Biomimetic and Biological Applications of DNA Coacervates
Yuqi Zeng
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLong Zhao
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorYihao Liu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tianhuan Peng
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yifan Lyu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Furong Laboratory, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Quan Yuan
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYuqi Zeng
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorLong Zhao
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorYihao Liu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tianhuan Peng
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yifan Lyu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Furong Laboratory, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Quan Yuan
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Biology, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Comprehensive Summary
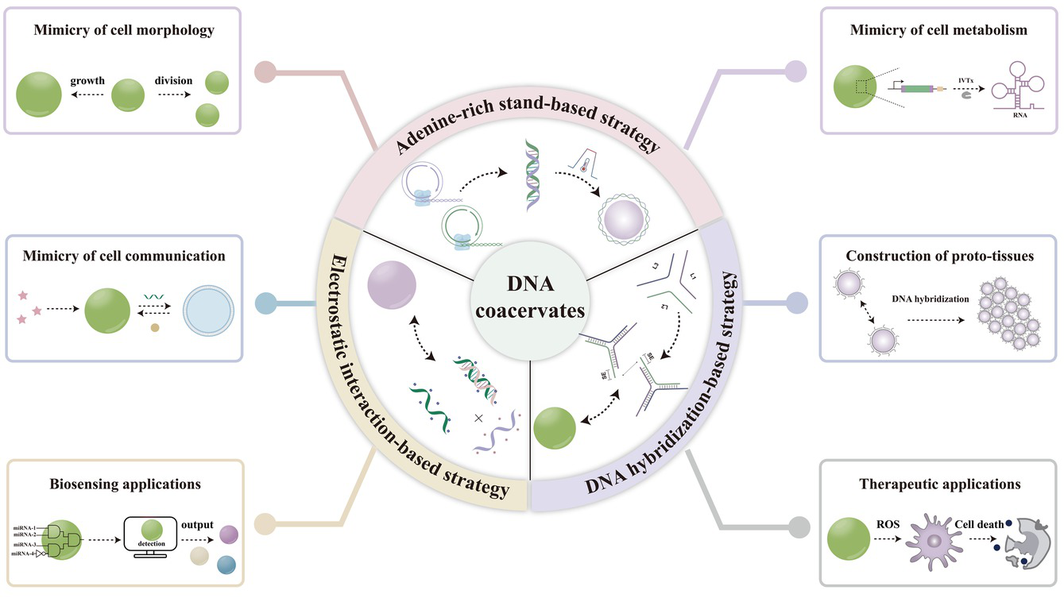
Recent progress in nanotechnology and synthetic biology has demonstrated the potential of DNA coacervates for biomimetic and biological applications. DNA coacervates are micron-scale, membrane-free, spherical structures formed by liquid-liquid phase separation of DNA materials. They uniquely combine the programmability of DNA with the fluidic properties of coacervates, allowing for controlled modulation of their structures, biomimetic and biological functions, and dynamic behaviors through rational sequence design. This review summarizes methods for the formation of different DNA coacervates and explores their extensive applications in biomimicry, biosensing and therapeutics. Limitations and prospects of DNA coacervates are also discussed.
Key Scientists

References
- 1 Visser, B. S.; Lipiński, W. P.; Spruijt, E. The role of biomolecular condensates in protein aggregation. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 686–700.
- 2 Pederson, T. The nucleolus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a000638.
- 3 Gall, J. G. The centennial of the Cajal body. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 975–980.
- 4 Shin, Y.; Brangwynne, C. P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 2017, 357, eaaf4382.
- 5 Miller, S. L.; Schopf, J. W.; Lazcano, A. Oparin's “Origin of Life”: Sixty Years Later. J. Mol. Evol. 1997, 44, 351–353.
- 6 Yu, X. L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G. Y.; Wang, L.; Dou, H. J. Hierarchical Structures in Macromolecule-Assembled Synthetic Cells. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, 2100926.
- 7 Seeman, N. C. DNA in a material world. Nature 2003, 421, 427–431.
- 8 Udono, H.; Gong, J.; Sato, Y.; Takinoue, M. DNA Droplets: Intelligent, Dynamic Fluid. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2200180.
- 9 Priftis, D.; Laugel, N.; Tirrell, M. Thermodynamic Characterization of Polypeptide Complex Coacervation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15947–15957.
- 10 Vieregg, J. R.; Tang, T. D. Polynucleotides in cellular mimics: coacervates and lipid vesicles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 26, 50–57.
- 11 Bungenberg de Jong, H. G.; Kruyt, H. R. Coacervation (Partial Miscibility in Colloid Systems). Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie Van Wetenschappen, 1929, pp. 849–856.
- 12 Teif, V. B.; Bohinc, K. Condensed DNA: condensing the concepts. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 208–222.
- 13 Razin, S.; Gavrilov, A. The role of liquid-liquid phase separation in the compartmentalization of cell nucleus and spatial genome organization. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2020, 85, 643–650.
- 14 Alberti, S.; Gladfelter, A.; Mittag, T. Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell 2019, 176, 419–434.
- 15 Martin, N.; Tian, L. F.; Spencer, D.; Coutable-Pennarun, A.; Anderson, J. L. R.; Mann, S. Photoswitchable Phase Separation and Oligonucleotide Trafficking in DNA Coacervate Microdroplets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14594–14598.
- 16 Lu, T. M.; Spruijt, E. Multiphase Complex Coacervate Droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2905–2914.
- 17 Mountain, G. A.; Keating, C. D. Formation of Multiphase Complex Coacervates and Partitioning of Biomolecules within them. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 630–640.
- 18 Nakatani, N.; Sakuta, H.; Hayashi, M.; Tanaka, S.; Takiguchi, K.; Tsumoto, K.; Yoshikawa, K. Specific Spatial Localization of Actin and DNA in a Water/Water Microdroplet: Self-Emergence of a Cell-Like Structure. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 1370–1374.
- 19 Liu, X. J.; Xiong, Y. S.; Zhang, C. J.; Lai, R. J.; Liu, H.; Peng, R. Z.; Fu, T.; Liu, Q. L.; Fang, X. H.; Mann, S. et al. G-Quadruplex-Induced Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation in Biomimetic Protocells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11036–11043.
- 20 Nott, T. J.; Petsalaki, E.; Farber, P.; Jervis, D.; Fussner, E.; Plochowietz, A.; Craggs, T. D.; Bazett-Jones, D. P.; Pawson, T.; Forman-Kay, J. D. Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles. Mol. Cell. 2015, 57, 936–947.
- 21 Ji, Y. L. M.; Li, F.; Qiao, Y. Modulating liquid–liquid phase separation of FUS: mechanisms and strategies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 8616–8628.
- 22 Koga, S.; Williams, D. S.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Peptide-nucleotide microdroplets as a step towards a membrane-free protocell model. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 720–724.
- 23 Song, S. Y.; Ivanov, T.; Yuan, D. D.; Wang, J. Q.; da Silva, L. C.; Xie, J.; Cao, S. P. Peptide-Based Biomimetic Condensates via Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation as Biomedical Delivery Vehicles. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 5468–5488.
- 24 Jing, H. R.; Bai, Q. W.; Lin, Y. N.; Chang, H. J.; Yin, D. X.; Liang, D. H. Fission and Internal Fusion of Protocell with Membraneless “Organelles” Formed by Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8017–8026.
- 25 Yin, Y. D.; Niu, L.; Zhu, X. C.; Zhao, M. P.; Zhang, Z. X.; Mann, S.; Liang, D. H. Non-equilibrium behaviour in coacervate-based protocells under electric-field-induced excitation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10658.
- 26 Shapiro, J. T.; Leng, M.; Felsenfeld, G. Deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine complexes. Structure and nucleotide specificity. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 3219–3232.
- 27 Vieregg, J.; Lueckheide, M.; Leon, L.; Marciel, A.; Tirrell, M. Nucleic acid-peptide complexes controlled by DNA hybridization. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 566a.
- 28 Wee, W. A.; Sugiyama, H.; Park, S. Photoswitchable single-stranded DNA-peptide coacervate formation as a dynamic system for reaction control. iScience 2021, 24, 103455.
- 29 Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T. S.; Mitrea, D. M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T. M.; Kriwacki, R. W.; Pappu, R. V.; Brangwynne, C. P. Coexisting liquid phases underlie nucleolar subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697.
- 30 Fraccia, T. P.; Martin, N. Non-enzymatic oligonucleotide ligation in coacervate protocells sustains compartment-content coupling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2606.
- 31 Mao, S.; Kuldinow, D.; Haataja, M. P.; Košmrlj, A. Phase behavior and morphology of multicomponent liquid mixtures. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1297–1311.
- 32 Vieregg, J. R.; Lueckheide, M.; Marciel, A. B.; Leon, L.; Bologna, A. J.; Rivera, J. R.; Tirrell, M. V. Oligonucleotide-Peptide Complexes: Phase Control by Hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1632–1638.
- 33 Hayashi, K.; Chaya, H.; Fukushima, S.; Watanabe, S.; Takemoto, H.; Osada, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Miyata, K.; Kataoka, K. Influence of RNA strand rigidity on polyion complex formation with block catiomers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 486–493.
- 34 Jing, H. R.; Chang, H. J.; Lin, Y. N.; Bai, Q. W.; Liang, D. H. Protocells with hierarchical structures as regulated by liquid-liquid and liquid- solid phase separations. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 12041–12044.
- 35 Wang, Q. F.; Schlenoff, J. B. The Polyelectrolyte Complex/Coacervate Continuum. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3108–3116.
- 36 Shakya, A.; King, J. T. DNA local-flexibility-dependent assembly of phase-separated liquid droplets. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1840–1847.
- 37 Fraccia, T. P.; Jia, T. Z. Liquid Crystal Coacervates Composed of Short Double-Stranded DNA and Cationic Peptides. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15071–15082.
- 38 Jia, T. Z.; Fraccia, T. P. Liquid Crystal Peptide/DNA Coacervates in the Context of Prebiotic Molecular Evolution. Crystals 2020, 10, 964.
- 39 Liu, Z. J.; Chen, J. X.; Bai, Q. W.; Lin, Y. N.; Liang, D. H. Coacervate Formed by an ATP-Binding Aptamer and Its Dynamic Behavior under Nonequilibrium Conditions. Langmuir 2022, 38, 6425–6434.
- 40 Zhang, Y. W.; Chen, Y. F.; Yang, X. H.; He, X. X.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Y.; Wang, K. M.; Liu, J. B.; Mann, S. Giant Coacervate Vesicles as an Integrated Approach to Cytomimetic Modeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2866–2874.
- 41 Chen, Y. F.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y. W.; Liu, S. Y.; Yang, X. H.; Wang, K. M.; Liu, J. B. Construction of coacervate-in-coacervate multi-compartment protocells for spatial organization of enzymatic reactions. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 8617–8625.
- 42 Peng, Y. H.; Hsiao, S. K.; Gupta, K.; Ruland, A.; Auernhammer, G. K.; Maitz, M. F.; Boye, S.; Lattner, J.; Gerri, C.; Honigmann, A. et al. Dynamic matrices with DNA-encoded viscoelasticity for cell and organoid culture. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1463–1473.
- 43 Merindol, R.; Delechiave, G.; Heinen, L.; Catalani, L. H.; Walther, A. Modular Design of Programmable Mechanofluorescent DNA Hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 528.
- 44 Benson, E.; Mohammed, A.; Gardell, J.; Masich, S.; Czeizler, E.; Orponen, P.; Högberg, B. DNA rendering of polyhedral meshes at the nanoscale. Nature 2015, 523, 441–444.
- 45 He, Y.; Ye, T.; Su, M.; Zhang, C.; Ribbe, A. E.; Jiang, W.; Mao, C. Hierarchical self-assembly of DNA into symmetric supramolecular polyhedra. Nature 2008, 452, 198–201.
- 46 Rossi-Gendron, C.; El Fakih, F.; Bourdon, L.; Nakazawa, K.; Finkel, J.; Triomphe, N.; Chocron, L.; Endo, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Bellot, G. et al. Isothermal self-assembly of multicomponent and evolutive DNA nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1311–1318.
- 47 Li, L.; Yin, J.; Ma, W.; Tang, L. G.; Zou, J. H.; Yang, L. Z.; Du, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. H.; Yang, Z. et al. A DNA origami device spatially controls CD95 signalling to induce immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 993–1001.
- 48 Yin, J.; Wang, S. Y.; Wang, J. H.; Zhang, Y. W.; Fan, C. H.; Chao, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L. H. An intelligent DNA nanodevice for precision thrombolysis. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 854–862.
- 49 Biffi, S.; Cerbino, R.; Bomboi, F.; Paraboschi, E. M.; Asselta, R.; Sciortino, F.; Bellini, T. Phase behavior and critical activated dynamics of limited-valence DNA nanostars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 15633–15637.
- 50 Nguyen, D. T.; Jeon, B. J.; Abraham, G. R.; Saleh, O. A. Length- Dependence and Spatial Structure of DNA Partitioning into a DNA Liquid. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14849–14854.
- 51 Lee, T.; Do, S.; Lee, J. G.; Kim, D. N.; Shin, Y. The flexibility-based modulation of DNA nanostar phase separation. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17638–17647.
- 52 Jeon, B. J.; Nguyen, D. T.; Saleh, O. A. Sequence-Controlled Adhesion and Microemulsification in a Two-Phase System of DNA Liquid Droplets. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 8888–8895.
- 53 Do, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, T.; Kim, D. N.; Shin, Y. Engineering DNA-based synthetic condensates with programmable material properties, compositions, and functionalities. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj1771.
- 54 Gong, J.; Tsumura, N.; Sato, Y.; Takinoue, M. Computational DNA Droplets Recognizing miRNA Sequence Inputs Based on Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. Adv. Func. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202322.
- 55 Sato, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Takinoue, M. Sequence-based engineering of dynamic functions of micrometer-sized DNA droplets. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3471.
- 56 Tran, M. P.; Chatterjee, R.; Dreher, Y.; Fichtler, J.; Jahnke, K.; Hilbert, L.; Zaburdaev, V.; Göpfrich, K. A DNA Segregation Module for Synthetic Cells. Small 2023, 19, 2202711.
- 57 Conrad, N.; Kennedy, T.; Fygenson, D. K.; Saleh, O. A. Increasing valence pushes DNA nanostar networks to the isostatic point. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 7238–7243.
- 58 Agarwal, S.; Dizani, M.; Osmanovic, D.; Franco, E. Light-controlled growth of DNA organelles in synthetic cells. Interface Focus. 2023, 13, 20230017.
- 59 Nguyen, D. T.; Saleh, O. A. Tuning phase and aging of DNA hydrogels through molecular design. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5421–5427.
- 60 Jeon, B. J.; Nguyen, D. T.; Abraham, G. R.; Conrad, N.; Fygenson, D. K.; Saleh, O. A. Salt-dependent properties of a coacervate-like, self-assembled DNA liquid. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 7009–7015.
- 61 Agarwal, S.; Osmanovic, D.; Klocke, M. A.; Franco, E. The Growth Rate of DNA Condensate Droplets Increases with the Size of Participating Subunits. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11842–11851.
- 62 Sato, Y.; Takinoue, M. Sequence-dependent fusion dynamics and physical properties of DNA droplets. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 1919–1925.
- 63 Leathers, A.; Walczak, M.; Brady, R. A.; Al Samad, A.; Kotar, J.; Booth, M. J.; Cicuta, P.; Di Michele, L. Reaction-Diffusion Patterning of DNA-Based Artificial Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 17468–17476.
- 64 Walczak, M.; Brady, R. A.; Mancini, L.; Contini, C.; Rubio-Sánchez, R.; Kaufhold, W. T.; Cicuta, P.; Di Michele, L. Responsive core-shell DNA particles trigger lipid-membrane disruption and bacteria entrapment. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4743.
- 65 Deng, J.; Walther, A. Programmable ATP-fueled DNA coacervates by transient liquid-liquid phase separation. Chem 2020, 6, 3329–3343.
- 66 Liu, W.; Deng, J.; Song, S. Y.; Sethi, S.; Walther, A. A facile DNA coacervate platform for engineering wetting, engulfment, fusion and transient behavior. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 100.
- 67 Merindol, R.; Loescher, S.; Samanta, A.; Walther, A. Pathway-controlled formation of mesostructured all-DNA colloids and superstructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 730–738.
- 68 Liu, W.; Samanta, A.; Deng, J.; Akintayo, C. O.; Walther, A. Mechanistic Insights into the Phase Separation Behavior and Pathway-Directed Information Exchange in all-DNA Droplets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208951.
- 69 Ralec, C.; Henry, E.; Lemor, M.; Killelea, T.; Henneke, G. Calcium- driven DNA synthesis by a high-fidelity DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12425–12440.
- 70 Korolev, N.; Lyubartsev, A. P.; Rupprecht, A.; Nordenskiöld, L. Competitive binding of Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, and K+ ions to DNA in oriented DNA fibers: experimental and Monte Carlo simulation results. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2736–2749.
- 71 Ahmad, R.; Arakawa, H.; Tajmir-Riahi, H. A comparative study of DNA complexation with Mg(II) and Ca(II) in aqueous solution: major and minor grooves bindings. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2460–2466.
- 72 Kumar, B. V. V. S. P.; Patil, A. J.; Mann, S. Enzyme-powered motility in buoyant organoclay/DNA protocells. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 1154–1163.
- 73 Jang, W. S.; Kim, H. J.; Gao, C.; Lee, D.; Hammer, D. A. Enzymatically Powered Surface-Associated Self-Motile Protocells. Small 2018, 14, 1801715.
- 74 Qiao, Y.; Li, M.; Booth, R.; Mann, S. Predatory behaviour in synthetic protocell communities. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 110–119.
- 75 Gao, N.; Xu, C.; Yin, Z. P.; Li, M.; Mann, S. Triggerable Protocell Capture in Nanoparticle-Caged Coacervate Microdroplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3855–3862.
- 76 Mu, W.; Jia, L.; Zhou, M.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Mann, S.; Qiao, Y. Superstructural ordering in self-sorting coacervate-based protocell networks. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 158–167.
- 77
Qiao, Y.; Li, M.; Qiu, D.; Mann, S. Response-retaliation behavior in synthetic protocell communities. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17922–17927.
10.1002/ange.201909313 Google Scholar
- 78 Joesaar, A.; Yang, S.; Bögels, B.; van der Linden, A.; Pieters, P.; Kumar, B. V. V. S. P.; Dalchau, N.; Phillips, A.; Mann, S.; de Greef, T. F. A. DNA-based communication in populations of synthetic protocells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 369–378.
- 79 Ji, Y. L. M.; Lin, Y. Y.; Qiao, Y. Plant Cell-Inspired Membranization of Coacervate Protocells with a Structured Polysaccharide Layer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 12576–12585.
- 80 Rothemund, P. W. K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302.
- 81 Koshland, D. E. The Seven Pillars of Life. Science 2002, 295, 2215–2216.
- 82 Wilken, S.; Chaderjian, A.; Saleh, O. A. Spatial Organization of Phase-Separated DNA Droplets. Phys. Rev. X 2023, 13, 031014.
- 83 Samanta, A.; Sabatino, V.; Ward, T. R.; Walther, A. Functional and morphological adaptation in DNA protocells via signal processing prompted by artificial metalloenzymes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 914–921.
- 84 Maruyama, T.; Gong, J.; Takinoue, M. Temporally controlled multistep division of DNA droplets for dynamic artificial cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7397.
- 85 Saleh, O. A.; Jeon, B. J.; Liedl, T. Enzymatic degradation of liquid droplets of DNA is modulated near the phase boundary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 117, 16160–16166.
- 86 Saleh, O. A.; Wilken, S.; Squires, T. M.; Liedl, T. Vacuole dynamics and popping-based motility in liquid droplets of DNA. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3574.
- 87 Deng, N. N.; Huck, W. T. S. Microfluidic Formation of Monodisperse Coacervate Organelles in Liposomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9736–9740.
- 88 Malouf, L.; Tanase, D. A.; Fabrini, G.; Brady, R. A.; Paez-Perez, M.; Leathers, A.; Booth, M. J.; Di Michele, L. Sculpting DNA-based synthetic cells through phase separation and phase-targeted activity. Chem 2023, 9, 3347–3364.
- 89 Waters, C. M.; Bassler, B. L. Quorum Sensing: Cell-to-Cell Communication in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 319–346.
- 90 Zhao, Q. H.; Cao, F. H.; Luo, Z. H.; Huck, W. T. S.; Deng, N. N. Photoswitchable Molecular Communication between Programmable DNA-Based Artificial Membraneless Organelles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117500.
- 91 Chen, H.; Xu, W. Y.; Shi, H.; Qiao, Y.; He, X. X.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, S. H.; Yang, X. H.; Wang, K. M.; Liu, J. B. DNA-Based Artificial Receptors as Transmembrane Signal Transduction Systems for Protocellular Communication. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301559.
- 92 Abbas, M.; Lipiński, W. P.; Wang, J.; Spruijt, E. Peptide-based coacervates as biomimetic protocells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 3690–3705.
- 93 Dora Tang, T. Y.; Rohaida Che Hak, C.; Thompson, A. J.; Kuimova, M. K.; Williams, D. S.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Fatty acid membrane assembly on coacervate microdroplets as a step towards a hybrid protocell model. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 527–533.
- 94 Liu, S. Y.; Zhang, Y. W.; He, X. X.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. H.; Wang, K. M.; Mann, S.; Liu, J. B. Signal processing and generation of bioactive nitric oxide in a model prototissue. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5254.
- 95 Zhang, Y. W.; Wang, Z. F.; Li, M.; Xu, C.; Gao, N.; Yin, Z. P.; Wang, K. M.; Mann, S.; Liu, J. B. Osmotic-Induced Reconfiguration and Activation in Membranized Coacervate-Based Protocells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10396–10403.
- 96 Chang, H. J.; Jing, H. R.; Yin, Y. D.; Zhang, Q. F.; Liang, D. H. Membrane-mediated transport in a non-equilibrium hybrid protocell based on coacervate droplets and a surfactant. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13849–13852.
- 97 Liu, S. Y.; Zhang, Y. W.; Li, M.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, Z. J.; Yang, X. H.; He, X. X.; Wang, K. M.; Liu, J. B.; Mann, S. Enzyme-mediated nitric oxide production in vasoactive erythrocyte membrane-enclosed coacervate protocells. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 1165–1173.
- 98 Samanta, A.; Hörner, M.; Liu, W.; Weber, W.; Walther, A. Signal- processing and adaptive prototissue formation in metabolic DNA protocells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3968.
- 99 Chen, Y. F.; Zhang, Y. W.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Y.; Yang, X. H.; Wang, K. M.; Mann, S.; Liu, J. B. Self-immobilization of coacervate droplets by enzyme-mediated hydrogelation. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5438–5441.
- 100 Smokers, L. B.; Visser, B. S.; Slootbeek, A. D.; Huck, W. T.; Spruijt, E. How Droplets Can Accelerate Reactions─Coacervate Protocells as Catalytic Microcompartments. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 1885–1895.
- 101 Li, J. C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L. Z.; Li, C. Y.; Xie, S. T.; Fu, T.; Zhang, Z. W.; Li, L. J.; Qi, L. B.; Lyu, Y. F. et al. Phase Separation of DNA-Encoded Artificial Cells Boosts Signal Amplification for Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306691.
- 102 Sun, W.; Yin, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Xiong, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Endogenous miRNA and K+ Co-Activated Dynamic Assembly of DNA Coacervates for Intracellular miRNA Imaging and Mitochondrial Intervention. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 14101–14110.
- 103 Hu, R.; Wang, X. W.; Zhan, X. Q. Multi-parameter systematic strategies for predictive, preventive and personalised medicine in cancer. EPMA J. 2013, 4, 1–12.
- 104 Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D. S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535.
- 105 Walczak, M.; Mancini, L.; Xu, J.; Raguseo, F.; Kotar, J.; Cicuta, P.; Di Michele, L. A Synthetic Signaling Network Imitating the Action of Immune Cells in Response to Bacterial Metabolism. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301562.
- 106 Li, C. Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, H. Y.; Fu, T.; He, L.; Han, D.; Tan, W. H. Leveraging DNA-Encoded Cell-Mimics for Environment-Adaptive Transmembrane Channel Release-Induced Cell Death. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202406186.
- 107 Hu, Q.; Lan, H. B.; Tian, Y. M.; Li, X. N.; Wang, M. M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y. L.; Chen, W.; Kong, L.; Guo, Y. Y. Biofunctional coacervate-based artificial protocells with membrane-like and cytoplasm-like structures for the treatment of persistent hyperuricemia. J. Control. Release 2024, 365, 176–192.
- 108 Zhang, Y. W.; Liu, S. Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y. F.; Zhou, S. H.; Yang, X. H.; Wang, K. M.; Liu, J. B. Invasion and Defense Interactions between Enzyme-Active Liquid Coacervate Protocells and Living Cells. Small 2020, 16, 2002073.
- 109 Wang, C.; Yang, X. Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Y.; Shang, L. R. Glucose Responsive Coacervate Protocells from Microfluidics for Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2400712.
- 110 Ishak, J.; Unsunnidhal, L.; Martien, R.; Kusumawati, A. Evaluation of chitosan-DNA plasmid complex encoding Jembrana disease virus env-tm protein as a vaccine candidate. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 7–16.
- 111 Zhou, Q.; Xiang, J. J.; Hao, L. Q.; Xu, X. J.; Zhou, Z. X.; Tang, J. B.; Ping, Y.; Shen, Y. Q. Polyplex nanovesicles of single strand oligonucleotides for efficient cytosolic delivery of biomacromolecules. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101221.
- 112 Zhao, P. C.; Guo, J. X.; Jiang, T. S.; Xu, X. Y.; Chen, S. R.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. K.; Li, G.; Bian, L. M. Vacuolated coacervate mediates the bimodal release kinetics of diverse macromolecular drugs in vivo. Mater. Today 2023, 66, 26–35.
- 113 Liang, T. X.; Dong, Y. X.; Cheng, L.; Wen, P.; Li, F. Q.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q.; Ren, E.; Liu, P. F.; Li, H. J. et al. In situ formation of biomolecular condensates as intracellular drug reservoirs for augmenting chemotherapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 8, 1469–1482.
- 114 Thirunavukarasu, D.; Chen, T.; Liu, Z.; Hongdilokkul, N.; Romesberg, F. E. Selection of 2’-Fluoro-Modified Aptamers with Optimized Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2892–2895.
- 115 Roberts, T. C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M. J. A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2020, 19, 673–694.
- 116 Yang, B.; Zhou, B.; Li, C. F.; Li, X. W.; Shi, Z. W.; Li, Y. X.; Zhu, C. Y.; Li, X.; Hua, Y.; Pan, Y. F. et al. A Biostable l-DNA Hydrogel with Improved Stability for Biomedical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202520.
- 117 Holtmannspötter, A. L.; Machatzke, C.; Begemann, C.; Salibi, E.; Donau, C.; Späth, F.; Boekhoven, J.; Mutschler, H. Regulating nucleic acid catalysis using active droplets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202412534.
- 118 Samanta, A.; Baranda Pellejero, L.; Masukawa, M.; Walther, A. DNA-empowered synthetic cells as minimalistic life forms. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 454–470.
- 119 Huang, Z. Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. T.; Peng, R.; Tan, W. H. Leveraging Aptamer-Based DNA Nanotechnology for Bioanalysis and Cancer Therapeutics. Acc. Mater. Res. 2024, 5, 438–452.




