Preparation of Peptide Selenoesters from Their Corresponding Acyl Hydrazides†
Yunxue Li
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiazhi Liu
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorQingqing Zhou
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Zhao
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ping Wang
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYunxue Li
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiazhi Liu
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorQingqing Zhou
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Zhao
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ping Wang
Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author†Dedicated to the Special Issue of Xplorer Prize in 2020.
Main observation and conclusion
Selenoesters are useful substitutes for traditional thioesters in protein ligation chemistry due to their high reactivity in the trans-thio/selenoesterification reaction. However, existing synthetic routes to access peptide selenoester require a selenoesterification reaction between a selenide and a protected peptide with a free carboxylate at the C-terminus. Herein, we introduce an efficient method to convert peptide acyl hydrazide, a convenient thioester surrogate, into the desired selenoester for peptide ligation. Our methodology can be applied to fully de-protected peptides with various C-terminal amino acid residues in high yield without racemization. We believe that this method provides a useful alternative to access peptide C-terminal selenoesters for protein ligation.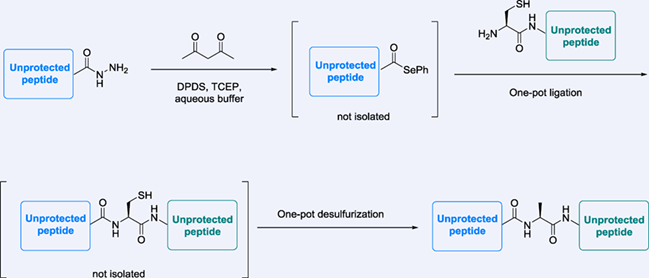
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202100086-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 7.8 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Tan, Y.; Wu, H.; Wei, T.; Li, X. Chemical Protein Synthesis: Advances, Challenges, and Outlooks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20288–20298; (b) Agouridas, V.; El Mahdi, O.; Melnyk, O. Chemical Protein Synthesis in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 15140–15152.
- 2(a) Boutureira, O.; Bernardes, G. J. L. Advances in Chemical Protein Modification. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2174–2195; (b) Wang, C.; Zou, P.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Cheng, L.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, P. R. Dynamic Modifications of Biomacromolecules: Mechanism and Chemical Interventions. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1459–1471; (c) Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Recent Developments in Peptide Ligation Independent of Amino Acid Side-Chain Functional Group. Sci. China Chem. 2018, 61, 97–112; (d) Lin, J. D.; Liu, X. W. Recent Development in Ligation Methods for Glycopeptide and Glycoprotein Synthesis. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 2548–2557; (e) Hu, J. J.; He, P. Y.; Li, Y. M. Chemical Modifications of Tryptophan Residues in Peptides and Proteins. J. Pept. Sci. 2021, 27, e3286.
- 3(a) Bode, J. W.; Fox, R. M.; Baucom, K. D. Chemoselective Amide Ligations by Decarboxylative Condensations of N-Alkylhydroxylamines and Α-Ketoacids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1248–1252; (b) Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Lam, H. Y.; Lee, C. L.; Li, X. Protein Chemical Synthesis by Serine and Threonine Ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 6657–6662; (c) Xu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J. Recent Advances in Enzyme-Mediated Peptide Ligation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1009–1016; (d) Giesler, R. J.; Erickson, P. W.; Kay, M. S. Enhancing Native Chemical Ligation for Challenging Chemical Protein Syntheses. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 58, 37–44.
- 4(a) Dawson, P.; Muir, T.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Kent, S. Synthesis of Proteins by Native Chemical Ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779; (b) Dawson, P. E.; Kent, S. B. Synthesis of Native Proteins by Chemical Ligation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 923–960.
- 5 Li, H.; Dong, S. Recent Advances in the Preparation of Fmoc-SPPS- Based Peptide Thioester and Its Surrogates for Ncl-Type Reactions. Sci. China Chem. 2017, 60, 201–213.
- 6 Lu, D.; Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, F.; Huang, W.; Wang, P. Chemical Synthesis of the Homogeneous Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony- Stimulating Factor through Se-Auxiliary-Mediated Ligation. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 1652–1660.
- 7 Chatterjee, C.; McGinty, R. K.; Pellois, J. P.; Muir, T. W. Auxiliary-Mediated Site-Specific Peptide Ubiquitylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2814–2818.
- 8(a) Yin, H.; Lu, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. Development of Powerful Auxiliary-Mediated Ligation to Facilitate Rapid Protein Assembly. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5138–5142; (b) Agouridas, V.; El Mahdi, O.; Diemer, V.; Cargoët, M.; Monbaliu, J. C. M.; Melnyk, O. Native Chemical Ligation and Extended Methods: Mechanisms, Catalysis, Scope, and Limitations. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7328–7443.
- 9(a) Wan, Q.; Danishefsky, S. J. Free-Radical-Based, Specific Desulfurization of Cysteine: A Powerful Advance in the Synthesis of Polypeptides and Glycopolypeptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9248–9252; (b) Yin, H.; Zheng, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P. Stereoselective and Divergent Construction of Β-Thiolated/ Selenolated Amino Acids via Photoredox-Catalyzed Asymmetric Giese Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14201–14209.
- 10(a) Unverzagt, C.; Kajihara, Y. Chemical Assembly of N-Glycoproteins: A Refined Toolbox to Address a Ubiquitous Posttranslational Modification. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4408–4420; (b) Yan, B.; Shi, W.; Ye, L.; Liu, L. Acyl Donors for Native Chemical Ligation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 46, 33–40; (c) Wang, S.; Thopate, Y. A.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, P. Chemical Protein Synthesis by Native Chemical Ligation and Variations Thereof. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 1181–1193.
- 11(a) Blanco-Canosa, J. B.; Dawson, P. E. An Efficient Fmoc-Spps Approach for the Generation of Thioester Peptide Precursors for Use in Native Chemical Ligation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6851–6855; (b) Blanco-Canosa, J. B.; Nardone, B.; Albericio, F.; Dawson, P. E. Chemical Protein Synthesis Using a Second-Generation N-Acylurea Linker for the Preparation of Peptide-Thioester Precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7197–7209; (c) Wang, J. X.; Fang, G. M.; He, Y.; Qu, D. L.; Yu, M.; Hong, Z. Y.; Liu, L. Peptide O-Aminoanilides as Crypto-Thioesters for Protein Chemical Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 2194–2198; (d) Pira, S. L.; El Mahdi, O.; Raibaut, L.; Drobecq, H.; Dheur, J.; Boll, E.; Melnyk, O. Insight into the Sea Amide Thioester Equilibrium. Application to the Synthesis of Thioesters at Neutral Ph. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 7211–7216.
- 12(a) Fang, G. M.; Li, Y. M.; Shen, F.; Huang, Y. C.; Li, J. B.; Lin, Y.; Cui, H. K.; Liu, L. Protein Chemical Synthesis by Ligation of Peptide Hydrazides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7645–7649; (b) Zheng, J. S.; Tang, S.; Qi, Y. K.; Wang, Z. P.; Liu, L. Chemical Synthesis of Proteins Using Peptide Hydrazides as Thioester Surrogates. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2483–2495.
- 13(a) Li, Y. M.; Yang, M. Y.; Huang, Y. C.; Li, Y. T.; Chen, P. R.; Liu, L. Ligation of Expressed Protein Α-Hydrazides Via Genetic Incorporation of an Α-Hydroxy Acid. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1015–1022; (b) Adams, A. L.; Cowper, B.; Morgan, R. E.; Premdjee, B.; Caddick, S.; Macmillan, D. Cysteine Promoted C-Terminal Hydrazinolysis of Native Peptides and Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13062–13066; (c) Tsuda, Y.; Shigenaga, A.; Tsuji, K.; Denda, M.; Sato, K.; Kitakaze, K.; Nakamura, T.; Inokuma, T.; Itoh, K.; Otaka, A. Development of a Chemical Methodology for the Preparation of Peptide Thioesters Applicable to Naturally Occurring Peptides Using a Sequential Quadruple Acyl Transfer System. ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 448–452.
- 14 Staudinger, H.; Meyer, J. Über Neue Organische Phosphorverbindungen Iii. Phosphinmethylenderivate Und Phosphinimine. Helv. Chim. Acta 1919, 2, 635–646.
- 15 Flood, D. T.; Hintzen, J. C. J.; Bird, M. J.; Cistrone, P. A.; Chen, J. S.; Dawson, P. E. Leveraging the Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis for the Facile Generation of Thioester Surrogates for Use in Native Chemical Ligation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11634–11639.
- 16 Huber, R. E.; Criddle, R. S. Comparison of the Chemical Properties of Selenocysteine and Selenocystine with Their Sulfur Analogs. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1967, 122, 164–173.
- 17(a) Hondal, R. J.; Nilsson, B. L.; Raines, R. T. Selenocysteine in Native Chemical Ligation and Expressed Protein Ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5140–5141; (b) Quaderer, R.; Sewing, A.; Hilvert, D. Selenocysteine-Mediated Native Chemical Ligation. Helv. Chim. Acta 2001, 84, 1197–1206; (c) Gieselman, M. D.; Xie, L.; van der Donk, W. A. Synthesis of a Selenocysteine-Containing Peptide by Native Chemical Ligation. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1331–1334; (d) Metanis, N.; Keinan, E.; Dawson, P. E. Traceless Ligation of Cysteine Peptides Using Selective Deselenization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7049–7053; (e) Dawson, P. E. Native Chemical Ligation Combined with Desulfurization and Deselenization: A General Strategy for Chemical Protein Synthesis. Isr. J. Chem. 2011, 51, 862–867; (f) Mousa, R.; Reddy, P. S.; Metanis, N. Chemical Protein Synthesis through Selenocysteine Chemistry. Synlett 2017, 28, 1389–1393; (g) Mousa, R.; Notis Dardashti, R.; Metanis, N. Selenium and Selenocysteine in Protein Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15818–15827; (h) Dardashti, R. N.; Metanis, N. Revisiting Ligation at Selenomethionine: Insights into Native Chemical Ligation at Selenocysteine and Homoselenocysteine. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4983–4989; (i) Kulkarni, S. S.; Sayers, J.; Premdjee, B.; Payne, R. J. Rapid and Efficient Protein Synthesis through Expansion of the Native Chemical Ligation Concept. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0122.
- 18 Zhong, L.; Arnér, E. S.; Holmgren, A. Structure and Mechanism of Mammalian Thioredoxin Reductase: The Active Site Is a Redox-Active Selenolthiol/Selenenylsulfide Formed from the Conserved Cysteine- Selenocysteine Sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000, 97, 5854–5859.
- 19(a) Townsend, S. D.; Tan, Z.; Dong, S.; Shang, S.; Brailsford, J. A.; Danishefsky, S. J. Advances in Proline Ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3912–3916; (b) Sayers, J.; Karpati, P. M. T.; Mitchell, N. J.; Goldys, A. M.; Kwong, S. M.; Firth, N.; Chan, B.; Payne, R. J. Construction of Challenging Proline–Proline Junctions via Diselenide–Selenoester Ligation Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13327–13334.
- 20(a) Fécourt, F.; Delpech, B.; Melnyk, O.; Crich, D. Se-(9-Fluorenylmethyl) Selenoesters; Preparation, Reactivity, and Use as Convenient Synthons for Selenoacids. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3758–3761; (b) Temperini, A.; Piazzolla, F.; Minuti, L.; Curini, M.; Siciliano, C. General, Mild, and Metal-Free Synthesis of Phenyl Selenoesters from Anhydrides and Their Use in Peptide Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 4588–4603; (c) Takei, T.; Andoh, T.; Takao, T.; Hojo, H. One-Pot Four- Segment Ligation Using Seleno- and Thioesters: Synthesis of Superoxide Dismutase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15708–15711; (d) Du, J. J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X. F.; Sun, H.; Guo, J. Peptidyl Omega-Asp Selenoesters Enable Efficient Synthesis of N-Linked Glycopeptides. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–9.
- 21 Durek, T.; Alewood, P. F. Preformed Selenoesters Enable Rapid Native Chemical Ligation at Intractable Sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12042–12045.
- 22(a) Mitchell, N. J.; Malins, L. R.; Liu, X.; Thompson, R. E.; Chan, B.; Radom, L.; Payne, R. J. Rapid Additive-Free Selenocystine–Selenoester Peptide Ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14011–14014; (b) Hanna, C. C.; Kulkarni, S. S.; Watson, E. E.; Premdjee, B.; Payne, R. J. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Peptide Selenoesters via a Side-Chain Anchoring Strategy. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5424–5427.
- 23 Raibaut, L.; Cargoët, M.; Ollivier, N.; Chang, Y. M.; Drobecq, H.; Boll, E.; Desmet, R.; Monbaliu, J.-C.; Melnyk, O. Accelerating Chemoselective Peptide Bond Formation Using Bis(2-Selenylethyl)Amido Peptide Selenoester Surrogates. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2657–2665.
- 24 Bang, D.; Chopra, N.; Kent, S. B. H. Total Chemical Synthesis of Crambin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1377–1383.




