Preparation of Nanostructured Polyaniline and its Super-Amphiphilic Behavior
Haibin Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jixiao Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China.Search for more papers by this authorZhibin Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhi Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorFengbao Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorShichang Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorHaibin Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jixiao Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China.Search for more papers by this authorZhibin Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhi Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorFengbao Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorShichang Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Chemical Engineering Research Center, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
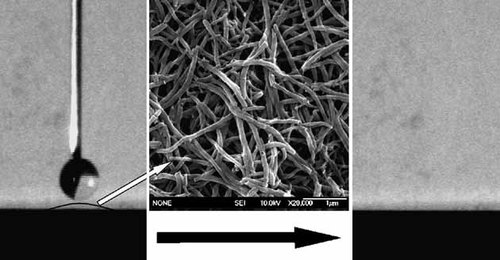
PANI nanofibers are prepared electrochemically by template-free method on a stainless steel electrode. Both the hydrophilicity and the lipophilicity of the modified SS surface are enhanced by the nanostructured PANI, and a super-amphiphilic surface is obtained in this way. The influence of polymerization conditions, such as polymerization potentials, polymerization time, the acidity, and the dopants on the super-amphiphilic property, has been systematically investigated. In addition, the mechanisms of obtaining a super-amphiphilic surface are briefly discussed.
Supporting Information
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2263/2008/marc200700446_s.pdf or from the author.
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Y. Tian, H. Q. Liu, A. F. Deng, Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5820.
- 2 M. Nicolas, F. Guittard, S. Géribaldi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2251.
- 3 M. Nicolas, F. Guittard, S. Géribaldi, Langmuir 2006, 22, 3081.
- 4 C. F. Wang, S. F. Chiou, F. H. Ko, C. T. Chou, H. C. Lin, C. F. Huang, F. C. Chang, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 333.
- 5 Q. D. Xie, J. Xu, L. Feng, L. Jiang, W. H. Tang, X. D. Luo, C. C. Han, Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 302.
- 6
H. J. Li,
X. B. Wang,
Y. L. Song,
Y. Q. Liu,
Q. S. Li,
L. Jiang,
D. B. Zhu,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
2001,
40,
1743.
10.1002/1521-3773(20010504)40:9<1743::AID-ANIE17430>3.0.CO;2-# CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 7 M. Takeuchi, K. Sakamoto, G. Martra, S. Coluccia, M. Anpo, J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15422.
- 8 Y. F. Gao, Y. Masuda, K. Koumoto, Langmuir 2004, 20, 3188.
- 9 X. J. Feng, L. Feng, M. H. Jin, J. Zhai, L. Jiang, D. B. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 62.
- 10 H. Liu, L. Feng, J. Zhai, L. Jiang, D. B. Zhu, Langmuir 2004, 20, 5659.
- 11 W. B. Zhong, X. H. Chen, S. M. Liu, Y. X. Wang, W. T. Yang, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 563.
- 12 W. B. Zhong, S. M. Liu, X. H. Chen, Y. X. Wang, W. T. Yang, Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3224.
- 13 L. Xu, W. Chen, A. Mulchandani, Y. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6009.
- 14 J. X. Wang, J. S. Wang, X. Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 84.
- 15 Z. M. Zhang, Z. X. Wei, M. X. Wan, Macromolecules 2002, 35, 5937.
- 16 H. J. Qiu, J. Zhai, S. H. Li, L. Jiang, M. X. Wan, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003, 13, 925.
- 17 S. M. Yang, K. H. Chen, Y. F. Yang, Synth. Met. 2005, 152, 65.
- 18 X. Y. Zhang, W. J. Goux, S. K. Manohar, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4502.
- 19 Y. F. Ma, J. M. Zhang, G. J. Zhang, H. X. He, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7097.
- 20 W. G. Li, H. L. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2278.
- 21 A. D. W. Carswell, E. A. O'Rear, B. P. Grady, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14793.
- 22 H. J. Ding, M. X. Wan, Y. Wei, Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 465.
- 23 N. R. Chiou, A. J. Epstein, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1679.
- 24 J. X. Huang, R. B. Kaner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 851.
- 25 J. X. Huang, R. B. Kaner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5817.
- 26 J. P. Yang, S. M. Burkinshaw, J. Zhou, A. P. Monkman, P. J. Brown, Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1081.
- 27
L. Liang,
J. Liu,
C. F. Windisch, Jr.,
G. J. Exarhos,
Y. H. Lin,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
2002,
41,
3665.
10.1002/1521-3773(20021004)41:19<3665::AID-ANIE3665>3.0.CO;2-B CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 28 W. G. Li, L. H. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1793.
- 29 V. Gupta, N. Miura, Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 995.
- 30 N. J. Shirtcliffe, G. McHale, M. I. Newton, C. C. Perry, P. Roach, Chem. Commun. 2005, 3135.
- 31 J. Q. Ma, H. H. Song, H. L. Frisch, S. Maaref, S. S. Sun, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 2287.
- 32 T. Sulimenko, J. Stejskal, I. Křivka, J. Prokeš, Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 219.
- 33 D. Mecerreyes, V. Alvaro, I. Cantero, M. Bengoetxea, P. A. Calvo, H. Grande, J. Rodriguez, J. A. Pomposo, Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 749.
- 34 J. Isaksson, C. Tengstedt, M. Fahlman, N. Robinson, M. Berggren, Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 316.