Ankle clonus
Key Clinical Message
Clonus is a series of involuntary, rhythmic, muscular contractions, and relaxations. It may be caused by interruption of the upper motor neuron fibers such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, or by metabolic alterations such as severe hepatic failure or serotonin syndrome. We present a video case of impressive left ankle clonus in a patient with old right middle cerebral artery stroke.
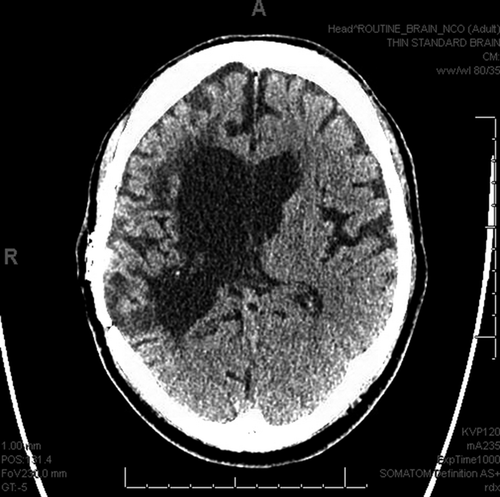
A 48-year-old, left-handed male with a history of right-middle cerebral artery territory infarct (Fig. 1) was admitted with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. On examination, he was found to have left hemiparesis, hyperreflexia, and expressive aphasia but intact sensorium. Dorsiflexion of the left ankle produced clonus, which was thought to be due to the old stroke (Video S1). Clonus is a series of involuntary, rhythmic, muscular contractions, and relaxations. It may be caused by interruption of upper motor neuron fibers such as stroke, multiple sclerosis or by metabolic alterations such as severe hepatic failure or serotonin syndrome 1. Treatment is aimed at correcting the cause.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.




