Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cancer Epidemiology & Prevention
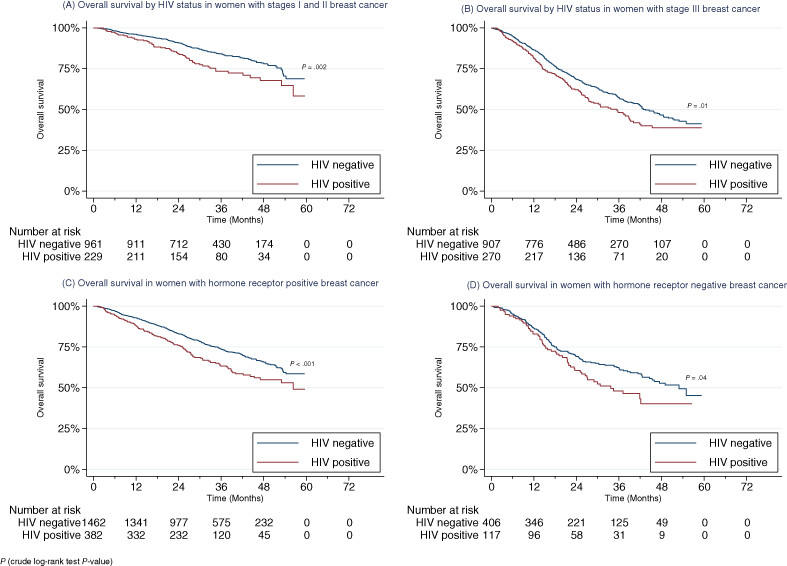
Impact of HIV infection on survival among women with stage I-III breast cancer: Results from the South African breast cancer and HIV outcomes study
- First Published: 26 February 2022
What's new?
Breast cancer patients living with HIV are a growing population globally. Associations between HIV status and breast cancer subtype, treatment and survival, however, remain unclear. In this investigation of women with nonmetastatic breast cancer in South Africa, patients living with HIV at breast cancer diagnosis were found to be at significantly greater risk of death from any cause than non-HIV-infected women with breast cancer. This finding persisted after accounting for differences in age, ethnicity, cancer stage, cancer subtype and treatments received. The findings cast light on adverse impacts linked to HIV infection in nonmetastatic breast cancer patients, despite antiretroviral therapy.
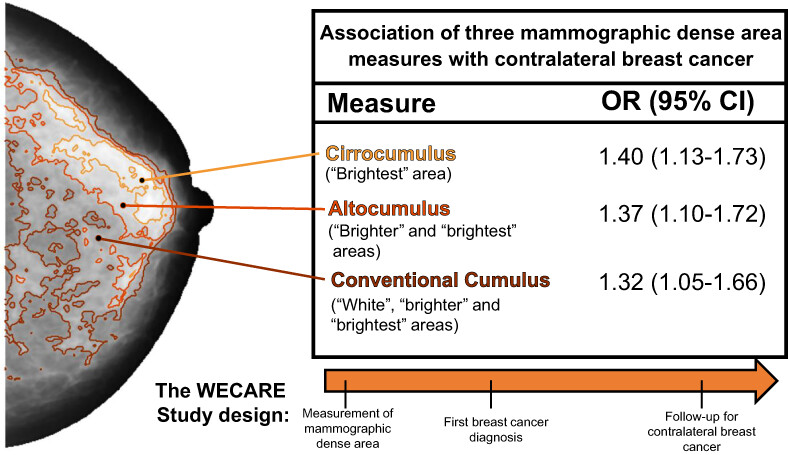
Association of contralateral breast cancer risk with mammographic density defined at higher-than-conventional intensity thresholds
- First Published: 22 March 2022
What's new?
Breast cancer survivors have a high risk of subsequent contralateral breast cancer. Recent studies have found that risk prediction of primary breast cancer risk might be improved by redefining mammographic dense area in breast cancer screening at higher-than-conventional intensity thresholds. Here, the authors found that a modified measure of the mammographic dense area using higher-intensity thresholds had a stronger association with contralateral breast cancer risk than conventional measures. These results further improve our understanding of mammographic density as a risk factor for contralateral breast cancer and provide a potential new risk stratification tool for breast cancer survivors.
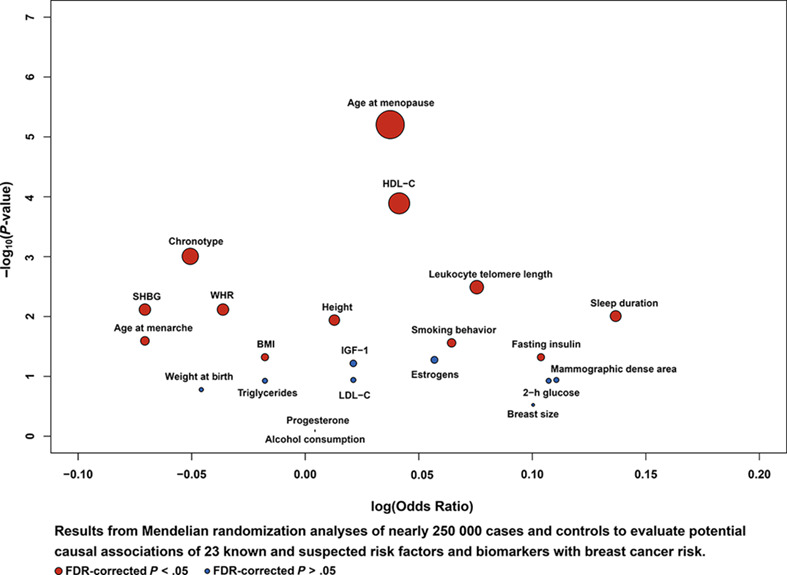
Mendelian randomization analyses of 23 known and suspected risk factors and biomarkers for breast cancer overall and by molecular subtypes
- First Published: 11 April 2022
What's new?
Many risk factors have been identified for breast cancer in observational studies. But the potential causality for some of these associations has not yet been established, and few studies have comprehensively investigated these associations by molecular subtype. This large two-sample Mendelian randomization study supports potential causal associations for 15 risk factors and blood biomarkers with the risk of breast cancer. The results also show that the association of breast cancer risk with certain risk factors and biomarkers may differ by estrogen receptor status and intrinsic subtype, highlighting the heterogeneous nature of this disease.
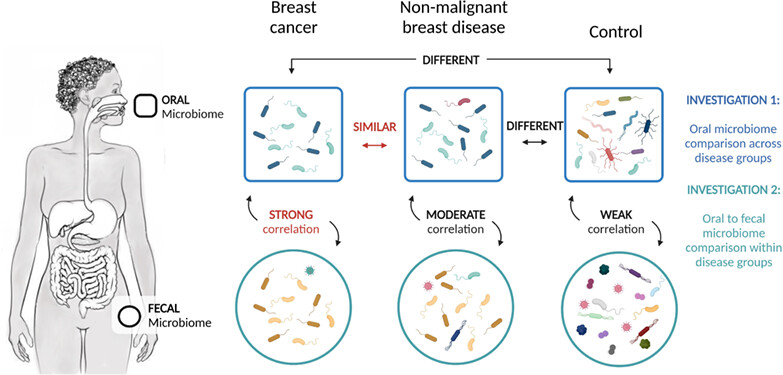
The oral microbiome and breast cancer and nonmalignant breast disease, and its relationship with the fecal microbiome in the Ghana Breast Health Study
- First Published: 03 June 2022
What's new?
Recently, researchers have begun investigating the relationship between the body's microbiome and various diseases, including cancers. Here, the authors looked at the oral microbiome and its association with both breast cancer and nonmalignant breast disease. Using data from 881 women enrolled in the Ghana Breast Health Study, including 369 breast cancers, 93 nonmalignant cases and 419 population-based controls, they found that the makeup of the oral microbiome was strongly associated with both conditions. They also identified a strong inverse correlation between a periodontal disease bacteria and a fecal microbe associated with breast cancer.
Survival outcomes for dose-dense paclitaxel plus carboplatin neoadjuvant vs standard adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II to III triple-negative breast cancer: A prospective cohort study with propensity-matched analysis
- First Published: 11 April 2022
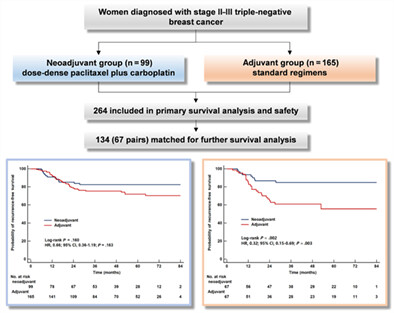
What's new?
Evidence for the long-term outcomes of platinum-based (anthracycline-free) neoadjuvant chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer remains scarce. In this prospective study conducted among stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer patients, patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy with dose-dense paclitaxel plus carboplatin (ddPCb) had a significantly better recurrence-free survival and overall survival, compared to the matched cohort receiving standard adjuvant chemotherapy. Moreover, ddPCb was related to less neutropenia and more thrombocytopenia. Altogether, the findings support the consideration of platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy for promising survival benefits, and the ddPCb regimen is emerging as an innovative and well-tolerated option.
Leptomeningeal metastases in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer: Real-world data from a multicentric European cohort
- First Published: 06 June 2022
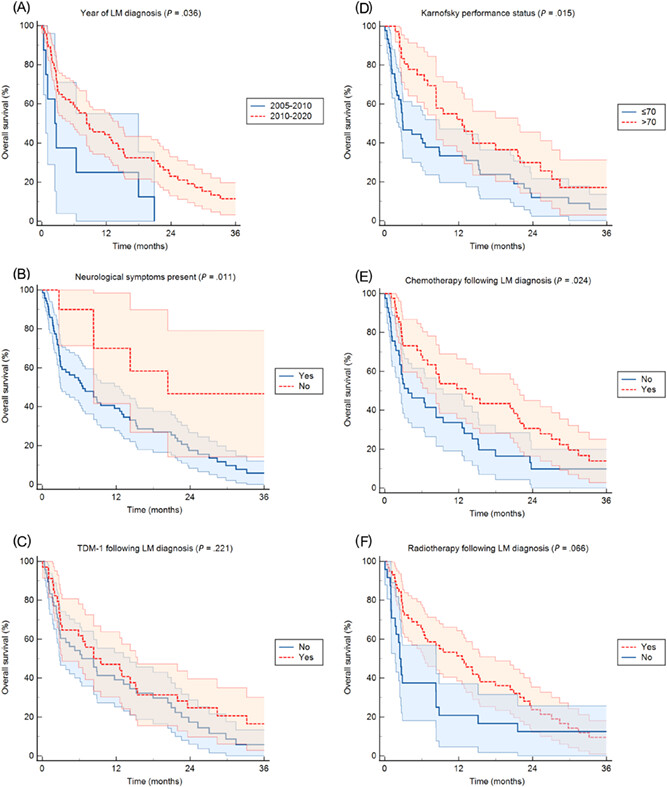
What's new?
Patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer and leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) are likely to suffer neurological damage. The degree to which neurological symptoms are evident and their impact on survival remain uncertain. Here, investigation of pathological features and survival in a European cohort of HER2+ breast cancer patients with LM shows that preexisting brain metastases are common at LM diagnosis, affecting as many as two-thirds of patients. Overall survival was longer among patients who lacked neurological symptoms and who received radiotherapy at LM diagnosis. Longer survival was further linked to the use of multimodality therapy.
Biological Insights
Amplified Ca2+ dynamics and accelerated cell proliferation in breast cancer tissue during purinergic stimulation
- First Published: 03 June 2022
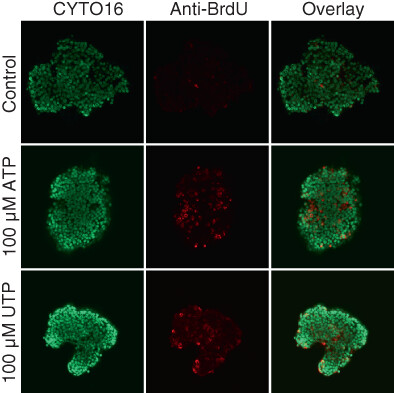
What's new?
Molecular mechanisms influencing intracellular Ca2+ dynamics are deregulated in cancer cell lines. However, many implications of deregulated Ca2+ signaling during carcinogenesis remain unclear. Using fresh human and murine tissue biopsies, here the authors show that resting intracellular Ca2+ levels, organellar Ca2+ storage and intracellular Ca2+ responses to nucleotides and cholinergic stimuli are elevated during breast, but not colon, carcinogenesis. Nucleotides stimulate proliferation in breast cancer tissue within the elevated nucleotide concentration range observed in the tumor microenvironment, whereas cell death is induced only at higher concentrations. The authors propose that amplified Ca2+ signals facilitate breast malignancy.
mdm2 gene amplification is associated with luminal breast cancer progression in humanized PDX mice and a worse outcome of estrogen receptor positive disease
- First Published: 20 December 2021
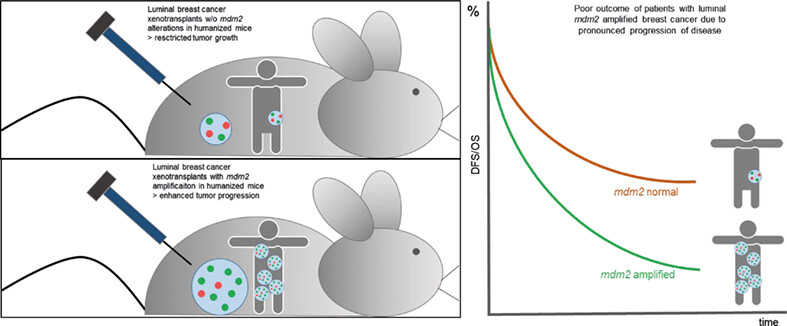
What's new?
Breast cancer is extremely heterogeneous, even within subtypes. For best outcomes, therapies must be tailored to the molecular profile of the particular tumor. Here, the authors searched for new biomarkers in ER-positive breast cancer using a humanized tumor mouse (HTM) model, which replicates a functional human immune system. They discovered that amplification of a gene, mdm2, was associated with tumor progression. Treatment with agents that inhibit mdm2 slowed down cell proliferation, viability and migration of cancer cells in vitro. Clinical testing for mdm2 status could help improve targeted treatment for these patients.
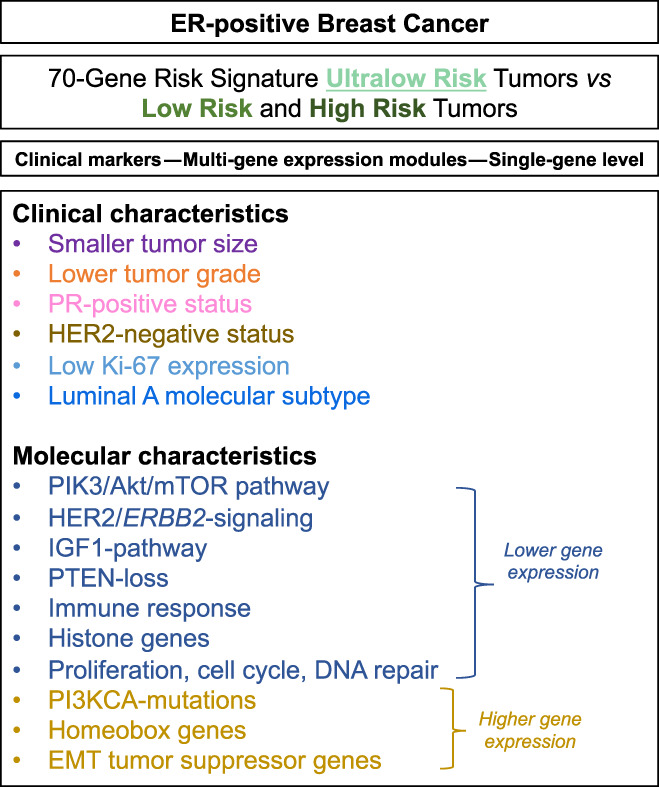
Clinical and molecular characteristics of estrogen receptor-positive ultralow risk breast cancer tumors identified by the 70-gene signature
- First Published: 18 February 2022
What's new?
The metastatic potential of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancers is heterogeneous, and distant recurrences may occur months to decades after primary diagnosis. However, the long-term risk of metastatic disease in breast cancer remains largely unexplored. Using a previously-established 70-gene signature to identify breast cancer patients with minimal long-term risk of fatal disease, here the authors show that ultralow-risk tumors differ from other ER-positive breast cancer tumors, including luminal molecular subtype tumors. Differences were found in both clinical breast cancer markers and molecular features. These results are important for the characterization and prediction of non-fatal vs fatal breast cancer.
Regulatory networks and 5′ partner usage of miRNA host gene fusions in breast cancer
- First Published: 19 February 2022
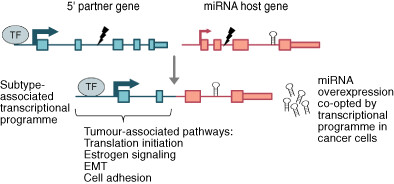
What's new?
Fusion transcripts have been identified in many tumour types, but it remains unclear how many of them represent functional tumour drivers versus passenger events. Among several mechanisms causing deregulation of miRNA expression in cancer, genomic rearrangements can create microRNA host gene fusions that alter microRNA expression regardless of the protein-coding potential of the fusion transcript. The authors show that the 5′ partners of host fusions are highly-expressed genes in subtype-specific pathways active in breast cancer. Host fusions can thereby provide material for genetic selection and tumour evolution in cancer cells, with miRNA host fusions potentially acting as tumour drivers.




