Visible Light-Induced Arylation/Alkylation/Phosphorylation of Isocyanides via EDA Complex Activation
Shichao Yang
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiangwen Tan
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan Liu
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorHuanfeng Jiang
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wanqing Wu
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorShichao Yang
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiangwen Tan
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorDan Liu
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorHuanfeng Jiang
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wanqing Wu
Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510640 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
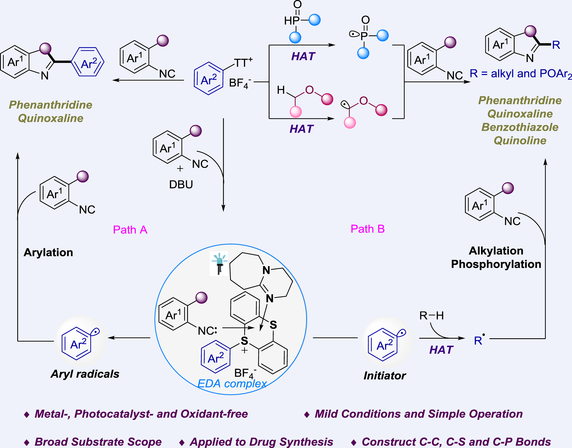
Herein, it is reported that the aryl radicals derived from aryl thianthrenium salts are used as coupling partner in the arylation reactions of isocyanides, simultaneously as initiators for the formation of alkyl and phosphoryl radicals from ethers and diarylphosphine oxides. This cascade cyclization reaction leads to diverse arylated, alkylated and phosphorylated heteroaromatic compounds. Notably, this transformation can be achieved without the aid of metals or photocatalysts, exhibiting a wide substrate applicability and operational simplicity. Mechanistic studies suggest the involvement of radical processes and electron donor-acceptor (EDA) complexes in this transformation.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202500088-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 10.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Hari, D. P.; König, B. The Photocatalyzed Meerwein Arylation: Classic Reaction of Aryl Diazonium Salts in a New Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4734–4743; (b) Hari, D. P.; Hering, T.; König, B. The Photoredox-Catalyzed Meerwein Addition Reaction: Intermolecular Amino-Arylation of Alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 725–728; (c) Ghosh, I.; Marzo, L.; Das, A.; Shaikh, R.; König, B. Visible Light Mediated Photoredox Catalytic Arylation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1566–1577; (d) Waldvogel, S. R.; Lips, S.; Selt, M.; Riehl, B.; Kampf, C. J. Electrochemical Arylation Reaction. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6706–6765.
- 2(a) Xiao, T.; Li, L.; Lin, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Mao, Z.; Zhou, L. Synthesis of 6-Substituted Phenanthridines by Metal-Free, Visible-Light Induced Aerobic Oxidative Cyclization of 2-Isocyanobiphenyls with Hydrazines. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2418–2421; (b) Yang, W.-C.; Wei, K.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, L. Cascade C(sp3)–S Bond Cleavage and Imidoyl C–S Formation: Radical Cyclization of 2-Isocyanoaryl Thioethers toward 2-Substituted Benzothiazoles. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3144–3147; (c) Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Song, Q. Modular Synthesis of Polysubstituted Quinolin-3-amines by Oxidative Cyclization of 2-(2-Isocyanophenyl)acetonitriles with Organoboron Reagents. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 6789–6794; (d) Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, H.-Y.; Song, H.-Y.; Li, H.-X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, T.-B.; He, W.-M. Visible-Light-Induced Annulation of Iodonium Ylides and 2-Isocyanobiaryls to Access 6-Arylated Phenanthridines. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 8360−8368; (e) Chiappini, N. D.; Geunes, E. P. E.; Bodak, T.; Knowles, R. R. Organobismuth Compounds as Aryl Radical Precursors via Light-Driven Single-Electron Transfer. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 2664–2670.
- 3 Anselmo, M.; Basso, A.; Protti, S.; Ravelli, D. Photoredox-Catalyzed Generation of Acetonyl Radical in Flow: Theoretical Investigation and Synthetic Applications. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2493–2500.
- 4 Kang, J.; Hwang, H. S.; Soni, V. K.; Cho, E. J. Direct C(sp3)–N Radical Coupling: Photocatalytic C–H Functionalization by Unconventional Intermolecular Hydrogen Atom Transfer to Aryl Radical. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6112–6116.
- 5 Ye, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, K.; McKenna, J. M.; Toste, F. D. Chiral Diaryliodonium Phosphate Enables Light Driven Diastereoselective α-C(sp3)–H Acetalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8350–8356.
- 6(a) Ruan, X.-Y.; Wu, D.-X.; Li, W.-A.; Lin, Z.; Sayed, M.; Han, Z.-Y.; Gong, L.-Z. Photoinduced Pd-Catalyzed Enantioselective Carboamination of Dienes via Aliphatic C–H Bond Elaboration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 12053–12062; (b) Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Deng, G.; Wei, W.; Feng, P.; Zi, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Walsh, P. J. Transition- Metal-Free C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H Dehydrogenative Coupling of Saturated Heterocycles with N-benzyl Imines. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7619–7625.
- 7 Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Sang, T.; Zhou, C.; Bao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huo, C. C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H Dehydrogenative Radical Coupling of Glycine Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7577–7582.
- 8(a) Yan, D.-M.; Xiao, C.; Chen, J.-R. Strong C(sp3)-H Arylation by Synergistic Decatungstate Photo-HAT and Nickel Catalysis. Chem 2018, 4, 2483–2498; (b) Perry, I. B.; Brewer, T. F.; Sarver, P. J.; Schultz, D. M.; DiRocco, D. A.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Direct arylation of strong aliphatic C–H bonds. Nature 2018, 560, 70–75; (c) Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, C.; Duan, C. Selective C(sp3)–H Activation of Simple Alkanes: Visible Light-Induced Metal-Free Synthesis of Phenanthridines with H2O2 as a Sustainable Oxidant. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6926–6930.
- 9(a) Wang, C.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-D. Autoxidation Photoredox Catalysis for the Synthesis of 2-Phosphinoylindoles. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2382−2385; (b) Liu, Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhu, S.-S.; Li, S.-J.; Song, Y.; Qu, L.-B.; Yu, B. 4CzIPN-tBu-Catalyzed Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer for Photosynthesis of Phosphorylated N-Heteroaromatics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 964−972; (c) Yu, J.-X.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Chen, B.; Tung, C.-H.; Wu, L.-Z. Cobaloxime Photocatalysis for the Synthesis of Phosphorylated Heteroaromatics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209293.
- 10(a) Cai, Y.; Ritter, T. Meerwein-type Bromoarylation with Arylthianthrenium Salts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209882; (b) Cai, Y.; Chatterjee, S.; Ritter, T. Photoinduced Copper-Catalyzed Late-Stage Azidoarylation of Alkenes via Arylthianthrenium Salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 13542−13548; (c) Yan, F.; Li, Q.; Fu, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, D.; Yao, S.; Song, M.; Deng, H.; Sui, X. Single-Electron-Transfer-Generated Aryl Sulfonyl Ammonium Salt: Metal-Free Photoredox-Catalyzed Modular Construction of Sulfonamides. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 5227−5235.
- 11(a) Sun, K.; Shi, A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiang, P.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Yu, B. A General Electron Donor–Acceptor Complex for Photoactivation of Arenes via Thianthrenation. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 5659–5666; (b) Xu, H.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Ji, S.; Zuo, J.; Lv, J.; Yang, D. Thianthrenium-Enabled Phosphorylation of Aryl C–H Bonds via Electron Donor–Acceptor Complex Photoactivation. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 3784−3789; (c) Patel, R. I.; Saxena, B.; Sharma, A. General Electron–Donor–Acceptor Complex Mediated Thioesterification Reaction via Site-Selective C–H Functionalization Using Aryl Sulfonium Salts. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 10265–10274.
- 12(a) Song, B.; Xu, B. Metal-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization Involving Isocyanides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1103–1123; (b) Giustiniano, M.; Basso, A.; Mercalli, V.; Massarotti, A.; Novellino, E.; Tron, G. C.; Zhu, J. To Each His Own: Isonitriles for All Flavors. Functionalized Isocyanides as Valuable Tools in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1295–1357; (c) Wang, Q.; Wang, D.-X.; Wang, M.-X.; Zhu, J. Still Unconquered: Enantioselective Passerini and Ugi Multicomponent Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1290−1300; (d) Xiong, Q.; Li, G.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Enantioselective Synthesis of Hydrothiazole Derivatives via an Isocyanide-Based Multicomponent Reaction. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8771−8775; (e) Xiong, Q.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, T.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. Catalytic Asymmetric Multicomponent Reactions of Isocyanide, Isothiocyanate and Alkylidene Malonates. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 7288–7291; (f) Russo, C.; Brunelli, F.; Tron, G. C.; Giustiniano, M. Isocyanide-Based Multicomponent Reactions Promoted by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203150; (g) He, Y.; Huang, T.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q. Recent Advances in Photocatalytic Reactions with Isocyanides. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 4220–4246; (h) Gao, M.; Lu, S.; Xu, B. C–H Functionalization Enabled by Multiple Isocyanides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10147–10170.
- 13 Yang, S.; Zhao, R.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, G.-J.; Wu, W. A Visible-Light-Induced Cascade Cyclization Strategy for the Synthesis of N,S-Containing Polycyclic Compounds. Org. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 5067–5076.
- 14 Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Lv, J.; Yang, D. Arylcyanation of Styrenes by Photoactive Electron Donor–Acceptor Complexes/Copper Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 7949–7955.
- 15 Sau, S.; Takizawa, S.; Kim, H. Y.; Oh, K. Visible Light-Induced Radical Cascade Functionalization of Quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones: Three-Component 1,2-Di(hetero)arylation Approach with Styrenes; Thianthrenium Salts. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 8821−8826.




