Neurovascular stent artifacts in 3D-TOF and 3D-PCMRI: Influence of stent design on flow measurement
Corresponding Author
Pierre Bouillot
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Laboratory for Hydraulic Machines (LMH), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Correspondence
P. Bouillot, Service de Neuroradiologie, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève, Rue Gabrielle-Perret-Gentil 4, Geneva, CH-1211, Switzerland.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorOlivier Brina
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Medical Imaging, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorBénédicte M. A. Delattre
Division of Radiology, Geneva University Hospitals, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorRafik Ouared
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorAlain Pellaton
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorHasan Yilmaz
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorPaolo Machi
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorKarl-Olof Lovblad
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorMohamed Farhat
Laboratory for Hydraulic Machines (LMH), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorVitor Mendes Pereira
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Medical Imaging, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorMaria Isabel Vargas
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Pierre Bouillot
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Laboratory for Hydraulic Machines (LMH), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Correspondence
P. Bouillot, Service de Neuroradiologie, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève, Rue Gabrielle-Perret-Gentil 4, Geneva, CH-1211, Switzerland.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorOlivier Brina
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Medical Imaging, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorBénédicte M. A. Delattre
Division of Radiology, Geneva University Hospitals, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorRafik Ouared
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorAlain Pellaton
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorHasan Yilmaz
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorPaolo Machi
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorKarl-Olof Lovblad
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorMohamed Farhat
Laboratory for Hydraulic Machines (LMH), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorVitor Mendes Pereira
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Medical Imaging, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Search for more papers by this authorMaria Isabel Vargas
Departement of Neuroradiology, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: Swiss National Science Foundation, Grant/Award Number: SNF 32003B_160222, SNF 320030_156813
Abstract
Purpose
The morphological and hemodynamic evaluations of neurovascular diseases treated with stents would benefit from noninvasive imaging techniques such as 3D time-of-flight MRI (3D-TOF) and 3D phase contrast MRI (3D-PCMRI). For this purpose, a comprehensive evaluation of the stent artifacts and their impact on the flow measurement is critical.
Methods
The artifacts of a representative sample of neurovascular stents were evaluated in vitro with 3D-TOF and 3D-PCMRI sequences. The dependency of the artifacts with respect to the orientation was analyzed for each stent design as well as the impact on the flow measurement accuracy. Furthermore, the 3D-PCMRI data of four patients carrying intracranial aneurysms treated with flow diverter stents were analyzed as illustrative examples.
Results
The stent artifacts were mainly confined to the stent lumen therefore indicating the leading role of shielding effect. The influence of the stent design and its orientation with respect to the transmitting MR coils were highlighted. The artifacts impacted the 3D-PCMRI velocities mainly in the low magnitude domains, which were discarded from the analysis ensuring reliable near-stent velocities. The feasibility of in-stent flow measurements was confirmed in vivo on two patients who showed strong correlation between flow and geometric features. In two other patients, the consistency of out-of-stent velocities was verified qualitatively through intra-aneurysmal streamlines except when susceptibility artifacts occurred.
Conclusion
The present results motivate the conception of low inductance or nonconductive stent design. Furthermore, the feasibility of near-stent 3D-PCMRI measurements opens the door to clinical applications like the post-treatment follow-up of stenoses or intracranial aneurysms.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| mrm27352-sup-0001-suppinfofs1.pdfPDF document, 6.8 MB |
FIGURE S1 Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of stent artifacts on 3D-TOF, parallel (blue) and orthogonal (red) to the magnetic field
|
| mrm27352-sup-0002-suppinfofs2.pdfPDF document, 7.1 MB |
FIGURE S2 Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of stent artifacts on 3D-PCMRI, parallel (blue) and orthogonal (red) to the magnetic field
|
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1Zhao J, Lin H, Summers R, Yang M, Cousins BG, Tsui J. Current treatment strategies for intracranial aneurysms: An overview. Angiology. 2017; 69: 17–30.
- 2Li H, Pan R, Wang H, et al. Clipping versus coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44: 29–37.
- 3Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Woo H, Rasmussen PA, Masaryk TJ, McDougall CG. Neuroform in-stent stenosis: Incidence, natural history, and treatment strategies. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59: 34–41.
- 4Chalouhi N, Drueding R, Starke RM, et al. In-stent stenosis after stent-assisted coiling: Incidence, predictors and clinical outcomes of 435 cases. Neurosurgery. 2013; 72: 390–396.
- 5John S, Bain MD, Hui FK, et al. Long-term follow-up of in-stent stenosis after Pipeline flow diversion treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2016; 78: 862–867.
- 6Kaufmann TJ, Huston J III, Mandrekar JN, Schleck CD, Thielen KR, Kallmes DF. Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography: evaluation of 19,826 consecutive patients. Radiology. 2007; 243: 812–819.
- 7Fifi JT, Meyers PM, Lavine SD, et al. Complications of modern diagnostic cerebral angiography in an academic medical center. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20: 442–447.
- 8Dawkins AA, Evans AL, Wattam J, et al. Complications of cerebral angiography: a prospective analysis of 2,924 consecutive procedures. Neuroradiology. 2007; 49: 753–759.
- 9Jamali S, Fahed R, Gentric J-C, et al. Inter- and intrarater agreement on the outcome of endovascular treatment of aneurysms using MRA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016; 37: 879–884.
- 10Lovblad KO, Yilmaz H, Chouiter A, et al. Intracranial aneurysm stenting: follow-up with MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006; 24: 418–422.
- 11van Amerongen MJ, Boogaarts HD, de Vries J, et al. MRA versus DSA for follow-up of coiled intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35: 1655–1661.
- 12Schenck J. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med Phys. 1996; 23: 815–850.
- 13Wang Y, Truong T, Yen C, et al. Quantitative evaluation of susceptibility and shielding effects of nitinol, platinum, cobalt-alloy, and stainless steel stents. Magn Reson Med. 2003; 49: 972–976.
- 14Camacho C, Plewes D, Henkelman R. Nonsusceptibility artifacts due to metallic objects in MR-imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1995; 5: 75–88.
- 15Bartels L, Bakker C, Viergever M. Improved lumen visualization in metallic vascular implants by reducing rf artifacts. Magn Reson Med. 2002; 47: 171–180.
- 16Anderson J, Klucznik R, Diaz O, et al. Quantification of velocity reduction after flow diverter placement in intracranial aneurysm: an ex vivo study with 3D printed replicas. In Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2015.
- 17Pereira VM, Brina O, Delattre BM, et al. Assessment of intra-aneurysmal flow modification after flow diverter stent placement with four-dimensional flow MRI: a feasibility study. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 7: 913–919.
- 18Eker OF, Boudjeltia KZ, Jerez RAC, et al. MR derived volumetric flow rate waveforms of internal carotid artery in patients treated for unruptured intracranial aneurysms by flow diversion technique. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015; 35: 2070–2079.
- 19MacDonald M, Dolati P, Mitha AP, Eesa M, Wong J, Frayne R. Hemodynamic alterations measured with phase-contrast MRI in a giant cerebral aneurysm treated with a flow-diverting stent. Radiol Case Rep. 2016; 10: 1109.
- 20Markl M, Frydrychowicz A, Kozerke S, Hope M, Wieben O. 4D flow MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 36: 1015–1036.
- 21Holton A, Walsh E, Brott B, et al. Evaluation of in-stent stenosis by magnetic resonance phase-velocity mapping in nickel-titanium stents. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005; 22: 248–257.
- 22Walsh E, Holton A, Brott B, Venugopalan R, Anayiotos A. Magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping through NiTi stents in a flow phantom model. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005; 21: 59–65.
- 23Bunck AC, Juettner A, Kroeger JR, et al. 4D phase contrast flow imaging for in-stent flow visualization and assessment of stent patency in peripheral vascular stents - a phantom study. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81: E929–E937.
- 24Kuehne T, Saeed M, Moore P, et al. Influence of blood-pool contrast media on MR imaging and flow measurements in the presence of pulmonary arterial stents in swine. Radiology. 2002; 223: 439–445.
- 25Choi JW, Roh HG, Moon WJ, Chun YI, Hwan Kang C. Optimization of MR parameters of 3D TOF-MRA for various intracranial stents at 3.0T MRI. Neurointervention. 2011; 6: 71–77.
- 26Karacozoff AM, Shellock FG, Wakhloo AK. A next-generation, flow-diverting implant used to treat brain aneurysms: in vitro evaluation of magnetic field interactions, heating and artifacts at 3-T. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 31: 145–149.
- 27Bouillot P, Brina O, Ouared R, Lovblad KO, Farhat M, Mendes Pereira V. Particle imaging velocimetry evaluation of intracranial stents in sidewall aneurysm: hemodynamic transition related to the stent design. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e113762.
- 28Bouillot P, Brina O, Ouared R, Lovblad KO, Mendes Pereira V, Farhat M. Multi-time-lag PIV analysis of steady and pulsatile flows in a sidewall aneurysm. Exp Fluids. 2014; 55: 1746.
- 29Bouillot P, Brina O, Ouared R, Lovblad KO, Farhat M, Pereira VM. Hemodynamic transition driven by stent porosity in sidewall aneurysms. J Biomech. 2015; 48: 1300–1309.
- 30Bouillot P, Brina O, Ouared R, et al. Computational fluid dynamics with stents: quantitative comparison with particle image velocimetry for three commercial off the shelf intracranial stents. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8: 309–315.
- 31Bouillot P, Delattre B, Brina O, et al. 3D phase contrast MRI: partial volume correction for robust blood flow quantification in small intracranial vessels. Magn Reson Med. 2018; 79: 129–140.
- 32Pelc NJ, Bernstein MA, Shimakawa A, Glover GH. Encoding strategies for 3-direction phase-contrast MR imaging of flow. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1991; 1: 405–413.
- 33Walker PG, Cranney GB, Scheidegger MB, Waseleski G, Pohost GM, Yoganathan AP. Semiautomated method for noise-reduction and background phase error correction in MR phase-velocity data. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1993; 3: 521–530.
- 34Klemm T, Duda S, Machann J, et al. MR imaging in the presence of vascular stents: a systematic assessment of artifacts for various stent orientations, sequence types, and field strengths. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000; 12: 606–615.
- 35Bartels L, Smits H, Bakker C, Viergever M. MR imaging of vascular stents: effects of susceptibility, flow, and radiofrequency eddy currents. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12: 365–371.
- 36Starcukova J, Starcuk Z Jr, Hubalkova H, Linetskiy I. Magnetic susceptibility and electrical conductivity of metallic dental materials and their impact on MR imaging artifacts. Dent Mater. 2008; 24: 715–723.
- 37Syha R, Ketelsen D, Kaempf M, et al. In vitro stent lumen visualisation of various common and newly developed femoral artery stents using MR angiography at 1.5 and 3 tesla. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23: 588–595.
- 38Maintz D, Kugel H, Schellhammer F, Landwehr P. In vitro evaluation of intravascular stent artifacts in three-dimensional MR angiography. Invest Radiol. 2001; 36: 218–224.
- 39Attali J, Benaissa A, Soize S, Kadziolka K, Portefaix C, Pierot L. Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated by flow diverter: comparison of three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography (3D-TOF-MRA) and contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA) sequences with digital subtraction angiography as the gold standard. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8: 81–86.
- 40Prabhakaran S, Warrior L, Wells KR, Jhaveri MD, Chen M, Lopes DK. The utility of quantitative magnetic resonance angiography in the assessment of intracranial in-stent stenosis. Stroke. 2009; 40: 991–993.
- 41Amin-Hanjani S, Alaraj A, Calderon-Arnulphi M, Aletich VA, Thulborn KR, Charbel FT. Detection of intracranial in-stent restenosis using quantitative magnetic resonance angiography. Stroke. 2010; 41: 2534–2538.
- 42Chong W, Zhang Y, Qian Y, Lai L, Parker G, Mitchell K. Computational hemodynamics analysis of intracranial aneurysms treated with flow diverters: correlation with clinical outcomes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 35: 136–142.
- 43Kulcsar Z, Augsburger L, Reymond P, et al. Flow diversion treatment: intra-aneurismal blood flow velocity and wss reduction are parameters to predict aneurysm thrombosis. Acta Neurochir. 2012; 154: 1827–1834.
- 44Mut F, Raschi M, Scrivano E, et al. Association between hemodynamic conditions and occlusion times after flow diversion in cerebral aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 7: 286–290.
- 45Ouared R, Larrabide I, Brina O, et al. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of flow reduction induced by flow-diverting stents in intracranial aneurysms: a patient-unspecific hemodynamics change perspective. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 8: 1288–1293.
- 46Pereira VM, Bonnefous O, Ouared R, et al. A dsa-based method using contrast-motion estimation for the assessment of the intra-aneurysmal flow changes induced by flow-diverter stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34: 808–815.



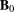 . For each stent, the mid-plane 3D-TOF magnitude interpolated from raw MRI dataset is displayed in gray-scale together with its quantitative value
. For each stent, the mid-plane 3D-TOF magnitude interpolated from raw MRI dataset is displayed in gray-scale together with its quantitative value
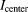 along the center of the tube normalized with the out-of-stent vessel magnitude (
along the center of the tube normalized with the out-of-stent vessel magnitude (
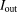 ). The vertical dashed lines show the physical limits of the stents while the horizontal dotted lines represent the out-of-stent vessel magnitude. The direction of flow is from right to left. For guidance, a vasoCT volume rendering of each stent provides the location of the radio-opaque wires and markers
). The vertical dashed lines show the physical limits of the stents while the horizontal dotted lines represent the out-of-stent vessel magnitude. The direction of flow is from right to left. For guidance, a vasoCT volume rendering of each stent provides the location of the radio-opaque wires and markers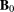 . For each stent, the mid-plane 3D-PCMRI magnitude interpolated from raw MRI dataset is displayed in gray-scale together with its quantitative value
. For each stent, the mid-plane 3D-PCMRI magnitude interpolated from raw MRI dataset is displayed in gray-scale together with its quantitative value
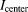 along the center of the tube normalized with the out-of-stent vessel magnitude (
along the center of the tube normalized with the out-of-stent vessel magnitude (
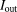 ). Due to shielding in the stent lumen the calculated values of mean flow rate (q) and maximal through-plane time averaged velocity (
). Due to shielding in the stent lumen the calculated values of mean flow rate (q) and maximal through-plane time averaged velocity (
 ) show deviations from the real values assuming a Poiseuille flow, which are indicated by the dotted lines. The extent of the deviations depends on the individual stents. The vertical dashed lines show the physical limits of the stents. The direction of flow is from right to left. For guidance, a vasoCT volume rendering of each stent provides the location of the radio-opaque wires and markers
) show deviations from the real values assuming a Poiseuille flow, which are indicated by the dotted lines. The extent of the deviations depends on the individual stents. The vertical dashed lines show the physical limits of the stents. The direction of flow is from right to left. For guidance, a vasoCT volume rendering of each stent provides the location of the radio-opaque wires and markers
