In Situ Generated Iron Oxide Nanocrystals as Efficient and Selective Catalysts for the Reduction of Nitroarenes using a Continuous Flow Method†
Dr. David Cantillo
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mostafa Baghbanzadeh
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. C. Oliver Kappe
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.netSearch for more papers by this authorDr. David Cantillo
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mostafa Baghbanzadeh
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. C. Oliver Kappe
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.net
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Microwave Chemistry (CDLMC) and Institute of Chemistry, Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Heinrichstrasse 28, 8010 Graz (Austria) http://www.maos.netSearch for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by a grant from the Christian Doppler Research Society (CDG). D.C. thanks the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of Spain for a scholarship. We also thank W. Gössler, W. Haas, and S. Mitsche for ICP-MS, TEM, and XRD analyses, respectively, and B. Gutmann for assistance with the continuous-flow experimentation.
Graphical Abstract
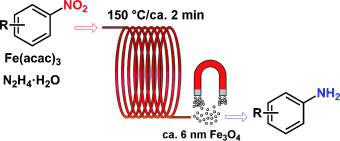
The best of both worlds: The benefits of homogeneous and heterogeneous nanocatalysis are combined, whereby highly reactive colloidal Fe3O4 nanocrystals are generated in situ that remain in solution long enough to allow the efficient and selective reduction of nitroarenes to anilines in continuous-flow mode (see scheme). After completion of the reaction, the nanoparticles aggregate and can be recovered by a magnet.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201205792_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf512.3 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. S. Downing, P. J. Kunkeler, H. van Bekkum, Catal. Today 1997, 37, 121;
- 1bN. Ono, The Nitro Group in Organic Synthesis, Wiley-VCH, New York, 2001.
10.1002/0471224480 Google Scholar
- 2
- 2aS. Nishimura, Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2001;
- 2bH. Arnold, F. Döbert, J. Gaube, Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 2008, pp. 3266–3284.
- 3
- 3aA. Corma, P. Serna, Science 2006, 313, 332;
- 3bL. He, L.-C. Wang, H. Sun, J. Ni, Y. Cao, H.-Y. He, K.-N. Fan, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9702; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9538;
- 3cM. Li, L. Hu, X. Cao, H. Hong, J. Lu, H. Gu, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2763;
- 3dH. Wu, L. Zhuo, Q. He, X. Liao, B. Shi, Appl. Catal. A 2009, 366, 44;
- 3eA. J. Amali, R. K. Rana, Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1781;
- 3fJ. Li, X. Shi, Y. Bi, J. Wei, Z. Chen, ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 657.
- 4A. M. Tafesh, J. Weiguny, Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2035.
- 5H. Berthold, T. Schotten, H. Hönig, Synthesis 2002, 1607.
- 6
- 6aK. Junge, B. Wendt, N. Shaikh, M. Beller, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1769;
- 6bL. Pehlivan, E. Métay, S. Laval, W. Dayoub, P. Demonchaux, G. Mignani, M. Lemaire, Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 1939.
- 7J. W. Bae, Y. J. Cho, S. H. Lee, C. O. M. Yoon, C. M. Yoon, Chem. Commun. 2000, 1857.
- 8X. Lin, M. Wu, D. Wu, S. Kuga, T. Endoe, Y. Huang, Green Chem. 2011, 13, 283.
- 9
- 9aG. Wienhöfer, I. Sorribes, A. Boddien, F. Westerhaus, K. Junge, H. Junge, R. Llusar, M. Beller, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12875;
- 9bI. Sorribes, G. Wienhöfer, C. Vicent, K. Junge, R. Llusar, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. 2012, DOI: ; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, DOI: .
- 10
- 10aA. Vass, J. Dudas, J. Toth, R. S. Varma, Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 5347;
- 10bM. Kumarraja, K. Pitchumani, Appl. Catal. A 2004, 265, 135;
- 10cQ. Shi, R. Lu, K. Jin, Z. Zhang, D. Zhao, Green Chem. 2006, 8, 868;
- 10dS. Kim, E. Kim, B. M. Kim, Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 1921;
- 10eU. Sharma, P. K. Verma, N. Kumar, V. Kumar, M. Bala, B. Singh, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 5903;
- 10fR. V. Jagadeesh, G. Wienhöfer, F. A. Westerhaus, A.-E. Surkus, M.-M. Pohl, H. Junge, K. Junge, M. Beller, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10972;
- 10gQ. Shi, R. Lu, L. Lu, X. Fu, D. Zhao, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1877;
- 10hP. Luo, K. Xu, R. Zhang, L. Huang, J. Wang, W. Xing, J. Huang, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 301.
- 11B. Plietker, Iron Catalysis in Organic Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008.
10.1002/9783527623273 Google Scholar
- 12For recent reviews on magnetic nanocatalysts see:
- 12aS. Shylesh, V. Schünemann, W. R. Thiel, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 3504;
10.1002/ange.200905684 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3428;
- 12bV. Polshettiwar, R. Luque, A. Fihri, H. Zhu, M. Bouhrara, J.-M. Basset, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3036.
- 13For some recent examples of iron oxide nanocatalysts see:
- 13aR. Luque, B. Baruwati, R. S. Varma, Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1540;
- 13bT. Zeng, W.-W. Chen, C. M. Cirtiu, A. Moores, G. Song, C.-J. Li, Green Chem. 2010, 12, 570;
- 13cN. Koukabi, E. Kolvari, A. Khazaei, M. A. Zolfigol, B. Shirmardi-Shaghasemi, H. R. Khavasi, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9230;
- 13dC. Yang, J. Wu, Y. Hou, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5130.
- 14
- 14aW.-W. Wang, Y.-J. Zhu, M.-L. Ruan, J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 419;
- 14bE. A. Osborne, T. M. Atkins, D. A. Gilbert, S. M. Kauzlarich, K. Liu, A. Y. Louie, Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 215602.
- 15Attempts to reduce aliphatic nitro compounds under these conditions were unsuccessful.
- 16T. N. Glasnov, C. O. Kappe, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 3089, and references therein.
- 17The calculated TOF for the nano-Fe3O4 catalyst for the nitro group reductions described herein is 3000 to 12000 h−1 (for comparison: 100 h−1,[10a] 0.6 h−1,[10c] 5 h−1,[10d] 28 h−1,[10e] and 10 h−1,[10f] each of them with larger excess of reducing reagent).
- 18T. N. Glasnov, C. O. Kappe, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 11956.
- 19
- 19aC. Wiles, P. Watts, Micro Reaction Technology in Organic Synthesis, CRC, Boca Raton, 2011;
- 19b Handbook of Micro Reactors (Eds.: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2009;
- 19c Microreactors in Organic Synthesis and Catalysis (Ed.: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008.
- 20For selected recent reviews on continuous-flow/microreactor chemistry, see:
- 20aC. Wiles, P. Watts, Green Chem. 2012, 14, 38;
- 20bT. Noël, S. L. Buchwald, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5010;
- 20cM. Baumann, I. R. Baxendale, S. V. Ley, Mol. Diversity 2011, 15, 613;
- 20dR. L. Hartman, J. P. McMullen, K. F. Jensen, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 7642;
10.1002/ange.201004637 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7502;
- 20eJ. Wegner, S. Ceylan, A. Kirschning, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4583;
- 20fJ.-I. Yoshida, H. Kim, A. Nagaki, ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 331.
- 21For a detailed description of the Uniqsis FlowSyn set-up, see: B. Gutmann, J.-P. Roduit, D. Roberge, C. O. Kappe, J. Flow Chem. 2012, 2, 8.