Phytochemical Analysis and Anti-dyslipidemia and Antioxidant Activities of Pluchea dioscoridis: In Vitro, In Silico and In Vivo Studies
Wageha S. Sultan
Department of Chemistry, Research Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ayman M. Mahmoud
Department of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science & Engineering, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, M1 5GD UK
Molecular Physiology Division, Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead), Supervision (lead), Validation (lead), Visualization (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorShimaa A. Ahmed
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorReem S. Alruhaimi
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, 11671 Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting), Resources (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMohammed A. Alzoghaibi
Physiology Department, College of Medicine, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11461 Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting), Resources (equal), Writing - review & editing (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorAshraf A. El-Bassuony
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Resources (equal), Supervision (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorNabil A. Hasona
Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (equal), Supervision (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorEmadeldin M. Kamel
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Supervision (supporting), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorWageha S. Sultan
Department of Chemistry, Research Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ayman M. Mahmoud
Department of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science & Engineering, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, M1 5GD UK
Molecular Physiology Division, Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Methodology (lead), Supervision (lead), Validation (lead), Visualization (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorShimaa A. Ahmed
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorReem S. Alruhaimi
Department of Biology, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, 11671 Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting), Resources (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorMohammed A. Alzoghaibi
Physiology Department, College of Medicine, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11461 Saudi Arabia
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting), Resources (equal), Writing - review & editing (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorAshraf A. El-Bassuony
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Resources (equal), Supervision (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorNabil A. Hasona
Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (equal), Supervision (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorEmadeldin M. Kamel
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, 62514 Egypt
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Supervision (supporting), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
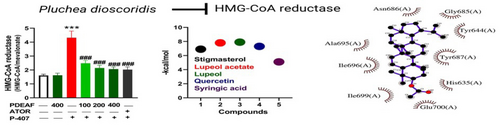
Pluchea dioscoridis (L.) DC. is a flowering wild plant used traditionally in the treatment of rhematic disorders. This study investigated the phytochemical and in vitro radical scavenging activity (RSA), and in vivo anti-hyperlipidemic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of P. dioscoridis. The antihyperlipidemic efficacy was determined in a rat model of dyslipidemia. The extract and fractions of P. dioscoridis showed RSA with the ethyl acetate (EA) fraction exhibiting the most potent activity. The phytochemical analysis of P. dioscoridis EA fraction (PDEAF) led to the isolation of five compounds (lupeol, quercetin, lupeol acetate, stigmasterol, and syringic acid). To evaluate its anti-hyperlipidemic effect, three doses of PDEAF were supplemented to rats for 14 days and poloxamer-407 was administered on day 15 to induce dyslipidemia. All doses of PDEAF decreased plasma triglycerides, cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL−C) and very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (vLDL−C), and increased plasma lipoprotein lipase (LPL). PDEAF upregulated hepatic LDL receptor and suppressed 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, decreased lipid peroxidation and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and enhanced reduced glutathione (GSH) and enzymatic antioxidants in dyslipidmeic rats. In silico findings revealed the binding affinity of the isolated compounds towards LPL, HMG-CoA reductase, and LDL receptor. In conclusion, P. dioscoridis is rich in phytoconstituents, exhibited RSA and its EA fraction effectively prevented acute dyslipidemia and its associated oxidative stress and inflammatory response.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202400842-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. J. Berberich, R. A. Hegele, Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 611–653.
- 2G. A. Roth, G. A. Mensah, C. O. Johnson, G. Addolorato, E. Ammirati, L. M. Baddour, N. C. Barengo, A. Z. Beaton, E. J. Benjamin, C. P. Benziger, A. Bonny, M. Brauer, M. Brodmann, T. J. Cahill, J. Carapetis, A. L. Catapano, S. S. Chugh, L. T. Cooper, J. Coresh, M. Criqui, N. DeCleene, K. A. Eagle, S. Emmons-Bell, V. L. Feigin, J. Fernández-Solà, G. Fowkes, E. Gakidou, S. M. Grundy, F. J. He, G. Howard, F. Hu, L. Inker, G. Karthikeyan, N. Kassebaum, W. Koroshetz, C. Lavie, D. Lloyd-Jones, H. S. Lu, A. Mirijello, A. M. Temesgen, A. Mokdad, A. E. Moran, P. Muntner, J. Narula, B. Neal, M. Ntsekhe, G. M. d. Oliveira, C. Otto, M. Owolabi, M. Pratt, S. Rajagopalan, M. Reitsma, A. L. P. Ribeiro, N. Rigotti, A. Rodgers, C. Sable, S. Shakil, K. Sliwa-Hahnle, B. Stark, J. Sundström, P. Timpel, I. M. Tleyjeh, M. Valgimigli, T. Vos, P. K. Whelton, M. Yacoub, L. Zuhlke, C. Murray, V. Fuster, G. A. Roth, G. A. Mensah, C. O. Johnson, G. Addolorato, E. Ammirati, L. M. Baddour, N. C. Barengo, A. Beaton, E. J. Benjamin, C. P. Benziger, A. Bonny, M. Brauer, M. Brodmann, T. J. Cahill, J. R. Carapetis, A. L. Catapano, S. Chugh, L. T. Cooper, J. Coresh, M. H. Criqui, N. K. DeCleene, K. A. Eagle, S. Emmons-Bell, V. L. Feigin, J. Fernández-Sola, F. G. R. Fowkes, E. Gakidou, S. M. Grundy, F. J. He, G. Howard, F. Hu, et al., J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021.
- 3J. D. Horton, J. L. Goldstein, M. S. Brown, J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109, 1125–1131.
- 4R. Sato, T. Takano, Cell Struct. Funct. 1995, 20, 421–427.
- 5A. Afshin, P. J. Sur, K. A. Fay, L. Cornaby, G. Ferrara, J. S. Salama, E. C. Mullany, K. H. Abate, C. Abbafati, Z. Abebe, The Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972.
- 6
- 6aR.-L. Yang, Y.-H. Shi, G. Hao, W. Li, G.-W. Le, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2008, 43, 154–158;
- 6bU. N. Singh, S. Kumar, S. Dhakal, International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research 2017, 4, 1204–1207.
- 7S. Furukawa, T. Fujita, M. Shimabukuro, M. Iwaki, Y. Yamada, Y. Nakajima, O. Nakayama, M. Makishima, M. Matsuda, I. Shimomura, J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 1752–1761.
- 8
- 8aS. H. Aladaileh, S. A. M. Saghir, K. Murugesu, A. Sadikun, A. Ahmad, G. Kaur, A. M. Mahmoud, V. Murugaiyah, Biomedicine 2019, 7, 72;
- 8bM. O. Germoush, H. A. Elgebaly, S. Hassan, E. M. Kamel, M. Bin-Jumah, A. M. Mahmoud, Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 9, 22;
- 8cR. H. Elsayed, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, A. A. El-Bassuony, M. Bin-Jumah, A. M. Lamsabhi, S. A. Ahmed, Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2020, 138, 111202;
- 8dR. S. Alruhaimi, G. Mostafa-Hedeab, M. S. Abduh, A. Bin-Ammar, E. H. M. Hassanein, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1204641;
- 8eA. E. Farage, W. Abdo, A. Osman, M. A. Abdel-Kareem, Z. H. Hakami, A. Alsulimani, A. Bin-Ammar, A. S. Alanazi, B. Alsuwayt, M. M. Alanazi, S. A. Antar, E. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, Life Sci. 2023, 322, 121688;
- 8fK. N. Hossain, M. S. Islam, S. H. Rahman, S. Sarker, M. Mondal, M. A. Rahman, S. K. Alhag, L. A. Al-Shuraym, O. A. Alghamdi, M. T. Islam, A. Al-Farga, M. El-Shazly, M. J. Alam, H. A. S. El-Nashar, ACS Omega 2023, 8, 47001–47011.
- 9
- 9aE. M. Kamel, A. Bin-Ammar, A. A. El-Bassuony, M. M. Alanazi, A. Altharawi, A. F. Ahmeda, A. S. Alanazi, A. M. Lamsabhi, A. M. Mahmoud, RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 12361–12374;
- 9bE. M. Kamel, A. M. Mahmoud, S. A. Ahmed, A. M. Lamsabhi, Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2094–2106;
- 9cA. M. Mahmoud, M. Y. Alexander, Y. Tutar, F. L. Wilkinson, A. Venditti, Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 2508909;
- 9dA. M. Abdul-Rahman, A. Elwekeel, R. S. Alruhaimi, E. M. Kamel, A. Bin-Ammar, A. M. Mahmoud, A. S. Moawad, M. A. Zaki, Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101762.
- 10A. Hamdy, H. Kassem, G. Awad, S. El-Kady, M. T. Benito, E. Doyagüez, M. Jimeno, N. Lall, A. A. Hussein, S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 109, 90–95.
- 11L. Boulos, Cairo, 2002.
- 12A. I. Elshamy, A. El Gendy, A. Farrag, M. I. Nassar, Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 65–72.
- 13A. M. Elgamal, R. F. Ahmed, A. M. Abd-ElGawad, A. E.-N. G. El Gendy, A. I. Elshamy, M. I. Nassar, Plants 2021, 10, 667.
- 14A. S. Awaad, R. El-Meligy, S. Qenawy, A. Atta, G. A. Soliman, J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 367–373.
- 15J. Cheel, C. Theoduloz, J. A. Rodríguez, P. D. Caligari, G. Schmeda-Hirschmann, Food Chem. 2007, 102, 36–44.
- 16
- 16aA. A. Zanwar, M. V. Hegde, S. R. Rojatkar, S. L. Bodhankar, Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 656–663;
- 16bM. S. Abduh, S. A. M. Saghir, A. M. Al Hroob, A. Bin-Ammar, A. H. Al-Tarawni, V. Murugaiyah, A. M. Mahmoud, Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1134812.
- 17K. J. Livak, T. D. Schmittgen, Methods (San Diego, Calif.) 2001, 25, 402–408.
- 18O. Trott, A. J. Olson, J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461.
- 19E. F. Pettersen, T. D. Goddard, C. C. Huang, G. S. Couch, D. M. Greenblatt, E. C. Meng, T. E. Ferrin, J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612.
- 20S. El-Toumy, S. Ahmed, E. Kamel, Int. J. Appl. Res. Nat. Prod. 2014, 7, 1–10..
- 21S. A. Ahemd, E. M. Kamel, Der Pharma Chemica 2013, 5, 109–114.
- 22
- 22aA. M. González-Paramás, B. Ayuda-Durán, S. Martínez, S. González-Manzano, C. Santos-Buelga, Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6976–6990;
- 22bA. M. Sayed, E. H. M. Hassanein, S. H. Salem, O. E. Hussein, A. M. Mahmoud, Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118173.
- 23
- 23aH. R. Chaudhary, D. R. Brocks, Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013, 65–73;
- 23bT. P. Johnston, W. K. Palmer, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 46, 1037–1042.
- 24Leon, K. M. Wasan, K. Sachs-Barrable, T. P. Johnston, Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1597–1607.
- 25G. V. Gnoni, G. Paglialonga, L. Siculella, Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 39, 761–768.
- 26M. Zhang, Z. Xie, W. Gao, L. Pu, J. Wei, C. Guo, Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 271–279.
- 27X. Jiang, J. Yu, X. Wang, J. Ge, N. Li, Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 827–839.
- 28V. Sudhahar, S. A. Kumar, P. Varalakshmi, Life Sci. 2006, 78, 1329–1335.
- 29A. C. Mirza, S. S. Panchal, A. A. Allam, S. I. Othman, M. Satia, S. N. Mandhane, Molecules 2022, 27.
- 30A. K. Batta, G. Xu, A. Honda, T. Miyazaki, G. Salen, Metabolism. 2006, 55, 292–299.
- 31R. H. Eckel, N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1060–1068.
- 32K. Lu, M. Han, H. L. Ting, Z. Liu, D. Zhang, J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 672–678.
- 33D. Kshatriya, X. Li, G. M. Giunta, B. Yuan, D. Zhao, J. E. Simon, Q. Wu, N. T. Bello, Nutr. Res. 2019, 68, 19–33.
- 34T. A. Korolenko, T. P. Johnston, F. V. Tuzikov, N. A. Tuzikova, A. B. Pupyshev, V. K. Spiridonov, N. V. Goncharova, I. V. Maiborodin, N. A. Zhukova, Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 16.
- 35M. Maligłówka, M. Kosowski, M. Hachuła, M. Cyrnek, Ł. Bułdak, M. Basiak, A. Bołdys, G. Machnik, R. J. Bułdak, B. Okopień, Metabolites 2022, 12, 256.
- 36S. Hummelgaard, J. P. Vilstrup, C. Gustafsen, S. Glerup, K. Weyer, Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 249, 108480.
- 37H. J. Kwon, T. A. Lagace, M. C. McNutt, J. D. Horton, J. Deisenhofer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1820–1825.
- 38L. Joseph, J. G. Robinson, Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 19–31.
- 39A. Pirillo, G. D. Norata, A. L. Catapano, Mediators Inflammation 2013, 2013, 152786.
- 40J. A. van Diepen, J. F. Berbée, L. M. Havekes, P. C. Rensen, Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 306–315.
- 41
- 41aM. F. Saja, H. T. Cook, M. M. Ruseva, M. Szajna, M. C. Pickering, K. J. Woollard, M. Botto, Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 192, 337–347;
- 41bS.-S. Park, T.-W. Kim, Y.-H. Sung, Y.-J. Park, M.-K. Kim, M.-S. Shin, Int Neurourol J 2021, 25, S81–89.