Imidodiphosphorimidates (IDPis): Catalyst Motifs with Unprecedented Reactivity and Selectivity
Jun Kee Cheng
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorShao-Hua Xiang
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin Tan
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJun Kee Cheng
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorShao-Hua Xiang
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin Tan
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The conceptually designed imidodiphosphorimidates (IDPis) have emerged as one of the most potent classes of chiral acid catalysts. They are characterized by enzyme-like, highly confined active site and high acidity, which underlie their wide-reaching applications as Brønsted acid catalysts and as precatalysts for silylium Lewis acids. Many carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bond formation reactions that were deemed intractable could now be attained with spectacular reactivity and selectivity. Substrates that are small, unbiased and/or possess insufficient reactivity such as simple alkenes could now be engaged. The high structural confinement is particularly invaluable to control stereo- and chemoselectivity. The well-defined steric environment offers unique opportunity to control high-energy but structurally unbiased cation intermediates such as the norbonyl cations. Beyond practical appeals such as good scalability as well as ease and modularity of preparation, the extremely low pre-catalyst loadings required to achieve high turnover and stereoselectivity have also come to define a new frontier in organocatalysis. 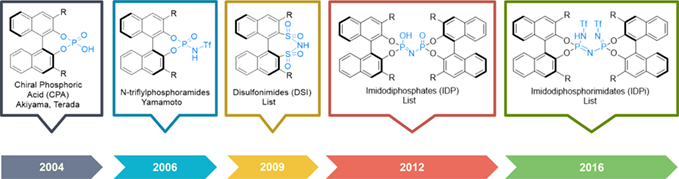
References
- 1 Acid Catalysis in Modern Organic Synthesis, Eds.: H. Yamamoto; K. Ishihara, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008.
- 2
Lewis Acids in Organic Synthesis, Ed.: H. Yamamoto, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2000.
10.1002/9783527618309 Google Scholar
- 3 Akiyama, T.; Itoh, J.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Enantioselective Mannich-Type Reaction Catalyzed by a Chiral Brønsted Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566−1568.
- 4 Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. Chiral Brønsted Acid-Catalyzed Direct Mannich Reactions via Electrophilic Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356−5357.
- 5 Parmar, D.; Sugiono, E.; Raja, S.; Rueping, M. Complete Field Guide to Asymmetric BINOL-Phosphate Derived Brønsted Acid and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Brønsted Acidity, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion Pairing, and Metal Phosphates. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9047–9153.
- 6 Parmar, D.; Sugiono, E.; Raja, S.; Rueping, M. Addition and Correction to Complete Field Guide to Asymmetric BINOL-Phosphate Derived Brønsted Acid and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Brønsted Acidity, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion Pairing, and Metal Phosphates. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10608–10620.
- 7 Lv, X.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z. Visible Light-Driven Cooperative DPZ and Chiral Hydrogen-Bonding Catalysis. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1480–1488.
- 8 Zhu, S.-F. Catalytic Hydrogen Transfer Reactions. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3211–3218.
- 9 Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z. Chiral Spirocyclic Phosphoric Acids and Their Growing Applications. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 802–824.
- 10 Da, B.-C.; Xiang, S.-H.; Li, S.; Tan, B. Chiral Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Asymmetric Synthesis of Axially Chiral Compounds. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1787–1796.
- 11 Li, S.; Xiang, S.-H.; Tan, B. Chiral Phosphoric Acid Creates Promising Opportunities for Enantioselective Photoredox Catalysis. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 213–214.
- 12
Yagupolskii, L. M.; Petrik, V. N.; Kondratenko, N. V.; Sooväli, L.; Kaljurand, I.; Leito, I.; Koppel, I. A. The immense acidifying effect of the supersubstituent =NSO2CF3 on the acidity of amides and amidines of benzoic acids in acetonitrile. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 2002, 1950–1955.
10.1039/B204172C Google Scholar
- 13 Nakashima, D.; Yamamoto, H. Design of Chiral N-Triflyl Phosphoramide as a Strong Chiral Brønsted Acid and Its Application to Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9626–9627.
- 14 Cheon, C. H.; Yamamoto, H. Super Brønsted acid catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3043–3056.
- 15 Akiyama, T.; Mori, K. Stronger Brønsted Acids: Recent Progress. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9277–9306.
- 16 Carreira, E. M.; Singer, R. A. Metal Versus Silyl Triflate Catalysis in The Mukaiyama Aldol Addition Reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 4323–4326.
- 17 Mayer, S.; List, B. Asymmetric Counteranion-Directed Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4193–4195.
- 18 Mahlau, M.; List, B. Asymmetric Counteranion-Directed Catalysis: Concept, Definition, and Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 518–533.
- 19 García-García, P.; Lay, F.; García-García, P.; Rabalakos, C.; List, B. A Powerful Chiral Counteranion Motif for Asymmetric Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4363–4366.
- 20 James, T.; van Gemmeren, M.; List, B. Development and Applications of Disulfonimides in Enantioselective Organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9388–9409.
- 21 Čorić, I.; List, B. Asymmetric Spiroacetalization Catalysed by Confined Brønsted Acids. Nature 2012, 483, 315–319.
- 22 Liao, S.; Čorić, I.; Wang, Q.; List, B. Activation of H2O2 by Chiral Confined Brønsted Acids: A Highly Enantioselective Catalytic Sulfoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10765–10768.
- 23 Kim, J. H.; Čorić, I.; Palumbo, C.; List, B. Resolution of Diols via Catalytic Asymmetric Acetalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1778–1781.
- 24 Liu, L.; Leutzsch, M.; Zheng, Y.; Alachraf, M. W.; Thiel, W.; List, B. Confined Acid-Catalyzed Asymmetric Carbonyl–Ene Cyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13268−13271.
- 25 Kim, J. H.; Tap, A.; Liu, L.; List, B. Catalytic Asymmetric Thioacetalization of Aldehydes. Synlett 2017, 28, 333–336.
- 26 Liu, L.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Tap, A.; List, B. A General Catalytic Asymmetric Prins Cyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10822−10825.
- 27 Kaib, P. S. J.; Schreyer, L.; Lee, S.; Properzi, R.; List, B. Extremely Active Organocatalysts Enable a Highly Enantioselective Addition of Allyltrimethylsilane to Aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13200–13203.
- 28 Schwengers, S. A.; Kanta De, C.; Grossmann, O.; Grimm, J. A. A.; Sadlowski, N. R.; Gerosa, G. G.; List, B. Unified Approach to Imidodiphosphate-Type Brønsted Acids with Tunable Confinement and Acidity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14835−14844.
- 29 Schreyer, L.; Properzi, R.; List, B. IDPi Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 58, 12761–12777.
- 30 Gatzenmeier, T.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Lingnau, J. B.; Goddard, R.; List, B. The Catalytic Asymmetric Mukaiyama–Michael Reaction of Silyl Ketene Acetals with α,β-Unsaturated Methyl Esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2464–2468.
- 31 Bae, H. Y.; Höfler, D.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Kasaplar, P.; De, C. K.; Döhring, A.; Lee, S.; Kaupmees, K.; Leito, I.; List, B. Approaching Sub-Ppm-Level Asymmetric Organocatalysis of a Highly Challenging and Scalable Carbon–Carbon Bond Forming Reaction. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 888–894.
- 32 Schreyer, L.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Wakchaure, V. N.; Obradors, C.; Properzi, R.; Lee, S.; List, B. Confined Acids Catalyze Asymmetric Single Aldolizations of Acetaldehyde Enolates. Science 2018, 362, 216–219.
- 33 Amatov, T.; Tsuji, N.; Maji, R.; Schreyer, L.; Zhou, H.; Leutzsch, M.; List, B. Confinement-Controlled, Either Syn- or Anti-Selective Catalytic Asymmetric Mukaiyama Aldolizations of Propionaldehyde Enolsilanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14475–14481.
- 34 Zhu, C.; Mandrelli, F.; Zhou, H.; Maji, R.; List, B. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Unprotected β2-Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 3312–3317.
- 35 Das, S.; Mitschke, B.; De, C. K.; Harden, I.; Bistoni, G.; List, B. Harnessing the Ambiphilicity of Silyl Nitronates in a Catalytic Asymmetric Approach to Aliphatic β3-Amino Acids. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 1043–1049.
- 36 Laina-Martín, V.; Fernández-Salas, J. A.; Alemán, J. Organocatalytic Strategies for the Development of the Enantioselective Inverse- electron-demand Hetero-Diels–Alder Reaction. Chem. - Eur. J. 2021, 27, 12509–12520.
- 37 Cycloaddition Reactions in Organic Synthesis, Eds.: S. Kobayashi; K. A. Jørgensen, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2002.
- 38 He, J.-X.; Si, X.-G.; Lu, Q.-T.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Cai, Q. An Enantioselective Approach to Heteroatom-containing Bicyclic Derivatives via Inverse- Electron-Demand Diels−Alder Reactions. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 21.
- 39 Liu, L.; Kim, H.; Xie, Y.; Farès, C.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Goddard, R.; List, B. Catalytic Asymmetric [4+2]-Cycloaddition of Dienes with Aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13656–13659.
- 40 Gatzenmeier, T.; Turberg, M.; Yepes, D.; Xie, Y.; Neese, F.; Bistoni, G.; List, B. Scalable and Highly Diastereo- and Enantioselective Catalytic Diels−Alder Reaction of α,β-Unsaturated Methyl Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12671–12676.
- 41 Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; De, C. K.; Yepes, D.; Neese, F.; Bistoni, G.; Leutzsch, M.; List, B. Strong and Confined Acids Control Five Stereogenic Centers in Catalytic Asymmetric Diels–Alder Reactions of Cyclohexadienones with Cyclopentadiene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12347–12351.
- 42 Kim, H.; Gerosa, G.; Aronow, J.; Kasaplar, P.; Ouyang, J.; Lingnau, J. B.; Guerry, P.; Farès, C.; List, B. A Multi-Substrate Screening Approach for the Identification of a Broadly Applicable Diels–Alder Catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 770.
- 43 Ghosh, S.; Erchinger, J. E.; Maji, R.; List, B. Catalytic Asymmetric Spirocyclizing Diels–Alder Reactions of Enones: Stereoselective Total and Formal Syntheses of α-Chamigrene, β-Chamigrene, Laurencenone C, Colletoic Acid, and Omphalic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6703-6708.
- 44 Ouyang, J.; Maji, R.; Leutzsch, M.; Mitschke, B.; List, B. Design of an Organocatalytic Asymmetric (4 + 3) Cycloaddition of 2-Indolylalcohols with Dienolsilanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 10156−10161.
- 45 Zhou, H.; Bae, H. Y.; Leutzsch, M.; Kennemur, J. L.; Bécart, D.; List, B. The Silicon−Hydrogen Exchange Reaction: A Catalytic σ-Bond Metathesis Approach to the Enantioselective Synthesis of Enol Silanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13695–13670.
- 46 Zhou, H.; Zhang, P.; List, B. The Silicon-Hydrogen Exchange Reaction: Catalytic Kinetic Resolution of 2-Substituted Cyclic Ketones. Synlett 2021, 32, 1953–1956.
- 47 Lee, S.; Kaib, P. S. J.; List, B. Asymmetric Catalysis via Cyclic, Aliphatic Oxocarbenium Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2156–2159.
- 48 Lee, S.; Bae, H. Y.; List, B. Can a Ketone Be More Reactive than an Aldehyde? Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Substituted Tetrahydrofurans. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12162–12166.
- 49 Grossmann, O.; Maji, R.; Aukland, M. H.; Lee, S.; List, B. Catalytic Asymmetric Additions of Enol Silanes to in Situ Generated Cyclic, Aliphatic N-Acyliminium Ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115036.
- 50 Properzi, R.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Leutzsch, M.; Pupo, G.; Mitra, R.; De, C. K.; Song, L.; Schreiner, P. R.; List, B. Catalytic Enantiocontrol over a non-Classical Carbocation. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 1174–1179.
- 51 Scharf, M. J.; List, B. A Catalytic Asymmetric Pictet−Spengler Platform as a Biomimetic Diversification Strategy toward Naturally Occurring Alkaloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 15451–1456.
- 52 Tsuji, N.; Kennemur, J. L.; Buyck, T.; Lee, S.; Prévost, S.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Bykov, D.; Farès, C.; List, B. Activation of Olefins via Asymmetric Brønsted Acid Catalysis. Science 2018, 359, 1501–1505.
- 53 Zhang, P.; Tsuji, N.; Ouyang, J.; List, B. Strong and Confined Acids Catalyze Asymmetric Intramolecular Hydroarylations of Unactivated Olefins with Indoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 675–680.
- 54 Zhou, H.; Han, J. T.; Nöthling, N.; Lindner, M. M.; Jenniches, J.; Kühn, C.; Tsuji, N.; Zhang, L.; List, B. Organocatalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Si-Stereogenic Silyl Ethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 10156−10161.
- 55 Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Bae, H. Y.; Leutzsch, M.; Li, Y.; De, C. K.; Cheng, G.-J.; List, B. Organocatalytic Stereoselective Cyanosilylation of Small Ketones. Nature 2022, 605, 84–89.
- 56 Cabirol, F. L.; Tan, P. L.; Tay, B.; Cheng, S.; Hanefeld, U.; Sheldon, R. A. Linum usitatissimum Hydroxynitrile Lyase Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates: A Recyclable Enantioselective Catalyst. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2329–2338.




