Nutraceutical Properties of the Hydroalcoholic Extract and Phenolic Compounds from Yucca aloifolia Edible Flowers
Abstract
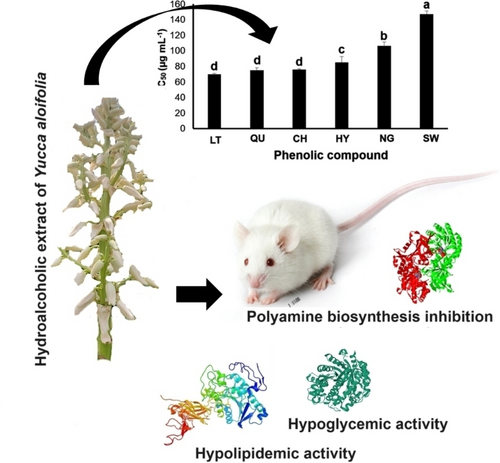
The flowers of Yucca aloifolia (“flor de izote”) are considered a millenary food in the Northeastern Highlands of Puebla, Mexico. The present investigation reports on the chemical and biological activities of the hydroalcoholic extract (YAHF) obtained from this edible source. HPLC-MS profiling revealed twenty bioactive phenolic compounds with chlorogenic acid (16.5 mg g−1 DW), quercetin (9.5 mg g−1 FW), and their glycosides (rutin and quercitrin), as well as caffeic acid (8.4 mg g−1 DW) and ferulic acid (7.9 mg g−1 DW) as major compounds dissolved in YAHF. Six metabolites had potent anti-lipase (IC50<100 μg mL−1) and anti-ornithine decarboxylase activity (IC50<100 μg mL−1), whereas thirteen exerted strong anti-alpha-glucosidase properties (IC50<100 μg mL−1). The evaluation of YAHF in mice subjected to standard oral glucose tolerance tests and prolonged administration of hypercaloric/atherogenic diet (30 days), unraveled their ability to improve glucose and lipid profiles. YAHF and six phenolic compounds significantly reduced DLD-1 cell viability (IC50, 117.9 μg mL−1) and avoided polyamine accumulation linked to anti-ornithine decarboxylase activity. YAHF and its twenty constituents exerted low toxicity in probiotics (>1000 μg mL−1) and 3T3 fibroblasts (>2.5 mg−mL−1), sustaining their safeness for human consumption.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.