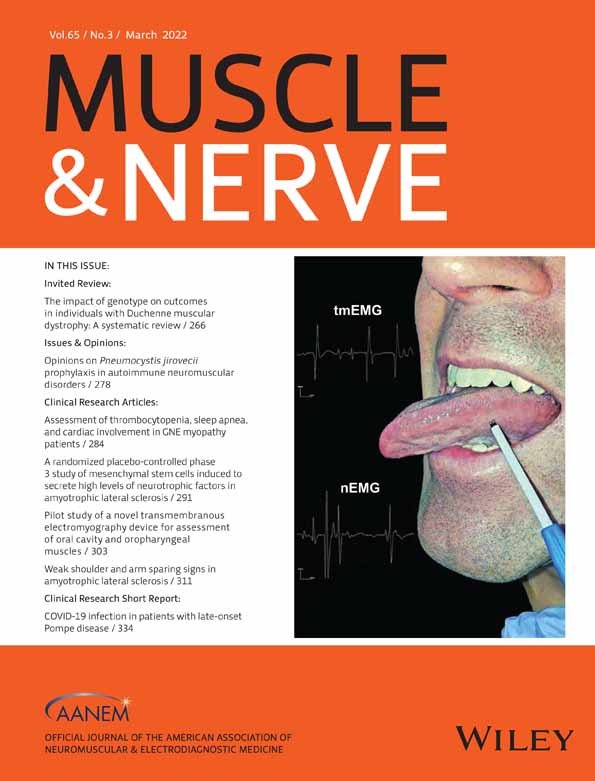
Pilot study of a novel transmembranous electromyography device for assessment of oral cavity and oropharyngeal muscles
Funding information: Powell Mansfield Inc.
Abstract
Introduction/Aims
Electromyography (EMG) can provide valuable insights into the pathophysiology of oropharyngeal muscles in various disease states, but the invasive nature of the conventional needle EMG (nEMG) has its limitations in this setting. We aimed to examine the inter-rater reliability (IRR) of a novel transmembranous EMG (tmEMG) sensor as a non-invasive technique for assessment of oral cavity and oropharyngeal muscles for neuromuscular pathology.
Methods
The study was a prospective, cohort, pilot study with blinded data analysis in healthy participants (n = 6), patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) (n = 5) and bulbar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (n = 5). Each patient underwent sampling from bilateral palatoglossus (PG) and genioglossus (GG), using both tmEMG and nEMG. IRR was expressed as percentage agreement and prevalence-adjusted bias-adjusted kappa coefficient (PABAK).
Results
Substantial IRR was found for participants with ALS (81.6%, PABAK 0.63) and OSA (78.8%, PABAK 0.61), and in healthy participants (87.1%, PABAK 0.74). A better IRR was seen with tmEMG (95.7%, PABAK 0.92) than with nEMG (73.9%, PABAK 0.48) for healthy participants and also for those with OSA. Studies from GG had higher IRR than PG. Only one participant had a minor adverse event (sore throat).
Discussion
The current study shows that analysis of PG and GG in both healthy and disease states using tmEMG has high IRR compared with nEMG analysis. Further validation studies can be undertaken to test its utility in analysis of oral cavity and oropharyngeal muscles.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Dr. Mansfield, Dr. Bril, and Mr. Studer have equity ownership in Powell Mansfield, Inc. Dr. Sheean, Dr. O'Leary, and Mr. Cordice serve or have served as consultants to Powell Mansfield, Inc.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request