Strain- and torsion-induced resonance energy tuning of Raman scattering in single-wall carbon nanotubes
Abstract
Raman excitation profiles for homogeneously deformed single-walled carbon nanotubes are calculated and systematically analyzed. A number of attractive and apparent effects significant in designing electromechanical devices are caused by torsion and uniaxial strain. The shift of radial breathing mode (RBM) phonon energies due to deformation is negligible. The linear dependence of electronic transition energy shift on deformation is confirmed and it is found that the slope of it is strongly related to the chiral angle of the tube. It is also shown that for some tubes the transition energy shift covers the entire visible-light interval, making them perfectly tunable light absorbers. Two types of deformation are compared, a relaxed (slow) deformation and an adiabatic (fast) one. It is found that transition energies are more sensitive to adiabatic deformation, which can be useful for optomechanical device designing.
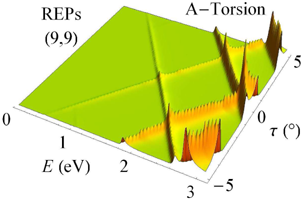
Raman excitation profile of a (9,9) nanotube under torsion.