Boronic Acid Shell-Crosslinked Dextran-b-PLA Micelles for Acid-Responsive Drug Delivery
Ziwei Zhao
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuemei Yao
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhe Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Chen
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoliang He
Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuesi Chen
Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZiwei Zhao
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuemei Yao
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhe Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Li Chen
Department of Chemistry, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, 130024 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoliang He
Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXuesi Chen
Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Herein, 3-carboxy-5-nitrophenylboronic acid (CNPBA) shell-crosslinked micelles based on amphiphilic dextran-block-polylactide (Dex-b-PLA) are prepared and used for efficient intracellular drug deliveries. Due to the reversible pH-dependent binding with diols to form boronate esters, CNPBA modified Dex-b-PLA shows excellent pH-sensitivity. In neutral aqueous conditions, CNPBA-Dex-b-PLA forms shell-crosslinked micelles to enable DOX loading, while in acid conditions, the boronate esters hydrolyze and the micelles de-crosslink to release loaded DOX. In vitro release studies indicate that the release of the DOX cargo is minimized at physiological conditions, while there is a burst release in response to low pHs. The cell viability of CNPBA-Dex-b-PLA investigated by MTT assay was more than 90%, indicating that, as a drug delivery system, CNPBA-Dex-b-PLA has good cytocompatibility. These features suggest that the pH-responsive biodegradable CNPBA-Dex-b-PLA can efficiently load and deliver DOX into tumor cells and enhance the inhibition of cellular proliferation in vitro, providing a favorable platform as a drug delivery system for cancer therapy.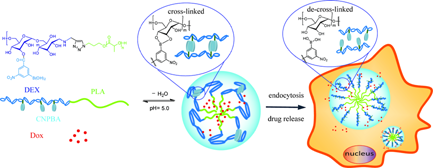
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| mabi201400251-sm-0001-SuppData.doc977.5 KB |
Figure S1.1H NMR spectrum of atactic PLA in CDCl3. Figure S2. 1H NMR spectra of dextran (a) and α-alkyne dextran (b) in DMSO-d6. Figure S3. FT-IR spectra of PDP-0 and PDP-3. Figure S4. UV-vis standard curve of CNPBA in DMSO. Figure S5. Plot of the emission intensity at 660 nm versus the log of concentration (mg mL−1) of PDP-0∼3 micelles at pH 7.4. Figure S6. Plot of the emission intensity at 660 nm versus the log of concentration (mg mL−1) of PDP-0 micelles at pH 5.5 and pH 7.4. Figure S7. Plot of the emission intensity at 660 nm versus the log of concentration (mg mL−1) of PDP-3 micelles at pH 5.5 and pH 7.4. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 X. Chen, L. Chen, X. Yao, Z. Zhang, C. He, J. Zhang, X. Chen, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3789.
- 2 F. Shi, J. Ding, C. Xiao, X. Zhuang, C. He, L. Chen, X. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14168.
- 3 J.-H. Park, H.-J. Cho, H. Y. Yoon, I.-S. Yoon, S.-H. Ko, J.-S. Shim, J.-H. Cho, J. H. Park, K. Kim, I. C. Kwon, J. Controlled Release 2014, 174, 98.
- 4 M. Delcea, H. Möhwald, A. G. Skirtach, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2011, 63, 730.
- 5 Y. K. Joung, J. Y. Jang, J. H. Choi, D. K. Han, K. D. Park, Molecular Pharmaceutics 2012, 10, 685.
- 6 H. Kim, Y. Lee, I. H. Lee, S. Kim, D. Kim, P. E. Saw, J. Lee, M. Choi, Y.-C. Kim, S. Jon, S. J. Controlled Release 2014, 178, 118.
- 7 J. Ding, F. Shi, D. Li, L. Chen, X. Zhuang, X. Chen, Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 633.
- 8 S. Deshayes, H. Cabral, T. Ishii, Y. Miura, S. Kobayashi, T. Yamashita, A. Matsumoto, Y. Miyahara, N. Nishiyama, K. Kataoka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15501.
- 9 Y. Li, W. Xiao, K. Xiao, L. Berti, J. Luo, H. P. Tseng, G. Fung, K. S. Lam, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 2918.
- 10 L. Jiang, J. W. de Folter, J. Huang, A. P. Philipse, W. K. Kegel, A. V. Petukhov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3364.
- 11 B. M. Dicheva, T. Lt. Hagen, L. Li, D. Schipper, A. L. Seynhaeve, G. Cv. Rhoon, A. M. Eggermont, L. H. Lindner, G. A. Koning, Nano Lett. 2012, 13, 2324.
- 12 S. Mathew, T. Murakami, H. Nakatsuji, H. Okamoto, N. Morone, J. E. Heuser, M. Hashida, H. Imahori, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8908.
- 13 A. G. Skirtach, C. Dejugnat, D. Braun, A. S. Susha, A. L. Rogach, W. J. Parak, H. Möhwald, G. B. Sukhorukov, Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1371.
- 14 A. Zhang, Z. Zhang, F. Shi, C. Xiao, J. Ding, X. Zhuang, C. He, L. Chen, X. Chen, Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1249.
- 15 J. Ding, F. Shi, C. Xiao, L. Lin, L. Chen, C. He, X. Zhuang, X. Chen, Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 2857.
- 16 Y. Wang, K. Zhou, G. Huang, C. Hensley, X. Huang, X. Ma, T. Zhao, B. D. Sumer, R. J. DeBerardinis, J. Gao, Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 204.
- 17 A. G. Skirtach, A. Muñoz Javier, O. Kreft, K. Köhler, A. Piera Alberola, H. Möhwald, W. J. Parak, G. B. Sukhorukov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4612.
- 18 T. Wan, R. Huang, Q. Zhao, L. Xiong, L. Qin, X. Tan, G. Cai, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3404.
- 19 K. Miao, W. Shao, H. Liu, Y. Zhao, Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1191.
- 20 O. A. Adegoke, T. E. Adesuji, O. E. Thomas, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2014, 128, 147.
- 21 L. Li, Y. Xu, I. Milligan, L. Fu, E. A. Franckowiak, W. Du, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13699.
- 22 W. Yang, X. Gao, G. Springsteen, B. Wang, Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6339.
- 23 D. Roy, J. N. Cambre, B. S. Sumerlin, Chem. Commun. 2008, 21, 2477.
- 24 L. Zhu, S. H. Shabbir, M. Gray, V. M. Lynch, S. Sorey, E. V. Anslyn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1222.
- 25 L. Zhao, J. Ding, C. Xiao, P. He, Z. Tang, X. Pang, X. Zhuang, X. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12319.
- 26 Y. Wen, J. K. Oh, RSC Advances 2014, 4, 229.
- 27 T. Jiang, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Lv, J. Zhou, C. Li, L. Hou, Q. Zhang, Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9246.
- 28 W. Scarano, H. T. Duong, H. Lu, P. L. De Souza, M. H. Stenzel, Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 962.
- 29 Y.-J. Huang, W.-J. Ouyang, X. Wu, Z. Li, J. S. Fossey, T. D. James, Y.-B. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1700.
- 30 Q. Guo, Z. Wu, X. Zhang, L. Sun, C. Li, Soft Matter 2014, 10, 911.
- 31 R. Ma, L. Shi, Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1503.
- 32 Y. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Mu, C. Li, New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 796.
- 33 L. Zhang, Y. Lin, J. Wang, W. Yao, W. Wu, X. Jiang, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 534.
- 34 L. Li, Z. Bai, P. A. Levkin, Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8504.
- 35 Z. Zhao, Z. Zhang, L. Chen, Y. Cao, C. He, X. Chen, Langmuir 2013, 29, 13072.
- 36 J. L. Mynar, A. P. Goodwin, J. A. Cohen, Y. Ma, G. R. Fleming, J. M. Fréchet, Chem. Commun. 2007, 20, 2081.
- 37 C. Chen, G. Liu, X. Liu, S. Pang, C. Zhu, L. Lv, J. Ji, Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1389.