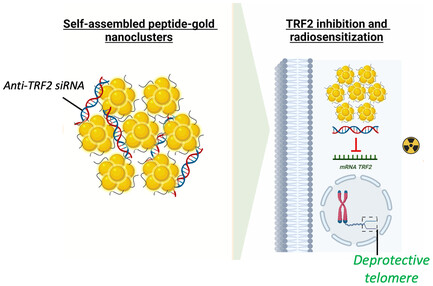
Lung cancer cells resistant to radiotherapy pose a challenge, linked to TRF2 protein's role in telomere protection. A self-assembling system with luminescent gold nanoclusters and siRNA downregulates TRF2, enhancing radiosensitivity. This 100 nm nonspherical structure boosts photoluminescence and penetrates cells, reducing TRF2 expression by 50% and clonogenic survival by 2.3-fold, promising improved radiotherapy.
A Corn-Based Electrically Conductive Glue for Integration of Edible Electronics
- First Published: 05 December 2024
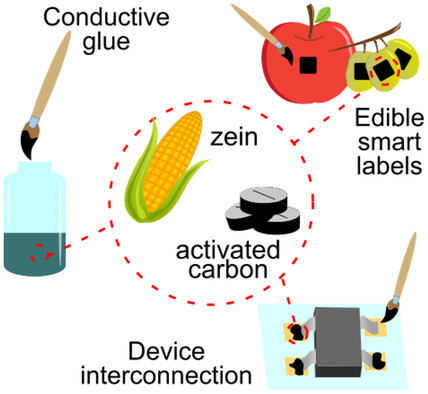
An electrically conductive glue is formulated using only food-grade materials (zein from corn and activated carbon) for the development of complex circuits in the field of edible electronics. As a proof-of-concept, the edible glue is applied in different examples, such as device-mounting on edible substrates, interconnection of edible batteries, and impedance analysis electrodes for fruit.
An In vitro Caco2-Based Model for Measuring Intestinal Bioadhesion Comparable to Ex vivo Models
- First Published: 03 December 2024
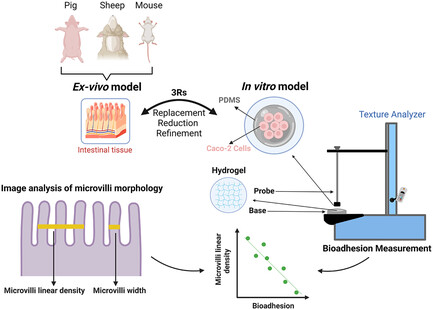
This study introduces an in vitro Caco-2 cell model for measuring intestinal bioadhesion, offering an alternative to animal-based ex vivo methods. Using a texture analyzer, the model predicts the bioadhesive properties of materials under varying forces and durations, replicating ex vivo findings. Moreover, the study provides valuable insights into the influence of microvilli morphology on bioadhesion.
Space-Confined Growth of Ultrathin 2D β-Ga2O3 Nanoflakes for Artificial Neuromorphic Application
- First Published: 12 September 2024
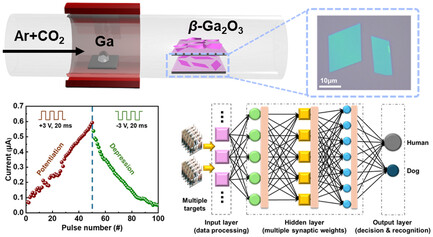
β-Ga2O3, a wide-bandgap semiconductor, has gained attention for its excellent properties, particularly in its 2D form. In this work, high-quality 2D β-Ga2O3 nanoflakes is synthesized using space-confined chemical vapor deposition, achieving excellent electrical switching and a 96% accuracy in handwritten numeral recognition. Also, in this work, the synthesis of 2D non-layered oxides and their applications in neuromorphic systems is advanced.
Renal Clearable H-Dots Leveraging Ligand Complexation for Enhanced Active Tumor Targeting
- First Published: 13 August 2024
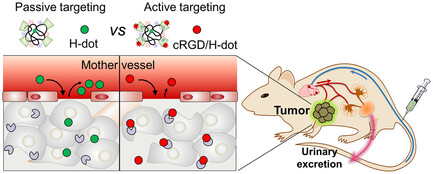
Renal clearable cyclic arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (cRGD)/H-dots demonstrate enhanced active tumor targeting by forming complexes with cRGD, while maintaining essential characteristics including minimum nonspecific uptake and rapid urinary excretion. This study offers significant promise for cRGD/H-dot as a prospective therapeutic nanoplatform in oncological interventions.
Instant Upcycling of Microplastics into Graphene and Its Environmental Application
- First Published: 07 August 2024
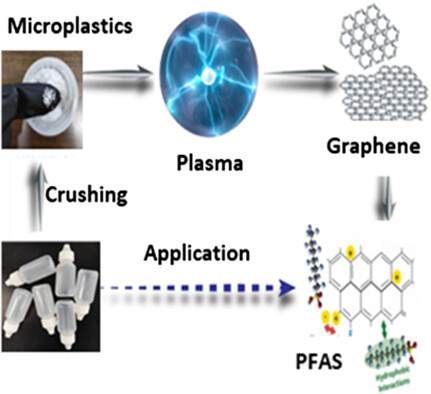
This study demonstrates the upcycling of polyethylene microplastics into high-quality graphene using atmospheric pressure microwave plasma (APMP) synthesis. APMP offers a sustainable, energy-efficient alternative to traditional methods, producing graphene with enhanced properties for specific applications. The graphene shows significant potential for environmental remediation, effectively adsorbing perfluorooctanoic acid from water.
Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal-Like Cells Promote 3D-Engineered Muscle Tissue Differentiation and Vessel Network Maturation
- First Published: 06 August 2024
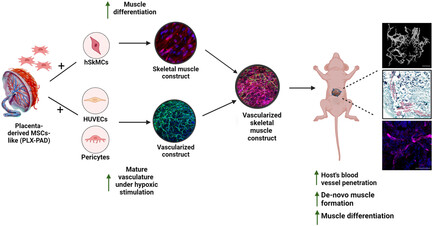
Research demonstrates that placenta-derived stromal-like cells (PLX-PAD) enhance vascularization and maturation in engineered skeletal muscle tissues. This study reveals that PLX-PAD cells promote muscle differentiation and vascular network formation in co-culture with myoblasts, endothelial cells, and support cells in 3D scaffolds. Such advancements suggest potential therapeutic applications in muscle tissue regeneration and recovery.
Efficient Nebulization and Pulmonary Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanocarriers in an Acute Lung Injury Preclinical Model
- First Published: 18 June 2024
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanocapsules (NCs) are investigated as inhalable nanotherapeutics. Stable aerosols can be produced using a commercial nebulizer without any significant alteration of the NCs. In vivo studies with healthy and acute lung injury animals show NCs homogeneously distributed throughout the lungs, arriving at even distal areas. NCs are internalized by alveolar type II cells, avoiding macrophage-mediated lung clearance.
Preclinical Development of a Genetically Engineered Albumin-Binding Nanoparticle of Paclitaxel
- First Published: 25 September 2024
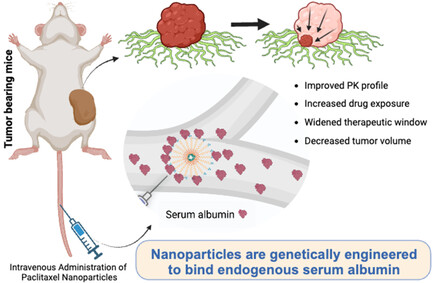
Genetically engineered paclitaxel nanoparticles bind endogenous serum albumin post administration, leveraging albumin's long half-life to improve circulation time, drug exposure, and therapeutic window. These albumin-binding nanoparticles double the therapeutic window compared to nonalbumin-binding counterparts and outperform nab-paclitaxel in various murine tumor models, with results independently confirmed by a contract research organization.
Multi-Organ Microphysiological Systems Targeting Specific Organs for Recapitulating Disease Phenotypes via Organ Crosstalk
- First Published: 19 September 2024
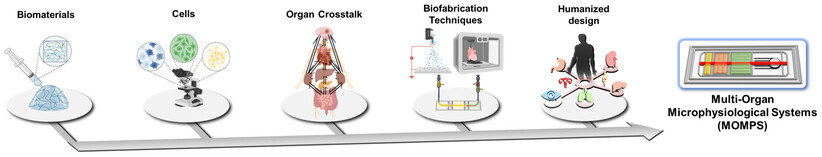
Multi-organ microphysiological systems (MOMPS) replicate human microphysiology and interorgan crosstalk. The precise fabrication of MOMPS requires various elements, including biomaterials, cell sources, accurate organ crosstalk, biofabrication techniques, and humanized design. The MOMPS enhances the understanding of systemic metabolic disease mechanisms, improves drug development, and increases the efficiency of preclinical studies by capturing the complexity of organ interactions and tissue-specific microenvironments..
Advancing Selective Extraction: A Novel Approach for Scandium, Thorium, and Uranium Ion Capture
- First Published: 28 August 2024
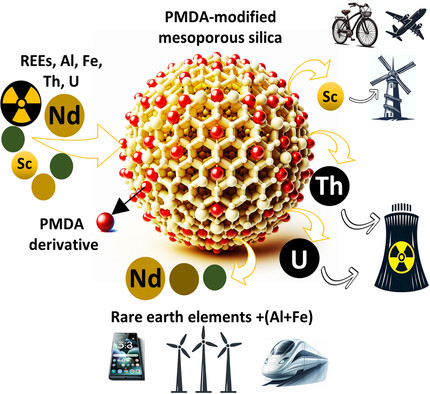
This study introduces an advanced functionalized mesoporous silica sorbent that demonstrates effectiveness in selectively extracting Sc, Th, and U from complex multi-element solutions containing REEs and competitive elements. It offers a dual solution: targeted extraction of Th, U, and Sc, and their separation from REEs, addressing a major challenge in critical materials recovery and separation.
A Glance into the Near Future: Cultivated Meat from Mammalian and Insect Cells
- First Published: 08 July 2024
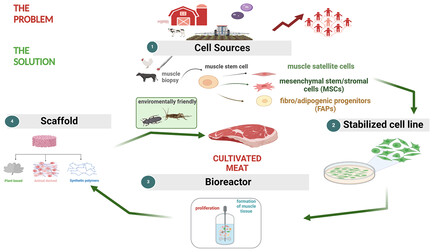
Growing demand for meat and environmental concerns are driving the search for sustainable alternatives for meat production. Cultured meat from animal stem cells, particularly insect stem cells, is emerging as an efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly option. This option not only meets continuing increase in global meat demand, but also highlights insects as a compelling alternative to conventional practices.
Modelling Human Gut-Microbiome Interactions in a 3D Bioelectronic Platform
- First Published: 22 April 2024
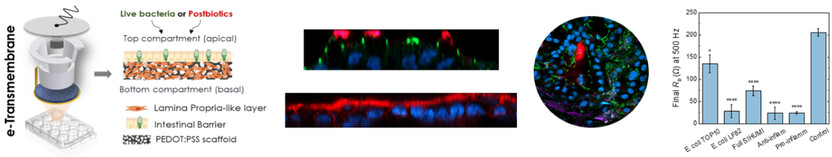
A novel 3D bioelectronic platform, “e-Transmembrane”, provides a unique biomimetic niche for the development and dynamic monitoring of an advanced human stratified intestinal model. Exposure of this bioengineered tissue to postbiotic cohorts or live bacteria showcases the unique capabilities of the platform to model gut–microbiota interactions, offering a new and sophisticated way to study such complex systems in vitro.
Quantifying Titanium Exposure in Lung Tissues: A Novel Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Elemental Imaging-Based Analytical Framework for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 03 March 2024
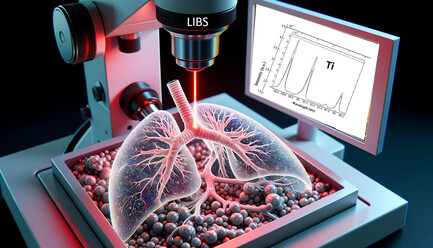
Herein, a novel analytical framework leveraging laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantifying titanium in lung tissues is introduced. Presenting a robust correlation with elemental concentrations, the method offers a significant advancement in volumetric organ analysis. The approach's efficacy is demonstrated through meticulous biomedical applications, providing a foundational technique for future elemental imaging research or clinical investigations.
Exploiting the Warburg Effect: Co-Delivery of Metformin and FOXK2 siRNA for Ovarian Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 29 January 2024
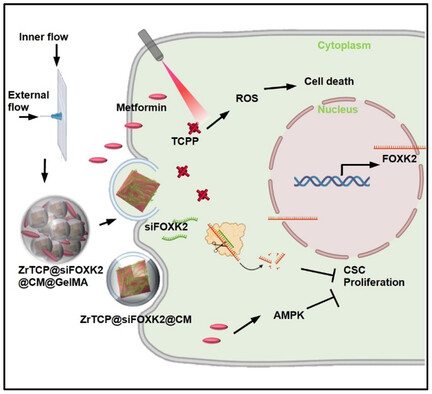
An innovative therapeutic approach leverages the Warburg effect in ovarian cancer, combining forkhead box protein K2 (FOXK2) siRNA and metformin. Using advanced microfluidic technology, zirconium and 5,10,15,20-tetra(4-pyridyl)porphyrin nanoparticles loaded with FOXK2 siRNA, enveloped in cell membrane, co-encapsulated with metformin in gelatin methacrylate microspheres (ZrTCP@siFOXK2@CM/Met@GelMA) hydrogel microspheres, are introduced, highlighting a transformative strategy to target cancer's metabolic vulnerabilities effectively.
The Counterbalancing Role of Oxygen Vacancy between the Electrochromic Properties and the Trapping Effect Passivation for Amorphous Tungsten Oxide Films
- First Published: 20 January 2024
Investigation of Atomic-Scale Mechanical Behavior by Bias-Induced Degradation in Janus and Alloy Polymorphic Monolayer TMDs via In Situ TEM
- First Published: 21 November 2023
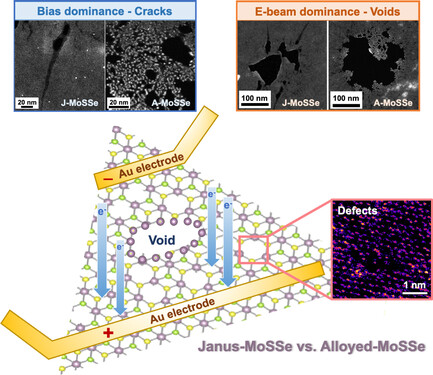
Janus and alloy polymorphic monolayer molybdenum sulfide selenide (MoSSe) prepared at different selenization temperatures exhibits different electrical and mechanical properties after biasing. In the structural degradation of MoSSe, powerful in situ transmission electron microscope (TEM) and annular dark-field scanning TEM are used to understand the individual effects of electron beams and bias.
An Open-Source Multifunctional Testing Platform for Optical Phase Change Materials
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Chalcogenide phase change materials show great promise for tunable nanophotonic devices. An open-source electrical switching platform enabling in situ, high-throughput, and multimodal testing of phase change materials is presented. The platform will accelerate the discovery and characterization of new phase change materials and facilitate their integration with on-chip photonic devices.
From Inside Out: How the Buried Interface, Shell Defects, and Surface Chemistry Conspire to Determine Optical Performance in Nonblinking Giant Quantum Dots
- First Published: 10 October 2023
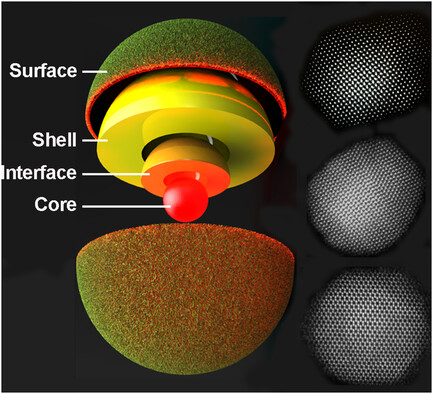
The functionally unique “giant” quantum dot—a nonblinking and nonphotobleaching room-temperature photon source—is the subject of numerous investigations of its optical properties and application demonstrations from 3D single-molecule tracking to light-emitting diodes. In this work, explicit synthesis–structure–function correlations are revealed as a blueprint for designing syntheses to produce nanoscale structures for long-term stability under harsh operating conditions of high-temperature and photon flux.