Recent Advances of Boron-Containing Chiral Luminescent Materials†
Jiaqi Di
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuran Han
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Pangkuan Chen
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiaqi Di
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuran Han
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Pangkuan Chen
Beijing Key Laboratory of Photoelectronic/Electrophotonic Conversion Materials, Key Laboratory of Medical Molecule Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 102488 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Boron Chemistry
Abstract
Comprehensive Summary
As a class of organic dyes, boron-containing compounds play an important role in organic luminescent materials. They have attracted considerable attention due to their unique photophysical properties. Chiral luminescent systems have a wide range of practical applications in biological imaging, optoelectronic devices, information storage and 3D display. Boron-containing chiral luminescent materials can not only effectively improve the luminescent properties of CPL materials, but also bring unique properties to the system, which enables them to be used as favorable CPL emitting materials for an expanded range of applications. Here, we review the research progress of boron-containing chiral luminescent materials by the detailed discuss according to different chiral skeletons, such as point chirality, 1,1’-binaphthyl, [n]helicenes, [2,2]paracyclophane and pillar[5]arenes. We believe that this review is of significance for the development of boron-containing compounds and CPL materials.
Key Scientists
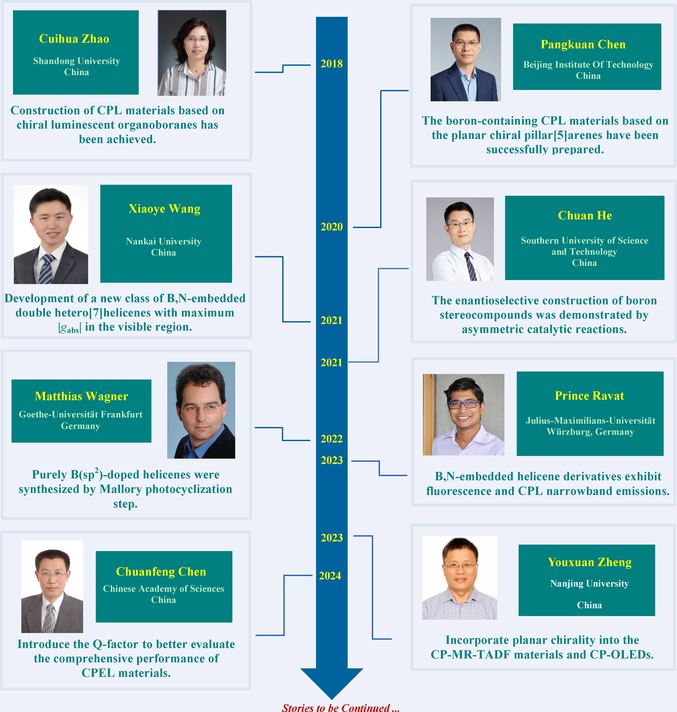
The studies of circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) based on small organic molecules have advanced significantly. However, boron-containing chiral luminescent materials have gained attention only in recent years. In 2019, Zhao's group prepared a binaphthalene derivative modified with triarylborane, representing the organic small molecule luminescent material to exhibit CPL characteristics responsive to both solvent and fluoride ions. In 2020, the Chen's group used the unique luminescence properties and steric effects of triarylborane and triphenylamine to prepare CPL materials based on the planar chiral pillar[5]arenes. In 2021, Wang's group developed a new class of B,N-embedded double hetero[7]helicenes molecules that exhibit strong chiroptical responses in the UV-visible region. In the same year, He's group used asymmetric reactions to synthesize boron-based point-chirality compounds with high efficiency and enantioselectivity. In 2023, Ravat synthesized 1,4-B,N-embedded helicenes exhibiting narrow-band fluorescence and CPL. During this period, Matthias Wagner et al obtained (BO)2-doped tetrathia[7]helicene via an efficient four-step synthesis, and Zheng reported the nearly pure green circularly polarized electroluminescent device (CP-OLED). In 2024, Chen's group prepared B,N-embedded hetero-[9]helicenes offering a pathway towards significantly enhanced efficiency in helicene-based CPEL.
References
- 1 Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Qin, M.; Ma, X.; Dou, X.; Feng, C. Highly Efficient Full-Color and White Circularly Polarized Luminescent Nanoassemblies and Their Performance in Light Emitting Devices. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6233–6238.
- 2 Zhang, M.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Jin, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhuang, T.; Yu, S. Processable Circularly Polarized Luminescence Material Enables Flexible Stereoscopic 3D Imaging. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi9944.
- 3 Zhan, X.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, Y. 3D Laser Displays Based on Circularly Polarized Lasing from Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Arrays. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104418.
- 4 Jiménez, J.; Cerdán, L.; Moreno, F.; Maroto, B.; García-Moreno, I.; Lunkley, J.; Muller, G.; de la Moya, S. Chiral Organic Dyes Endowed with Circularly Polarized Laser Emission. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 5287–5292.
- 5 Cerdán, L.; Moreno, F.; Johnson, M.; Muller, G.; de la Moya, S. García-Moreno, I. Circularly Polarized Laser Emission in Optically Active Organic Dye Solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22088–22093.
- 6 Furumi, S. Recent Progress in Chiral Photonic Band-Gap Liquid Crystals for Laser Applications. Chem. Rec. 2010, 10, 394–408.
- 7 Sherson, J.; Krauter, H.; Olsson, R.; Julsgaard, B.; Hammerer, K.; Cirac, I.; Polzik, E. Quantum Teleportation between Light and Matter. Nature 2006, 443, 557–560.
- 8 Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Tan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, M. Alkaline-Earth Metal Ion Turn-on Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Encrypted Selective Recognition of Amp. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000493.
- 9 Wagenknecht, C.; Li, C.; Reingruber, A.; Bao, X.; Goebel, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, K.; Pan, J. Experimental Demonstration of a Heralded Entanglement Source. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 549–552.
- 10 Han, J.; Guo, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. Recent Progress on Circularly Polarized Luminescent Materials for Organic Optoelectronic Devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800538.
- 11 Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Teng, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, W.; Chen, C. Chiral TADF-Active Polymers for High-Efficiency Circularly Polarized Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23619–23624.
- 12 Meng, G.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, D.; Duan, L. B-N Covalent Bond Embedded Double Hetero-[n]Helicenes for Pure Red Narrowband Circularly Polarized Electroluminescence with High Efficiency and Stability. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2307420.
- 13 Chen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Han, J.; Miao, J.; Qi, Y.; Zou, Y.; Xie, G.; Gong, S.; Yang, C. High-Performance Circularly Polarized Electroluminescence with Simultaneous Narrowband Emission, High Efficiency, and Large Dissymmetry Factor. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109147.
- 14 Ma, X.; Li, J.; Luo, P.; Hu, J.; Han, Z.; Dong, X.; Xie, G.; Zang, S. Carbene-Stabilized Enantiopure Heterometallic Clusters Featuring EQE of 20.8% in Circularly-Polarized OLED. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4121.
- 15 Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Chen, C. Recent Advances in Circularly Polarized Electroluminescence Based on Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1331–1343.
- 16
Jhun, B.; Park, S.; You, Y. Molecular Sensors Producing Circularly Polarized Luminescence Responses. Dyes Pigm. 2023, 208, 110786.
10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110786 Google Scholar
- 17 Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, F.; Zou, H. Aggregation Induced Emission Dynamic Chiral Europium(Iii) Complexes with Excellent Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Smart Sensors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2896.
- 18 Gong, J.; Zhang, X. Coordination-Based Circularly Polarized Luminescence Emitters: Design Strategy and Application in Sensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214329.
- 19 Zinna, F.; Di Bari, L. Lanthanide Circularly Polarized Luminescence: Bases and Applications. Chirality 2015, 27, 1–13.
- 20 Fan, Y.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, S.; Lian, Z.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H. Chiral Carbon Nanorings: Synthesis, Properties and Hierarchical Self-Assembly of Chiral Ternary Complexes Featuring a Narcissistic Chiral Self-Recognition for Chiral Amines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304623.
- 21 Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhuang, G.; Yang, S.; Du, P. An Unexpected Dual-Emissive Luminogen with Tunable Aggregation-Induced Emission and Enhanced Chiroptical Property. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3543.
- 22 Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Jin, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, P. Regulating the Excited State Chirality to Fabricate High-Performance-Solid-State Circularly Polarized Luminescence Materials. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 6074–6080.
- 23 Chen, Z.; Ni, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, H. Helicene-Type Β-Isoindigo-Based Boron-Dipyrromethene Analogs with Strong near-Infrared Chiroptical Activity. Aggregate 2024, 5, e498.
- 24 Wang, Q.; Yuan, L.; Qu, C.; Huang, T.; Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y. Constructing Highly Efficient Circularly Polarized Multiple-Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials with Intrinsically Helical Chirality. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2305125.
- 25 Takaishi, K.; Hinoide, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Ema, T. Axially Chiral Peri-Xanthenoxanthenes as a Circularly Polarized Luminophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11852–11857.
- 26 Yuan, Y.; Hu, M.; Xue, M.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Circularly Polarized Luminescence and SHG Chiral Signals of Helical TPE Macrocycles. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3353–3359.
- 27 Malinčík, J.; Gaikwad, S.; Mora-Fuentes, J.; Boillat, M.; Prescimone, A.; Häussinger, D.; Campaña, A.; Šolomek, T. Circularly Polarized Luminescence in a Möbius Helicene Carbon Nanohoop. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208591.
- 28 Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sue, A.; Cao, X.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Chiral Nanographene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215367.
- 29 Shi, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Kucheryavy, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, K.; Meng, G.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, N.; Zheng, X.; Jäkle, F.; Chen, P. Dynamic B/N Lewis Pairs: Insights into the Structural Variations and Photochromism via Light-Induced Fluorescence to Phosphorescence Switching. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213615.
- 30 Chen, B.; Jäkle, F. Boron-Nitrogen Lewis Pairs in the Assembly of Supramolecular Macrocycles, Molecular Cages, Polymers, and 3D Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202313379.
- 31 Liu, K.; Jiang, Z.; Lalancette, R.; Tang, X.; Jäkle, F. Near-Infrared-Absorbing B–N Lewis Pair-Functionalized Anthracenes: Electronic Structure Tuning, Conformational Isomerism, and Applications in Photothermal Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18908–18917.
- 32 Jin, T.; Kunze, L.; Breimaier, S.; Bolte, M.; Lerner, H.; Jäkle, F.; Winter, R.; Braun, M.; Mewes, J.; Wagner, M. Exploring Structure–Property Relations of B,S-Doped Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons through the Trinity of Synthesis, Spectroscopy, and Theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 13704–13716.
- 33 Li, P.; Shimoyama, D.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Y.; Hu, G.; Li, C.; Yin, X.; Wang, N.; Jäkle, F.; Chen, P. A New Platform of B/N-Doped Cyclophanes: Access to a Π-Conjugated Block-Type B3N3 Macrocycle with Strong Dipole Moment and Unique Optoelectronic Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200612.
- 34 Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Dou, C.; Wang, Y. Boron-Containing Organic Diradicaloids: Dynamically Modulating Singlet Diradical Character by Lewis Acid–Base Coordination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18272–18279.
- 35 Liu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Guo, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Dou, C. Photonic Modulation Enabled by Controlling the Edge Structures of Boron-Doped Molecular Carbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306911.
- 36 Oshimizu, R.; Ando, N.; Yamaguchi, S. Olefin–Borane Interactions in Donor–π–Acceptor Fluorophores That Undergo Frustrated-Lewis-Pair-Type Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209394.
- 37 Wang, J.; Zheng, A.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, J. BN-Embedded Cycloarenes: One-Pot Borylation Synthesis, Photoelectric Properties, and Application in Perovskite Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 14912–14921.
- 38 Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Tan, D.; Chen, X.; Ma, T.; Zhang, B.; Yang, D. Access to Tetracoordinate Boron-Doped Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons with Delayed Fluorescence and Aggregation-Induced Emission under Mild Conditions. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 5597–5605.
- 39 Guo, X.; Sheng, W.; Pan, H.; Guo, L.; Zuo, H.; Wu, Z.; Ling, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiao, L.; Hao, E. Tuning Shortwave-Infrared J-Aggregates of Aromatic Ring-Fused Aza-Bodipys by Peripheral Substituents for Combined Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapies at Ultralow Laser Power. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202319875.
- 40 Wang, L.; Cheng, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, Q.; Hao, E.; Jiao, L. Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (SNAr) as an Approach to Challenging Nitrogen-Bridged BODIPY Oligomers. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 3026–3031.
- 41 Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yue, S.; Shang, R.; Jiang, X.; Du, J. Engineering Aggregates of Julolidine-Substituted Aza-BODIPY Nanoparticles for NIR-II Photothermal Therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 109735.
- 42 Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Ni, Z.; Chen, W.; Gai, L.; Tian, J.; Guo, Z.; Lu, H. Rational Design of CT-Coupled J-Aggregation Platform Based on Aza-BODIPY for Highly Efficient Phototherapy. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 5973–5979.
- 43 Zhang, D.; Teng, K.; Zhao, L.; Niu, L.; Yang, Q. Ultra-Small Nano-Assemblies as Tumor-Targeted and Renal Clearable Theranostic Agent for Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209789.
- 44 Wang, S.; Gai, L.; Chen, Y.; Ji, X.; Lu, H.; Guo, Z. Mitochondria-Targeted Bodipy Dyes for Small Molecule Recognition, Bio-Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 3976–4019.
- 45 Li, H.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L.; Hao, E. BODIPY-Based Photocages: Rational Design and Their Biomedical Application. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 5770–5789.
- 46 Wang, J.; Gong, Q.; Jiao, L.; Hao, E. Research Advances in Bodipy-Assembled Supramolecular Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215367.
- 47 Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yan, M.; Ye, J.; Li, Y.; Dehaen, W.; Yin, S. Near-Infrared Boron–Dipyrrin (BODIPY) Nanomaterials: Molecular Design and Anti-Tumor Therapeutics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 506, 215718.
- 48 Gong, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, S.; Kuang, H.; Duan, P.; Yuan, M.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Tang, B.; Liu, M. Frontiers in Circularly Polarized Luminescence: Molecular Design, Self-Assembly, Nanomaterials, and Applications. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 2060–2104.
- 49 Liu, Y.; Xing, P. Circularly Polarized Light Responsive Materials: Design Strategies and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300968.
- 50 Wang, J.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, C. Advances in Circularly Polarized Luminescence Materials Based on Chiral Macrocycles. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 13089–13106.
- 51 Li, T.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, M. Circularly Polarized Luminescence from Chiral Macrocycles and Their Supramolecular Assemblies. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 3879–3903.
- 52 Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Han, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Tang, Z. Circularly Polarized Luminescence in Chiral Materials. Matter 2022, 5, 837–875.
- 53 Xue, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, P. Circularly Polarized Luminescent π-Conjugated Chiral Nanorings and Nanobelts. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2303322.
- 54
Su, W.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, W.; Yang, K.; Yu, P.; Song, Q. Copper-Catalysed Asymmetric Hydroboration of Alkenes with 1,2-Benzazaborines to Access Chiral Naphthalene Isosteres. Nat. Chem. 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41557–024–01505–0.
10.1038/s41557-024-01505-0 Google Scholar
- 55 Zhang, F.; Liao, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, C.; Lou, Y.; Wang, C.; Song, Q. An Olefinic 1,2-Α-Boryl Migration Enables 1,2-Bis(Boronic Esters) via Radical-Polar Crossover Reaction. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 582–588.
- 56 Xie, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, G. Insights into the Distinct Behaviors between Bifunctional and Binary Organoborane Catalysts through Terpolymerization of Epoxide, CO2, and Anhydride. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404207.
- 57 Chen, Y.; Jia, Q.; Ding, Y.; Sato, S.; Xu, L.; Zang, C.; Shen, X.; Kakuchi, T. B(C6F5)3-Catalyzed Group Transfer Polymerization of Acrylates Using Hydrosilane: Polymerization Mechanism, Applicable Monomers, and Synthesis of Well-Defined Acrylate Polymers. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 844–856.
- 58 Zhang, J.; Xie, Z. Broad Scope Extra-Annular [4+2] Cycloaddition of o-Carboryne with Styrenes: Efficient Route to Carborane-Fused Polycyclics. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 1041–1046.
- 59 Zu, B.; Guo, Y.; He, C. Catalytic Enantioselective Construction of Chiroptical Boron-Stereogenic Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16302–16310.
- 60 Zu, B.; Guo, Y.; Ren, L.-Q.; Li, Y.; He, C. Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Boron-Stereogenic Bodipys. Nat. Synth. 2023, 2, 564–571.
- 61 Zhang, P.; Zeng, J.; Zhuang, F.; Zhao, K.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Pei, J. Parent B2N2-Perylenes with Different Bn Orientations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23313–23319.
- 62 McConnell, C.; Liu, S. Late-Stage Functionalization of BN-Heterocycles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3436–3453.
- 63 Zhao, K.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Ding, L.; Xiong, M.; Wang, J.; Pei, J. “Spine Surgery” of Perylene Diimides with Covalent B–N Bonds toward Electron-Deficient BN-Embedded Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3091–3098.
- 64 Kalluvettukuzhy, N.; Sudhakar, P.; Eyyathiyil, J.; Hara, N.; Imai, Y.; Thilagar, P. Chiral B–N Aiegens: Intense Blue Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Piezochromism. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 6067–6071.
- 65 Gong, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.; Zhang, X. Iodization-Enhanced Fluorescence and Circularly Polarized Luminescence for Dual-Readout Probe Design. Sensors Actuat. B: Chem. 2021, 347, 130610.
- 66 Adewuyi, J.; Ung, G. High Quantum Yields from Perfluorinated Binolate Erbium Complexes and Their Circularly Polarized Luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 7097–7104.
- 67 Mukthar, N.; Schley, N.; Ung, G. Strong Circularly Polarized Luminescence at 1550 nm from Enantiopure Molecular Erbium Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6148–6153.
- 68 Yuan, Y.; Jia, J.; Song, Y.; Ye, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, S. Fluorescent Tpe Macrocycle Relayed Light-Harvesting System for Bright Customized-Color Circularly Polarized Luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5389–5399.
- 69 Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C. Chirality Relay in 2,2′-Substituted 1,1′-Binaphthyl: Access to Propeller Chirality of the Tricoordinate Boron Center. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16750–16754.
- 70 Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, D.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. 2,2′-Diamino-6,6′-Diboryl-1,1′-Binaphthyl: A Versatile Building Block for Temperature-Dependent Dual Fluorescence and Switchable Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4840–4846.
- 71 Zhang, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, N.; Yin, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, P. Molecular Design to Enhance Binaphthyl-Based Chiroptics Using Organoboron Chemistry in Isomeric Chiral Scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 1816–1824.
- 72 Zhang, K.; Hao, M.; Jin, T.; Shi, Y.; Tian, G.; Li, C.; Ma, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Q.; Chen, P. Synthesis of π-Conjugated Chiral Aza/Boracyclophanes with a meta and para Substitution. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202302950.
- 73 Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Qiao, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhou, G. BN-Embedded Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Oligomers: Synthesis, Aromaticity, and Reactivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7122–7130.
- 74 Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Yu, N.; Ren, Y. Facile Route to Novel Diazaphosphinine-Based Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212844.
- 75 Gotoh, H.; Nakatsuka, S.; Tanaka, H.; Yasuda, N.; Haketa, Y.; Maeda, H.; Hatakeyama, T. Syntheses and Physical Properties of Cationic BN-Embedded Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12835–12840.
- 76 Shi, Q.; Shi, X.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, N.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Peng, A.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Fu, H.; Xie, Z.; Marder, S.; Blakey, S.; Huang, H. Synthetic Routes for Heteroatom-Containing Alkylated/Arylated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2924–2928.
- 77 Tian, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Yin, X.; Liu, K.; Chen, P. Applying the B/N Lewis Pair Approach to Access Fusion-Expanded Binaphthyl-Based Chiral Analogues. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 15315–15319.
- 78 Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Ye, K.; Dou, C. Chiral Tetracoordinate Organoboranes Based on Double B←N Bridged Bipyridine with Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Mater. Chem. Front. 2022, 6, 600–606.
- 79 Chattopadhyay, B.; Dannatt, J.; Andujar-De Sanctis, I. L.; Gore, K.; Maleczka, R. Jr.; Singleton, D.; Smith, M. Ir-Catalyzed ortho-Borylation of Phenols Directed by Substrate–Ligand Electrostatic Interactions: A Combined Experimental/in Silico Strategy for Optimizing Weak Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7864–7871.
- 80 Hattori, I.; Hagai, M.; Ito, M.; Sakai, M.; Narita, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Yanai, T.; Yamaguchi, S. In Silico Screening and Experimental Verification of Near-Infrared-Emissive Two-Boron-Doped Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202403829.
- 81 Rapp, M.; Ziemann, P.; Zinna, F.; Di Bari, L.; Bettinger, H. Fruitful Interplay between Theory and Experiment in the Design of Circularly Polarized Luminescent Materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 15767–15773.
- 82 Shen, Y.; Yao, N.; Diao, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, H. A π-Extended Pentadecabenzo[9]Helicene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300840.
- 83 Xiao, X.; Pedersen, S.; Aranda, D.; Yang, J.; Wiscons, R.; Pittelkow, M.; Steigerwald, M.; Santoro, F.; Schuster, N.; Nuckolls, C. Chirality Amplified: Long, Discrete Helicene Nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 983–991.
- 84 Tan, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Vasylevskyi, S.; Lin, Z.; Kabe, R.; Zou, Y.; Müllen, K.; Narita, A.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of a π-Extended Double [9]Helicene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202218494.
- 85 Liu, G.; Koch, T.; Li, Y.; Doltsinis, N.; Wang, Z. Nanographene Imides Featuring Dual-Core Sixfold [5]Helicenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 178–183.
- 86 Tian, X.; Shoyama, K.; Mahlmeister, B.; Brust, F.; Stolte, M.; Würthner, F. Naphthalimide-Annulated [n]Helicenes: Red Circularly Polarized Light Emitters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9886–9894.
- 87 Li, G.; Matsuno, T.; Han, Y.; Wu, S.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Isobe, H.; Wu, J. Fused Quinoidal Dithiophene-Based Helicenes: Synthesis by Intramolecular Radical–Radical Coupling Reactions and Dynamics of Interconversion of Enantiomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10326–10333.
- 88 Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Jia, Y.; Duan, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N.; Chen, P. Red Emissive Double Aza[7]Helicenes with Antiaromaticity/Aromaticity Switching via the Redox-Induced Radical Cation and Dication Species. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302019.
- 89 Qu, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Ye, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Bridging of Cove Regions: A Strategy for Realizing Persistently Chiral Double Heterohelicenes with Attractive Luminescent Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202400661.
- 90 Artigas, A.; Rigoulet, F.; Giorgi, M.; Hagebaum-Reignier, D.; Carissan, Y.; Coquerel, Y. Overcrowded Triply Fused Carbo[7]Helicene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 15084–15087.
- 91 Duan, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, X. Azulene-Embedded [n]Helicenes (n = 5, 6 and 7). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201494.
- 92 Qiu, Z.; Ju, C.; Frédéric, L.; Hu, Y.; Schollmeyer, D.; Pieters, G.; Müllen, K.; Narita, A. Amplification of Dissymmetry Factors in π-Extended [7]-and [9]Helicenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4661–4667.
- 93 Qiu, S.; Valdivia, A.; Zhuang, W.; Hung, F.; Che, C.; Casado, J.; Liu, J. Nonalternant Nanographenes Containing N-Centered Cyclopenta[ef]Heptalene and Aza[7]Helicene Units. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024. 146, 16161–16172.
- 94 Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. Propeller Configuration Flipping of the Trivalent Boron-Inducing Substituent Dependence of the Circularly Polarized Luminescence Sign in Triarylborane-Based [7]Helicenes. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 4759–4763.
- 95 Zhao, Z.; Liang, X.; He, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C. Triarylborane-Based [5]Helicenes with Full-Color Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 9569–9573.
- 96 Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Shang, Q.; Wang, N.; Yin, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, P. [5]Helicene-Based Chiral Triarylboranes with Large Luminescence Dissymmetry Factors over a 10−2 Level: Synthesis and Design Strategy via Isomeric Tuning of Steric Substitutions. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 6226–6234.
- 97 Baser-Kirazli, N.; Lalancette, R.; Jäkle, F. Enhancing the Acceptor Character of Conjugated Organoborane Macrocycles: A Highly Electron-Deficient Hexaboracyclophane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8689–8697.
- 98 Wang, J.; Zhuang, G.; Chen, M.; Lu, D.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q.; Jia, H.; Cui, S.; Shao, X.; Yang, S.; Du, P. Selective Synthesis of Conjugated Chiral Macrocycles: Sidewall Segments of (−)/(+)-(12,4) Carbon Nanotubes with Strong Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1619–1626.
- 99 Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, T.; He, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ning, H.; Ren, J.; Bakulin, A.; Gao, F.; Yuan, J.; Zou, Y. The Synthesis of a Multiple D–A Conjugated Macrocycle and Its Application in Organic Photovoltaic. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202311645.
- 100 Shi, T.; Tong, S.; Wang, M. Construction of Hydrocarbon Nanobelts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7700–7705.
- 101 Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, C.; Di, J.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, X.; Chen, P. Synthesis of Π-Conjugated Chiral Organoborane Macrocycles with Blue to Near-Infrared Emissions and the Diradical Character of Cations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10092–10103.
- 102 Zhang, F.; Rauch, F.; Swain, A.; Marder, T.; Ravat, P. Efficient Narrowband Circularly Polarized Light Emitters Based on 1,4-B,N-Embedded Rigid Donor–Acceptor Helicenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202218965.
- 103 Menduti, L.; Baldoli, C.; Manetto, S.; Bolte, M.; Lerner, H.; Longhi, G.; Villani, C.; Licandro, E.; Wagner, M. (BO)2-Doped Tetrathia[7]Helicene: A Configurationally Stable Blue Emitter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215468.
- 104 Full, J.; Panchal, S.; Götz, J.; Krause, A.; Nowak-Król, A. Modular Synthesis of Organoboron Helically Chiral Compounds: Cutouts from Extended Helices. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4350–4357.
- 105 Volland, D.; Niedens, J.; Geppert, P.; Wildervanck, M.; Full, F.; Nowak-Król, A. Synthesis of a Blue-Emissive Azaborathia[9]Helicene by Silicon-Boron Exchange from Unusual Atropisomeric Teraryls. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304291.
- 106 Appiarius, Y.; Míguez-Lago, S.; Puylaert, P.; Wolf, N.; Kumar, S.; Molkenthin, M.; Miguel, D.; Neudecker, T.; Juríček, M.; Campaña, A. G.; Staubitz, A. Boosting Quantum Yields and Circularly Polarized Luminescence of Penta- and Hexahelicenes by Doping with Two Bn-Groups. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 466–476.
- 107 Li, J.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Sue, A.; Cao, X.; Wang, X. B,N-Embedded Double Hetero[7]Helicenes with Strong Chiroptical Responses in the Visible Light Region. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 17958–17963.
- 108 Tan, D.; Dong, J.; Ma, T.; Feng, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, D. Multiple Helicenes Defected by Heteroatoms and Heptagons with Narrow Emissions and Superior Photoluminescence Quantum Yields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304711.
- 109 Full, F.; Wölflick, Q.; Radacki, K.; Braunschweig, H.; Nowak-Król, A. Enhanced Optical Properties of Azaborole Helicenes by Lateral and Helical Extension. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202202280.
- 110 Full, J.; Wildervanck, M.; Dillmann, C.; Panchal, S.; Volland, D.; Full, F.; Meerholz, K.; Nowak-Król, A. Impact of Truncation on Optoelectronic Properties of Azaborole Helicenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202302808.
- 111 Domínguez, Z.; López-Rodríguez, R.; Álvarez, E.; Abbate, S.; Longhi, G.; Pischel, U.; Ros, A. Azabora[5]Helicene Charge-Transfer Dyes Show Efficient and Spectrally Variable Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 12660–12668.
- 112 Vázquez-Domínguez, P.; Rizo, J.; Arteaga, J.; Jacquemin, D.; Favereau, L.; Ros, A.; Pischel, U. Azaborahelicene Fluorophores Derived from Four-Coordinate N,C-Boron Chelates: Synthesis, Photophysical and Chiroptical Properties. Org. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 843–853.
- 113 Jiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, F. Synthesis of Nonsymmetric NBN-Embedded [6]-and [7]Helicenes with Amplified Activities. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 8766–8770.
- 114 Sun, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, L.; Jiao, Y.; Thiruvengadam, P.; Wu, D.; Zhang, F. Divergent Synthesis of Double Heterohelicenes as Strong Chiral Double Hydrogen-Bonding Donors. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6670–6675.
- 115 Guo, W.; Zhao, W.; Tan, K.; Li, M.; Chen, C. B,N-Embedded Hetero[9]Helicene toward Highly Efficient Circularly Polarized Electroluminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202401835.
- 116 Han, D.; Yang, X.; Han, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, T.; Duan, P. Sequentially Amplified Circularly Polarized Ultraviolet Luminescence for Enantioselective Photopolymerization. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5659.
- 117 Hassan, Z.; Spuling, E.; Knoll, D.; Bräse, S. Regioselective Functionalization of [2.2]Paracyclophanes: Recent Synthetic Progress and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2156–2170.
- 118
Otterbach, S.; Elsing, D.; Schulz, A.; Tappert, H.; Wenzel, W.; Kozlowska, M.; Röhm, H.; Bräse, S. Pseudo-para-Substituted [2.2]Paracyclophanes for Hole Transport in Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2309226.
10.1002/adfm.202309226 Google Scholar
- 119 Hassan, Z.; Spuling, E.; Knoll, D.; Lahann, J.; Bräse, S. Planar Chiral [2.2]Paracyclophanes: From Synthetic Curiosity to Applications in Asymmetric Synthesis and Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6947–6963.
- 120 Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Lu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, C. Solid-State Emissive Triarylborane-Based [2.2]Paracyclophanes Displaying Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6868–6871.
- 121 Zhang, M.; Liang, X.; Ni, D.; Liu, D.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. 2-(Dimesitylboryl)Phenyl-Substituted [2.2]Paracyclophanes Featuring Intense and Sign-Invertible Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 2–7.
- 122 Chen, C.; Zheng, W. Planar Chiral B–N Heteroarenes Based on [2.2]Paracyclophane as Circularly Polarized Luminescence Emitters. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 5554–5558.
- 123 Rapp, M.; Leis, W.; Zinna, F.; Di Bari, L.; Arnold, T.; Speiser, B.; Seitz, M.; Bettinger, H. Bright Luminescence by Combining Chiral [2.2]Paracyclophane with a Boron–Nitrogen-Doped Polyaromatic Hydrocarbon Building Block. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202104161.
- 124 Liao, X.; Pu, D.; Yuan, L.; Tong, J.; Xing, S.; Tu, Z.; Zuo, J.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y. Planar Chiral Multiple Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials for Efficient Circularly Polarized Electroluminescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217045.
- 125 Wang, K.; Tian, X.; Jordan, J.; Velmurugan, K.; Wang, L.; Hu, X. The Emerging Applications of Pillararene Architectures in Supramolecular Catalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 89–96.
- 126 Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F. Pillararene-Induced Intramolecular through-Space Charge Transfer and Single-Molecule White-Light Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202381.
- 127 Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L.; Hua, B.; Wang, M.; Liang, H.; Khashab, N.; Sessler, J.; Huang, F. Pillararene-Based Variable Stoichiometry Co-Crystallization: A Versatile Approach to Diversified Solid-State Superstructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 667–675.
- 128 Wang, K.; Jordan, J.; Velmurugan, K.; Tian, X.; Zuo, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, L. Role of Functionalized Pillararene Architectures in Supramolecular Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9205–9214.
- 129 Ohtani, S.; Kato, K.; Fa, S.; Ogoshi, T. Host–Guest Chemistry Based on Solid-State Pillar[n]arenes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 462, 214503.
- 130 Shi, T.; Akine, S.; Ohtani, S.; Kato, K.; Ogoshi, T. Friedel–Crafts Acylation for Accessing Multi-Bridge-Functionalized Large Pillar[n]arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318268.
- 131 Kato, K.; Kaneda, T.; Ohtani, S.; Ogoshi, T. Per-Arylation of Pillar[n]arenes: An Effective Tool to Modify the Properties of Macrocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6905–6913.
- 132 Chen, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Meng, G.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, S.; Chen, P. Planar Chiral Organoboranes with Thermoresponsive Emission and Circularly Polarized Luminescence: Integration of Pillar[5]arenes with Boron Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11267–11272.
- 133 Chen, J.; Gao, Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, P.; Wei, T. A Pillar[5]arene-Based Planar Chiral Charge-Transfer Dye with Enhanced Circularly Polarized Luminescence and Multiple Responsive Chiroptical Changes. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 987–993.
- 134 Chen, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, N.; Chen, P. Pillar[5]arene-Based Dual Chiral Organoboranes with Allowed Host–Guest Chemistry and Circularly Polarized Luminescence. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 12654–12663.




