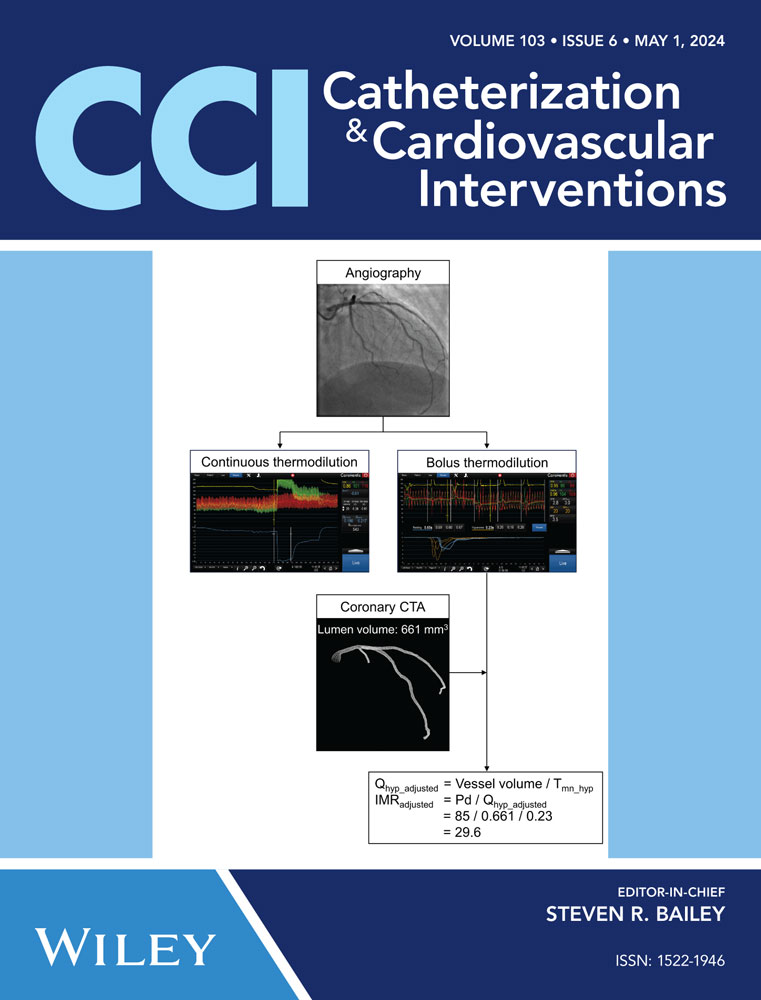
Impact of vessel volume on thermodilution measurements in patients with coronary microvascular dysfunction
Koshiro Sakai and Tatyana Storozhenko contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
Background
Two invasive methods are available to estimate microvascular resistance: bolus and continuous thermodilution. Comparative studies have revealed a lack of concordance between measurements of microvascular resistance obtained through these techniques.
Aims
This study aimed to examine the influence of vessel volume on bolus thermodilution measurements.
Methods
We prospectively included patients with angina with non-obstructive coronary arteries (ANOCA) undergoing bolus and continuous thermodilution assessments. All patients underwent coronary CT angiography to extract vessel volume. Coronary microvascular dysfunction was defined as coronary flow reserve (CFR) < 2.0. Measurements of absolute microvascular resistance (in Woods units) and index of microvascular resistance (IMR) were compared before and after volumetric adjustment.
Results
Overall, 94 patients with ANOCA were included in this study. The mean age was 64.7 ± 10.8 years, 48% were female, and 19% had diabetes. The prevalence of CMD was 16% based on bolus thermodilution, while continuous thermodilution yielded a prevalence of 27% (Cohen's Kappa 0.44, 95% CI 0.23–0.65). There was no correlation in microvascular resistance between techniques (r = 0.17, 95% CI −0.04 to 0.36, p = 0.104). The adjustment of IMR by vessel volume significantly increased the agreement with absolute microvascular resistance derived from continuous thermodilution (r = 0.48, 95% CI 0.31–0.63, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
In patients with ANOCA, invasive methods based on coronary thermodilution yielded conflicting results for the assessment of CMD. Adjusting IMR with vessel volume improved the agreement with continuous thermodilution for the assessment of microvascular resistance. These findings strongly suggest the importance of considering vessel volume when interpreting bolus thermodilution assessment.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
T. S. reports Fellowship Grant from the European Association of Percutaneous Coronary Interventions (EAPCI) Program. T. M. reports receiving consultancy fees from Zeon Medical Inc., research grants from Boston Scientific, and speaker fees from Abbott Vascular, CathWorks, and Boston Scientific. T. K. has received research grants from Boston Scientific, Volcano, Terumo, and Abbott Vascular. J. D. has received a research grant from Medtronic. B. D. B. reports receiving consultancy fees from Boston Scientific and Abbott Vascular, research grants from Coroventis Research, Pie Medical Imaging, CathWorks, Boston Scientific, Siemens, HeartFlow Inc, and Abbott Vascular, and owning equity in Siemens, GE, Philips, HeartFlow Inc, Edwards Life Sciences, Bayer, Sanofi, Celiad. C. C. reports receiving research grants from Biosensor, Coroventis Research, Medis Medical Imaging, Pie Medical Imaging, CathWorks, Boston Scientific, Siemens, HeartFlow Inc., Abbott Vascular, and consultancy fees from HeartFlow Inc., OpSens, Abbott Vascular, and Philips Volcano. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.