Shi Epoxidation: A Great Shortcut to Complex Compounds
Xiangqing Feng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Haifeng Du
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiangqing Feng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Haifeng Du
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Recognition and Function, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Shi epoxidation provides an extremely powerful tool to access optically active epoxides, which undoubtedly belongs to one of the earliest and most successful organocatalytic systems. Several generations of chiral ketones have been developed to realize the asymmetric epoxidation of each type of unfunctionalized alkenes, including trans-, trisubstituted olefins, cis-olefins, terminal olefins, and tetrasubstituted olefins. Due to its reliability and high regio- and enantioselectivity, Shi epoxidation has been widely applied in the synthesis of complex natural products and biologically active molecules.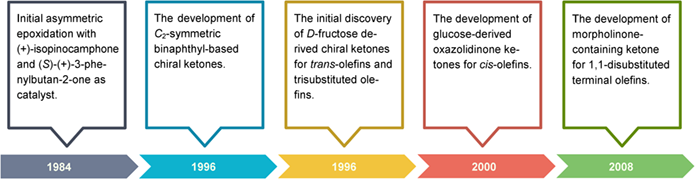
References
- 1For leading reviews, see: (a) Marco-Contelles, J.; Molina, M. T.; Anjum, S. Naturally Occurring Cyclohexane Epoxides: Sources, Biological Activities, and Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2857–2900; (b) Altmann, K.-H. The Merger of Natural Product Synthesis and Medicinal Chemistry: on the Chemistry and Chemical Biology of Epothilones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2137–2152; (c) Miyashita, K.; Imanishi, T. Syntheses of Natural Products Having an Epoxyquinone Structure. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4515–4536; (d) Crotti, P.; Pineschi, M. Epoxides in Complex Molecule Synthesis. In Aziridines and Epoxides in Organic Synthesis, Ed.: Yudin, A. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006, pp. 271–313; (e) Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T. Bioactive Macrolides and Polyketides from Marine Dinoflagellates of the Genus Amphidinium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 451–460; (f) Zhou, Z.-L.; Yang, Y.-X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.-C.; Miao, Z.-H. Triptolide: Structural Modifications, Structure-Activity Relationships, Bioactivities, Clinical Development and Mechanisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 457–475.
- 2For leading reviews, see: (a) Smith, J. G. Synthetically Useful Reactions of Epoxides. Synthesis 1984, 629–656; (b) Lauret, C. Epoxy Ketones as Versatile Building Blocks in Organic Synthesis. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2001, 12, 2359–2383; (c) Schneider, C. Synthesis of 1,2-Difunctionalized Fine Chemicals through Catalytic, Enantioselective Ring-Opening Reactions of Epoxides. Synthesis 2006, 3919–3944; (d) Nielsen, L. P. C.; Jacobsen, E. N. Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxide Ring-Opening Chemistry. In Aziridines and Epoxides in Organic Synthesis, Ed.: Yudin, A. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006, pp. 229–269; (e) Olofsson, B.; Somfai, P. Vinylepoxides in Organic Synthesis. In Aziridines and Epoxides in Organic Synthesis, Ed.: Yudin, A. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006, pp. 315–347; (f) Das, B.; Damodar, K. Epoxides and Oxetanes. In Heterocycles in Natural Product Synthesis, Eds.: Majumdar, K. C.; Chattopadhyay, S. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011, pp. 63–95.
- 3For leading reviews, see: (a) Besse, P.; Veschambre, H. Chemical and biological synthesis of chiral epoxides. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8885–8927; (b) Bonini, C.; Righi, G. A Critical Outlook and Comparison of Enantioselective Oxidation Methodologies of Olefins. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 4981–5021; (c) Xia, Q.-H.; Ge, H.-Q.; Ye, C.-P.; Liu, Z.-M.; Su, K.-X. Advances in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1603–1662; (d) Adolfsson, H. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Epoxidation of Alkenes. In Modern Oxidation Methods, Ed.: Bäckvall, J.-E., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010, pp. 21–49; (e) De Faveri, G.; Ilyashenko, G.; Watkinson, M. Recent Advances in Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation Using the Environmentally Benign Oxidant Hydrogen Peroxide and its Derivatives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1722–1760.
- 4For leading reviews, see: (a) Johnson, R. A.; Sharpless, K. B. Asymmetric Oxidations and Related Reactions: Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols. In Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis, Ed.: Ojima, I., Wiley-VCH, New York, 2000, pp. 229–280; (b) Li, Z.; Yamamoto, H. Hydroxamic Acids in Asymmetric Synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 506–518; (c) Katsuki, T. In Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis, Ed.: Ojima, I., Wiley-VCH, New York, 2000, pp. 287–325; (d) McGarrigle, E. M.; Gilheany, D. G. Chromium− and Manganese−salen Promoted Epoxidation of Alkenes. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1563–1602; (e) Berkessel, A. Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Enones and Related Compounds. In Asymmetric Synthesis-The Essentials, 2nd ed., Eds.: Christman, M.; Bräse, S., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008, p. 185.
- 5For leading reviews, see: (a) Dalko, P. I.; Moisan, L. Enantioselective Organocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3726–3748; (b) Dalko, P. I.; Moisan, L. Asymmetric Catalysis: in the Golden Age of Organocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5138–5175; (c) Guillena, G.; Ramón, D. J. Enantioselective α-Heterofunctionalisation of Carbonyl Compounds: Organocatalysis is the Simplest Approach. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2006, 17, 1465–1492; (d) Schwarz, M.; Reiser, O. Metal or No Metal: That Is the Question! Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10495–10497.
- 6For selective references on phase-transfer catalysts, see: (a) Macdonald, G.; Alcaraz, L.; Lewis, N. J.; Taylor, R. J. K. Asymmetric Synthesis of the mC7N Core of the Manumycin Family: Preparation of (+)-MT 35214 and a Formal Total Synthesis of (−)-Alisamycin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 5433–5436; (b) Kawai, H.; Okusu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Tokunaga, E.; Yamano, A.; Shiro, M.; Shibata, N. Enantioselective Synthesis of Epoxides Having a Tetrasubstituted Trifluoromethylated Carbon Center: Methylhydrazine-Induced Aerobic Epoxidation of β,β-Disubstituted Enones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2221–2225; (c) Corey, E. J.; Zhang, F.-Y. Mechanism and Conditions for Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of α,β-Enones Using Charge- Accelerated Catalysis by a Rigid Quaternary Ammonium Salt. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1287–1290; (d) Ooi, T.; Ohara, D.; Tamura, M.; Maruoka, K. Design of New Chiral Phase-Transfer Catalysts with Dual Functions for Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6844–6845.
- 7For leading reviews on peptide-catalyzed epoxidation of olefins, see: (a) Ebrahim, S.; Wills, M. Synthetic Applications of Polymeric α-Amino Acids. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1997, 8, 3163–3173; (b) Pu, L. Recent Developments in Asymmetric Catalysis Using Synthetic Polymers with Main Chain Chirality. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1998, 9, 1457–1477; (c) Porter, M. J.; Roberts, S. M.; Skidmore, J. Polyamino Acids as Catalysts in Asymmetric Synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 2145–2156; (d) Davie, E. A. C.; Mennen, S. M.; Xu, Y.; Miller, S. J. Asymmetric Catalysis Mediated by Synthetic Peptides. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5759–5812.
- 8For leading reviews on ketone-catalyzed asymmetric epoxidation, see: (a) Adam, W.; Saha-Möller, C. R.; Ganeshpure, P. A. Synthetic Applications of Nonmetal Catalysts for Homogeneous Oxidations. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3499–3548; (b) Shi, Y. In Handbook of Chiral Chemicals, 2nd ed., Ed.: Ager, D., CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2006, p. 147; (c) D. Goeddel; Y Shi. In Science of Synthesis, Ed.: Forsyth, C. J., Georg Thieme Verlag KG, Stuttgart, Germany, 2008, p. 277; (d) Yang, B. V. In Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II, Ed.: Li, J. J., John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2011, pp. 21–39; (e) Wong, O. A.; Ramirez, T. A.; Shi, Y. In Science of Synthesis: Asymmetric Organocatalysis 1, Ed.: List, B., Georg Thieme Verlag, New York, 2012, p. 783; (f) Wong, O. A.; Ramirez, T. A.; Shi, Y. In Comprehensive Chirality, Eds.: Carreira, E. M.; Yamamoto, H., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012, p. 528; (g) O. A. Wong; B. Nettles; Y Shi. In Carbohydrates−Tools for Stereoselective Synthesis, Ed.: Boysen, M. M. K., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2013, p. 321; (h) Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cornwall, R. G.; Shi, Y. Organocatalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation and Aziridination of Olefins and Their Synthetic Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8199−8256.
- 9For selective references on chiral iminium/enamine catalysts, see: (a) Marigo, M.; Franzén, J.; Poulsen, T. B.; Zhuang, W.; Jørgensen, K. A. Asymmetric Organocatalytic Epoxidation of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes with Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6964–6965; (b) Albrecht, Ł.; Jiang, H.; Dickmeiss, G.; Gschwend, B.; Hansen, S. G.; Jørgensen, K. A. Asymmetric Formal trans-Dihydroxylation and trans-Aminohydroxylation of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes via an Organocatalytic Reaction Cascade. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9188–9196; (c) Nicolaou, K. C.; Sarlah, D.; Wu, T. R.; Zhan, W. Total Synthesis of Hirsutellone B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6870–6874; (d) Egger, J.; Bretscher, P.; Freigang, S.; Kopf, M.; Carreira, E. M. Synthesis of Epoxyisoprostanes: Effects in Reducing Secretion of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and IL-12. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5382–5385.
- 10 Curci, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Serio, M. R. Asymmetric Epoxidation of Unfunctionalized Alkenes by Dioxirane Intermediates Generated from Potassium Peroxomonosulfate and Chiral Ketones. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1984, 155–156.
- 11(a) Yang, D.; Yip, Y.-C.; Tang, M.-W.; Wong, M.-K.; Zheng, J.-H.; Cheung, K.-K. A C2 Symmetric Chiral Ketone for Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Unfunctionalized Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 491–492; (b) Yang, D.; Wang, X.-C.; Wong, M.-K.; Yip, Y.-C.; Tang, M.-W. Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of trans-Stilbenes Catalyzed by Chiral Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11311–11312; (c) Yang, D.; Wong, M.-K.; Yip, Y.-C.; Wang, X.-C.; Tang, M.-W.; Zheng, J.-H.; Cheung, K.-K. Design and Synthesis of Chiral Ketones for Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Unfunctionalized Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5943–5952; (d) Yang, D.; Yip, Y.-C.; Chen, J.; Cheung, K.-K. Significant Effects of Nonconjugated Remote Substituents in Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 7659–7660.
- 12 Yang, D. Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 497–505.
- 13(a) Tu, Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. An Efficient Asymmetric Epoxidation Method for trans-Olefins Mediated by a Fructose-derived Ketone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9806–9807; (b) Wang, Z.-X.; Tu, Y.; Frohn, M.; Zhang, J.-R.; Shi, Y. An Efficient Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11224–11235; (c) Tu, Y.; Frohn, M.; Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. Synthesis of 1,2:4,5-Di-O-Isopropylidene-D- erythro-2,3-hexodiulo-2,6-pyranose. A Highly Enatioselective Ketone Catalyst for Epoxidation. Org. Synth. 2003, 80, 1–8; (d) Wang, Z.-X.; Shu, L.; Frohn, M.; Tu, Y.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation of trans-β- Methylstyrene and 1-Phenylcyclohexene Using a D-Fructose-Derived Ketone. Org. Synth. 2003, 80, 9–17; (e) Zhao, M.-X.; Shi, Y. Practical Synthesis of an L-Fructose-Derived Ketone Catalyst for Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5377–5379.
- 14For selective references on chiral ketones catalysts, see: (a) Denmark, S. E.; Forbes, D. C.; Hays, D. S.; DePue, J. S.; Wilde, R. G. Catalytic Epoxidation of Alkenes with Oxone. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1391–1407; (b) Song, C. E.; Kim, Y. H.; Lee, K. C.; Lee, S.-g.; Jin, B. W. New C2-symmetric Chiral Ketones for Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Unfunctionalized Olefins. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1997, 8, 2921–2926; (c) Adam, W.; Zhao, C.-G. Synthesis of Optically Active C2-symmetric Ketones for the Asymmetric Epoxidation of Prochiral Olefins by Dioxiranes Generated in situ with CaroateTM as a Peroxide Source. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1997, 8, 3995–3998; (d) Denmark, S. E.; Wu, Z. Catalytic Epoxidation of Alkenes with Oxone. 2. Fluoro Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8288–8289; (e) Armstrong, A.; Hayter, B. R. Catalytic Enantioselective Epoxidation of Alkenes with a Tropinone- derived Chiral Ketone. Chem. Commun. 1998, 621–622; (f) Armstrong, A.; Hayter, B. R. α-Functionalised Ketones as Promoters of Alkene Epoxidation by Oxone. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 11119–11126; (g) Armstrong, A.; Hayter, B. R.; Moss, W. O.; Reeves, J. R.; Wailes, J. S. Alkene Epoxidation Catalyzed by Bicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ones: Effects of Structural Modifications on Catalyst Efficiency and Epoxidation Enantioselectivity. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2000, 11, 2057–2061; (h) Matsumoto, K.; Tomioka, K. An Approach to a Chiral Cycloalkanone- Mediated Asymmetric Epoxidation of Stilbene with Oxone®. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1653–1657; (i) Denmark, S. E.; Matsuhashi, H. Chiral Fluoro Ketones for Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Alkenes with Oxone. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3479–3486; (j) Stearman, C. J.; Behar, V. Screening Chiral Fluorinated Binaphthyl Ketone Catalysts for Asymmetric Epoxidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1943–1946; (k) Chan, W.-K.; Yu, W.-Y.; Che, C.-M.; Wong, M.-K. A Cyclodextrin-Modified Ketoester for Stereoselective Epoxidation of Alkenes. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 6576–6582; (l) Romney, D. K.; Miller, S. J. A Peptide-Embedded Trifluoromethyl Ketone Catalyst for Enantioselective Epoxidation. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1138–1141.
- 15(a) Frohn, M.; Shi, Y. Chiral Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins. Synthesis 2000, 1979–2000; (b) Shi, Y. Organocatalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins by Chiral Ketones. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 488–496; (c) Wong, O. A.; Shi, Y. Organocatalytic Oxidation. Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins Catalyzed by Chiral Ketones and Iminium Salts. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3958–3987; (d) Shi, Y. Organocatalytic Oxidation. Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Alkenes and Synthetic Applications. In Modern Oxidation Methods, 2nd ed., Ed.: Bäckvall, J.-E., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010, pp. 85–115.
- 16 Frohn, M.; Dalkiewicz, M.; Tu, Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. Highly Regio- and Enantioselective Monoepoxidation of Conjugated Dienes. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2948–2953.
- 17(a) Cao, G.-A.; Wang, Z.-X.; Tu, Y.; Shi, Y. Chemo- and Enantioselective Epoxidation of Enynes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 4425–4428; (b) Wang, Z.-X.; Cao, G.-A.; Shi, Y. Chiral Ketone Catalyzed Highly Chemo- and Enantioselective Epoxidation of Conjugated Enynes. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7646–7650.
- 18(a) Zhu, Y.; Tu, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, Y. Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of Enol Silyl Ethers and Esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 7819–7822; (b) Zhu, Y.; Manske, K. J.; Shi, Y. Dual Mechanisms of Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangement of Enol Ester Epoxides: Enantioselective Formation of α-Acyloxy Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 4080–4081; (c) Feng, X.; Shu, L.; Shi, Y. Complete Conversion of Racemic Enol Ester Epoxides into Optically Active α-Acyloxy Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11002–11003; (d) Zhu, Y.; Shu, L.; Tu, Y.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Synthesis and Stereoselective Rearrangements of Enol Ester Epoxides. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1818–1826; (e) Adam, W.; Fell, R. T.; Saha-Möller, C. R.; Zhao, C.-G. Synthesis of Optically Active α-Hydroxy Ketones by Enantioselective Oxidation of Silyl Enol Ethers with a Fructose-derived Dioxirane. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1998, 9, 397–401.
- 19 Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. A pH Study on the Chiral Ketone Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Hydroxyalkenes. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3099–3104.
- 20 Warren, J. D.; Shi, Y. Chiral Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of 2,2-Disubstituted Vinylsilanes. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7675–7677.
- 21 Wong, O. A.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation of Fluoroolefins by Chiral Dioxirane. Fluorine Effect on Enantioselectivity. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 8377–8380.
- 22(a) Frohn, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.-R.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y. Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Cyclic Olefins via Chiral Dioxirane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 7718–7719; (b) Lorenz, J. C.; Frohn, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.-R.; Tang, Y.; Burke, C.; Shi, Y. Transition State Studies on the Dioxirane-Mediated Asymmetric Epoxidation via Kinetic Resolution and Desymmetrization. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 2904–2911.
- 23(a) Shu, L.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation Using Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) as Primary Oxidant. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 8721–8724; (b) Shu, L.; Shi, Y. An Efficient Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation Using Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) as Primary Oxidant. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5213–5218; (c) Shu, L.; Shi, Y. An Efficient Ketone-Catalyzed Epoxidation Using Hydrogen Peroxide as Oxidant. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 8807–8810.
- 24(a) Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. A New Type of Ketone Catalyst for Asymmetric Epoxidation. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8622–8623; (b) Wang, Z.-X.; Miller, S. M.; Anderson, O. P.; Shi, Y. A Class of C2 and Pseudo C2 Symmetric Ketone Catalysts for Asymmetric Epoxidation. Conformational Effect on Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 6443–6458.
- 25 Tian, H.; She, X.; Shi, Y. Electronic Probing of Ketone Catalysts for Asymmetric Epoxidation. Search for More Robust Catalysts. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 715–718.
- 26(a) Wu, X.-Y.; She, X.; Shi, Y. Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of α,β-Unsaturated Esters by Chiral Dioxirane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8792–8793; (b) Wang, B.; Wu, X.-Y.; Wong, O. A.; Nettles, B.; Zhao, M.-X.; Chen, D.; Shi, Y. A Diacetate Ketone-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 3986–3989; (c) Nieto, N.; Molas, P.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Vidal-Ferran, A. Practical Synthesis of Shi's Diester Fructose Derivative for Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidation of Alkenes. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 10143–10146; (d) Nieto, N.; Munslow, I. J.; Fernández-Pérez, H.; Vidal-Ferran, A. Exploring Substrate Scope of Shi-Type Epoxidations. Synlett 2008, 2856–2858.
- 27(a) Tian, H.; She, X.; Shu, L.; Yu, H.; Shi, Y. Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of cis-Olefins by Chiral Dioxirane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11551–11552; (b) Tian, H.; She, X.; Yu, H.; Shu, L.; Shi, Y. Designing New Chiral Ketone Catalysts. Asymmetric Epoxidation of cis-Olefins and Terminal Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 2435–2446; (c) Shu, L.; Wang, P.; Gan, Y.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation Catalyzed by N-Aryl-Substituted Oxazolidinone-containing Ketones: Further Evidence for Electronic Effects. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 293–296; (d) Shu, L.; Shen, Y.-M.; Burke, C.; Goeddel, D.; Shi, Y. An Improved Synthesis of a Ketone Catalyst for Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 4963–4965; (e) Zhao, M.-X.; Goeddel, D.; Li, K.; Shi, Y. A Practical Synthesis of N-Aryl-substituted Oxazolidinone- containing Ketone Catalysts for Asymmetric Epoxidation. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 8064–8068.
- 28(a) Shu, L.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation of cis-β-Methylstyrenes Catalyzed by N-aryl Substituted Oxazolidinone-containing Ketones. A Beneficial Substituent Effect. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 8115–8117; (b) Wong, O. A.; Shi, Y. Studies of Substituent Effect on Asymmetric Epoxidation of Chromenes by Chiral Dioxirane. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3973–3976.
- 29 Burke, C. P.; Shi, Y. Regio- and Enantioselective Epoxidation of Dienes by a Chiral Dioxirane: Synthesis of Optically Active Vinyl cis-Epoxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4475–4478.
- 30 Burke, C. P.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Epoxidation of Conjugated cis-Enynes by Chiral Dioxirane. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4093–4097.
- 31(a) Tian, H.; She, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Epoxidation of Terminal Olefins by Chiral Dioxirane. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1929–1931; (b) Goeddel, D.; Shu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wong, O. A.; Wang, B.; Shi, Y. Effective Asymmetric Epoxidation of Styrenes by Chiral Dioxirane. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 1715–1717; (c) Hickey, M.; Goeddel, D.; Crane, Z.; Shi, Y. Highly Enantioselective Epoxidation of Styrenes: Implication of an Electronic Effect on the Competition Between Spiro and Planar Transition States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 5794–5798.
- 32 Shen, Y.-M.; Wang, B.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Synthesis of 2-Aryl Cyclopentanones by Asymmetric Epoxidation and Epoxide Rearrangement. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1429–1432.
- 33 Wang, B.; Shen, Y.-M.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Synthesis of γ-Aryl-γ-butyrolactones by Sequential Asymmetric Epoxidation, Ring Expansion, and Baeyer−Villiger Oxidation. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 9519–9521.
- 34 Shen, Y.-M.; Wang, B.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective Synthesis of 2-Alkyl- 2-aryl Cyclopentanones by Asymmetric Epoxidation of Tetrasubstituted Cyclobutylidene Olefins and Epoxide Rearrangement. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 5455–5458.
- 35(a) Wang, B.; Wong, O. A.; Zhao, M.-X.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation of 1,1-Disubstituted Terminal Olefins by Chiral Dioxirane via a Planar-like Transition State. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9539–9543; (b) Wong, O. A.; Wang, B.; Zhao, M.-X.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric Epoxidation Catalyzed by α,α-Dimethylmorpholinone Ketone. Methyl Group Effect on Spiro and Planar Transition States. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6335–6338.
- 36 Hoard, D. W.; Moher, E. D.; Martinelli, M. J.; Norman, B. H. Synthesis of Cryptophycin 52 Using the Shi Epoxidation. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 1813–1815.
- 37 Kanada, R. M.; Itoh, D.; Nagai, M.; Niijima, J.; Asai, N.; Mizui, Y.; Abe, S.; Kotake, Y. Total Synthesis of the Potent Antitumor Macrolides Pladienolide B and D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4350–4355.
- 38 Ghosh, A. K.; Anderson, D. D. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Pladienolide B: A Potent Spliceosome Inhibitor. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4730–4733.
- 39 Kumar, V. P.; Chandrasekhar, S. Enantioselective Synthesis of Pladienolide B and Truncated Analogues as New Anticancer Agents. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3610–3613.
- 40 Smith, A. B., III; Walsh, S. P.; Frohn, M.; Duffey, M. O. Diversity-Oriented Synthesis of Polyketide Natural Products via Iterative Chemo- and Stereoselective Functionalization of Polyenoates: Development of a Unified Approach for the C(1−19) Segments of Lituarines A−C. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 139–142.
- 41 Bian, J.; Wingerden, M. V.; Ready, J. M. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (+)- and (−)-Nigellamine A2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7428–7429.
- 42 Lecornué, F.; Paugam, R.; Ollivier, J. Strategies for the Total Asymmetric Synthesis of Heliannuols K and L: Scope and Limitations. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2589–2598.
- 43 Taber, D. F.; He, Y. Opening of Aryl-substituted Epoxides to Form Quaternary Stereogenic Centers: Synthesis of (−)-Mesembrine. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 7711–7714.
- 44 Yu, M.; Snider, B. B. Synthesis of (+)- and (−)-Monanchorin. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1031–1032.
- 45 Harrison, T. J.; Ho, S.; Leighton, J. L. Toward More “Ideal” Polyketide Natural Product Synthesis: A Step-Economical Synthesis of Zincophorin Methyl Ester. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7308–7311.
- 46 An, C.; Jurica, J. A.; Walsh, S. P.; Hoye, A. T.; Smith, A. B. III. Total Synthesis of (+)-Irciniastatin A (a.k.a. Psymberin) and (−)-Irciniastatin B. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 4278–4296.
- 47 Adams, C. M.; Ghosh, I.; Kishi, Y. Validation of Lanthanide Chiral Shift Reagents for Determination of Absolute Configuration: Total Synthesis of Glisoprenin A. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4723–4726.
- 48 Morimoto, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Takaishi, M. Total Synthesis and Complete Assignment of the Stereostructure of a Cytotoxic Bromotriterpene Polyether (+)-Aurilol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5806–5807.
- 49 Kodama, T.; Aoki, S.; Kikuchi, S.; Matsuo, T.; Tachi, Y.; Nishikawa, K.; Morimoto, Y. A Convergent Total Synthesis of Antiplasmodial C2 Symmetric (+)-Ekeberin D4. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 5647–5649.
- 50 Mack, D. J.; Njardarson, J. T. Syntheses and Structural Confirmations of Members of a Heterocycle-Containing Family of Labdane Diterpenoids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1543–1547.
- 51 Clausen, D. J.; Wan, S.; Floreancig, P. E. Total Synthesis of the Protein Phosphatase 2A Inhibitor Lactodehydrothyrsiferol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5178–5181.
- 52For selected references on polycyclic ether formations via epoxide- opening cascade cyclization, see: (a) Cane, D. E.; Celmer, W. D.; Westley, J. W. Unified Stereochemical Model of Polyether Antibiotic Structure and Biogenesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 3594–3600; (b) Lee, M. S.; Qin, G.-W.; Nakanishi, K.; Zagorski, M. G. Biosynthetic Studies of Brevetoxins, Potent Neurotoxins Produced by the Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium Breve. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6234–6241; (c) Nicolaou, K. C. The Total Synthesis of Brevetoxin B: A Twelve-Year Odyssey in Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 588–607; (d) Morris, J. C.; Phillips, A. J. Marine Natural Products: Synthetic Aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 95–117; (e) Morten, C. J.; Byers, J. A.; Van Dyke, A. R.; Vilotijevic, I.; Jamison, T. F. The Development of endo-Selective Epoxide-opening Cascades in Water. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3175–3192; (f) Vilotijevic, I.; Jamison, T. F. Epoxide-Opening Cascades in the Synthesis of Polycyclic Polyether Natural Products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5250–5281.
- 53 Harding, W. W.; Lewis, P. A.; Jacobs, H.; McLean, S.; Reynolds, W. F.; Tay, L.-L.; Yang, J.-P. Glabrescol. A Unique Squalene-Derived Penta- THF Diol from Spathelia Glabrescens (rutaceae). Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 9137–9140.
- 54 Xiong, Z.; Corey, E. J. Simple Total Synthesis of the Pentacyclic Cs-Symmetric Structure Attributed to the Squalenoid Glabrescol and Three Cs-Symmetric Diastereomers Compel Structural Revision. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4831–4832.
- 55 Xiong, Z.; Corey, E. J. Simple Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Glabrescol, a Chiral C2-Symmetric Pentacyclic Oxasqualenoid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9328–9329.
- 56 Yang, P.; Li, P.-F.; Qu, J.; Tang, L.-F. Two Concise Enantioselective Total Syntheses of (-)-Glabrescol Implicate Alternative Biosynthetic Pathways Starting from Squalene. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3932–3935.
- 57 Morimoto, Y.; Takeuchi, E.; Kambara, H.; Kodama, T.; Tachi, Y.; Nishikawa, K. Biomimetic Epoxide-Opening Cascades of Oxasqualenoids Triggered by Hydrolysis of the Terminal Epoxide. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2966–2969.
- 58 Rodríguez-López, J.; Crisóstomo, F. P.; Ortega, N.; López-Rodríguez, M.; Martín, V. S.; Martín, T. Epoxide-Opening Cascades Triggered by a Nicholas Reaction: Total Synthesis of Teurilene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3659–3662.
- 59For selected references on the synthesis of fused polycyclic ethers via asymmetric epoxidation catalyzed by ketone 4 and subsequent cascade cyclization, see: (a) McDonald, F. E.; Wang, X.; Do, B.; Hardcastle, K. I. Synthesis of Oxepanes and trans-Fused Bisoxepanes via Biomimetic, endo-Regioselective Tandem Oxacyclizations of Polyepoxides. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 2917–2919; (b) McDonald, F. E.; Bravo, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Toganoh, M.; Rodríguez, J. R.; Do, B.; Neiwert, W. A.; Hardcastle, K. I. Endo-Oxacyclizations of Polyepoxides: Biomimetic Synthesis of Fused Polycyclic Ethers. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 2515–2523; (c) Bravo, F.; McDonald, F. E.; Neiwert, W. A.; Do, B.; Harddcastle, K. I. Biomimetic Synthesis of Fused Polypyrans: Oxacyclization Stereo- and Regioselectivity Is a Function of the Nucleophile. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2123–2126; (d) Bravo, F.; McDonald, F. E.; Neiwert, W. A.; Hardcastle, K. I. Alkene Substituents for Selective Activation of endo-Regioselective Polyepoxide Oxacyclizations. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4487–4489.
- 60 Valentine, J. C.; McDonald, F. E.; Neiwert, W. A.; Hardcastle, K. I. Biomimetic Synthesis of trans,syn,trans-Fused Polyoxepanes: Remarkable Substituent Effects on the endo-Regioselective Oxacyclization of Polyepoxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4586–4587.
- 61 Vilotijevic, I.; Jamison, T. F. Epoxide-Opening Cascades Promoted by Water. Science 2007, 317, 1189–1192.
- 62 Van Dyke, A. R.; Jamison, T. F. Functionalized Templates for the Convergent Assembly of Polyethers: Synthesis of the HIJK Rings of Gymnocin A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4430–4432.
- 63 Sittihan, S.; Jamison, T. F. Total Synthesis of the Marine Ladder Polyether Gymnocin B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11239−11244.




