Guided Isolation of New Cytotoxic Cassane Diterpenoids from Caesalpinia sappan
Yue Jin
Department of Pharmacology, Mudanjiang Medical College, Mudanjiang, 157011 P. R. China
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
These authors made equal contributions to the article.
Search for more papers by this authorZi-Wei Tong
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
These authors made equal contributions to the article.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hui-Yuan Gao
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhao-Hua Wu
Department of Pharmacology, Mudanjiang Medical College, Mudanjiang, 157011 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYue Jin
Department of Pharmacology, Mudanjiang Medical College, Mudanjiang, 157011 P. R. China
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
These authors made equal contributions to the article.
Search for more papers by this authorZi-Wei Tong
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
These authors made equal contributions to the article.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hui-Yuan Gao
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, 110016 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhao-Hua Wu
Department of Pharmacology, Mudanjiang Medical College, Mudanjiang, 157011 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
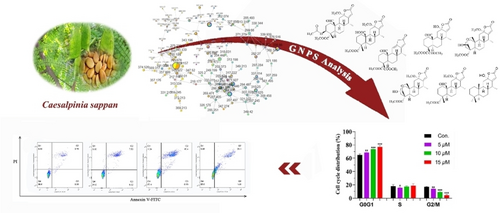
Guided by an MS/MS-based molecular networking, six undescribed cassane diterpenoids and three known ones were isolated and identified from the seeds of Caesalpinia sappan. Their structures were unequivocally elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analyses and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations. Cytotoxic evaluation showed that phanginin JA exhibited significant antiproliferative activities against human non-small cell lung cancer (A549) cells with IC50 values of 16.79±0.83 μM. Further flow cytometry analysis revealed that phanginin JA could exert apoptotic effect of A549 cells by arresting cell cycle in G0/G1 phase.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202300211-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.7 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1Editorial Committee of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, ‘Chinese Pharmacopoeia’, China Medical Science Press 2020, Part I, pp. 171.
- 2Editor Committee for Flora of China of Chinese Academy of Science, ‘Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae’, China Science Press 1988, 39, 105.
- 3O. Yodsaoue, S. Cheenpracha, C. Karalai, C. Ponglimanont, S. Chantrapromma, H. Fun, A. Kanjana-Opas, ‘Phanginin A–K, diterpenoids from the seeds of Caesalpinia sappan Linn’, Phytochem. 2008, 69, 1242–1249.
- 4J. Y. Zhang, W. M. Abdel-Mageed, M. M. Liu, P. Huang, W. N. He, L. Li, F. H. Song, H. Q. Dai, X. T. Liu, J. Y. Liang, L. X. Zhang, ‘Caesanines A–D, New Cassane Diterpenes with Unprecedented N Bridge from Caesalpinia sappan’, Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 4726–4729.
- 5G. Ma, H. Wu, D. Chen, N. Zhu, X. Xu, ‘Antimalarial and antiproliferative cassane diterpenes of caesalpinia sappan’, J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2364–2371.
- 6Z. T. Deng, J. Su, L. F. Ding, W. C. Tu, H. Yang, L. Y. Peng, Q. S. Zhao, L. D. Song, L. D. Wu, ‘Six new cassane diterpenoids from the seeds of Caesalpinia sappan’, Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 207–212.
- 7W. H. Jing, X. X. Zhang, H. X. Zhou, Y. Wang, M. Q. Yang, L. P. Long, H. Y. Gao, ‘Naturally occurring cassane diterpenoids (CAs) of Caesalpinia: A systematic review of its biosynthesis, chemistry and pharmacology’, Fitoterapia 2019, 134, 226–249.
- 8N. P. Nirmal, M. S. Rajput, R. G. S. V. Prasad, M. Ahmad, ‘Brazilin from Caesalpinia sappan heartwood and its pharmacological activities: A review’, Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 421–430.
- 9L. C. Fu, X. A. Huang, Z. Y. Lai, Y. J. Hu, H. J. Liu, X. L. Cai, ‘A new 3-benzylchroman derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan)’, Molecules. 2008, 13, 1923–1930.
- 10G. Xiang, M. M. Fan, Y. Z. Ma, M. Wang, J. Gao, J. W. Chen, X. Li, W. W. Xue, Y. X. Wang, H. Y. Gao, Y. Shen, Q. Xu, ‘Anti-inflammatory actions of Caesalpinin M2 in experimental colitis as a selective glucocoricoid receptor modulator’, Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 150–159.
- 11Z. W. Tong, L. Cheng, J. Z. Song, M. Wang, J. Z. Yuan, X. Z. Li, H. Y. Gao, ‘Therapeutic effects of Caesalpinia minax Hance on complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis and the anti-inflammatory activity of cassane diterpenes as main active components’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 226, 90–96.
- 12T. Liu, M. Wang, S. Z. Qi, X. Y. Shen, H. Y. Gao, ‘New cassane-type diterpenoids from kernels of Caesalpinia bonduc (Linn.) Roxb. and their inhibitory activities on phosphodiesterase (PDE) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) expression’, Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103573.
- 13Y. Jin, M. Wang, Y. F. Yan, X. X. Zhang, X. Z. Li, H. Y. Gao, ‘Bridged cassane derivatives from the seeds of Caesalpinia sappan L. and their cytotoxic activities’, Phytochemistry 2022, 197, 113111.
- 14X. X. Zhang, Y. Yin, Y. Zhou, T. L. Zhu, M. Wang, H. Y. Gao, ‘Distinctive Cassane Diterpenoids Corroborated Biogenetic Evolutionary Process from Caesalpinia mimosoides with Anti-renal Fibrosis Activity’, Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 617–627.
- 15X. M. Chen, W. Lu, Z. H. Zhang, J. Y. Zhang, T. Tuong, L. L. Liu, Y. H. Kim, C. H. Li, J. M. Gao, ‘Cassane diterpenoids from the aerial parts of caesalpinia pulcherrima and their antibacterial and anti-glioblastoma activity’, Phytochemistry 2022, 196, 113082.
- 16A. Raksat, S. Choodej, T. Aree, S. N. Ebrahimi, K. Pudhom, ‘Cassane-type diterpenes from roots of pterolobium macropterum and their anti-inflammatory activity’, Phytochemistry 2022, 196, 113074.
- 17W. C. Tu, L. F. Ding, L. Y. Peng, L. D. Song, X. D. Wu, Q. S. Zhao, ‘Cassane diterpenoids from the seeds of caesalpinia bonduc and their nitric oxide production and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities’, Phytochemistry 2022, 193, 112973.
- 18M. Wang, X. X. Zhang, M. Z. Qi, D. D. Guo, Y. N. Wang, H. Y. Gao, ‘New cassane- and norcassane-type diterpenoids from the seed kernels of caesalpinia sinensis and their anti-inflammatory activity in vitro’, Fitoterapia 2021, 153, 104978.
- 19M. Wang, S. Y. Yu, S. Z. Qi, B. H. Zhang, K. R. Song, T. Liu, H. Y. Gao, ‘Anti-inflammatory Cassane-Type Diterpenoids from the Seed Kernels of Caesalpinia sinensis’, J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 39, 1625–1634.
- 20R. J. Dong, J. Z. Yuan, S. L. Wu, J. Huang, X. T. Xu, Z. H. Wu, H. Y. Gao, ‘Anti-inflammation furanoditerpenoids from caesalpinia minax hance’, Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 325–331.
- 21M. Wang, Y. R. Yang, Y. Yin, K. R. Song, L. P. Long, X. Z. Li, B. Zhou, H. Y. Gao, ‘New Cassane Diterpenoids from the Seed Kernels of Caesalpinia cucullata, Exhibit Anti-inflammatory Effect in vitro by Inhibiting iNOS Enzymatic Activity’, Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1625–1634.
- 22P. Zhao, Z. Y. Li, S. Y. Qin, B. S. Xin, Y. Y. Liu, B. Lin, G. D. Yao, X. X. Huang, S. J. Song, ‘Three Unusual Sesquiterpenes with Distinctive Ring Skeletons from Daphne penicillata Uncovered by Molecular Networking Strategies’, J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 15298–15306.
- 23R. Guo, Q. Li, S. H. Mi, S. H. Jia, G. D. Yao, B. Lin, X. X. Huang, Y. Y. Liu, S. J. Song, ‘Target isolation of cytotoxic diterpenoid esters and orthoesters from Daphne tangutica maxim based on molecular networking’, Phytochemistry 2022, 203, 113358.
- 24L. F. Nothias, d. Petras, R. Schmid, K. Duhrkop, J. Rainer, A. Sarvepalli, I. Protsyuk, M. Ernst, H. Tsugawa, M. Fleischauer, F. Aicheler, A. A. Aksenov, O. Alka, P. M. Allard, A. Barsch, X. Cachet, A. M. Caraballo-Rodriguez, R. R. Da Silva, T. Dang, N. Garg, N. J. M. Gauglitz, A. Gurevich, G. Isaac, A. K. Jarmusch, Z. Kamenik, K. B. Kang, N. Kessler, I. Koester, A. Korf, A. Le Gouellec, M. Ludwig, H. C. Martin, L. I. McCall, J. McSayles, S. W. Meyer, H. Mohimani, M. Morsy, O. Moyne, S. Neumann, H. Neuweger, N. H. Nguyen, M. Nothias-Esposito, J. Paolini, V. V. Phelan, T. Pluskal, R. A. Quinn, S. Rogers, B. Shrestha, A. Tripathi, J. J. J. van der Hooft, F. Vargas, K. C. Weldon, M. Witting, H. J. Yang, Z. Zhang, F. Zubeil, O. Kohlbacher, S. Bocker, T. Alexandrov, N. Bandeira, M. X. Wang, P. C. Dorrestein, ‘Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment’, Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 905–908.
- 25J. Xu, X. R. Cao, F. Liu, J. Ma, X. Y. Liu, L. Tong, G. C. Su, Y. Ohizumi, D. H. Lee, L. Z. Wang, Y. Q. Guo, ‘Characterization of diterpenoids from Caesalpinia decapetala and their anti-TMV activities’, Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 144–150.
- 26C. Long, L. Marcourt, R. Raux, B. David, C. Gau, C. Menendez, M. Gao, M. F. Laroche, P. Schambel, C. Delaude, F. Ausseil, C. Lavaud, G. Massiot, ‘Meroterpenes from Dichrostachys cinerea Inhibit Protein Farnesyl Transferase Activity’, J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1804–1815.
- 27A. Raksat, S. Choodej, T. Aree, S. N. Ebrahimi, K. Pudhom, ‘Cassane-type diterpenes from roots of Pterolobium macropterum and their anti-inflammatory activity’, Phytochemistry 2022, 196, 113074.
- 28S. Sasidharan, K. S. Nishanth, H. J. Nair, ‘Ethanolic extract of Caesalpinia bonduc seeds triggers yeast metacaspase-dependent apoptotic pathway mediated by mitochondrial dysfunction through enhanced production of calcium and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Candida albicans’, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 970688.
- 29G. Evan, K. Vousden, ‘Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer’, Nature 2001, 411, 342–348.
- 30Gaussian 09, Revision B.01, M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J. L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J. A. Montgomery, Jr., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, T. Keith, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, N. Rega, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, J. E. Knox, J. B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R. E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A. J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, V. G. Zakrzewski, G. A. Voth, P. Salvador, J. J. Dannenberg, S. Dapprich, A. D. Daniels, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman, J. V. Ortiz, J. Cioslowski, and D. J. Fox, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT 2010.
- 31T. Bruhn, A. Schaumlöffel, Y. Hemberger, G. Bringmann, ‘SpecDis: Quantifying the Comparison of Calculated and Experimental Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectra’, Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249.
- 32S. Z. Qi, X. X. Zhang, Y. Jin, M. Wang, L. P. Long, W. H. Jing, K. R. Song, D. Wang, H. Y. Gao, ‘Phenylpropanoid-conjugated pentacyclic triterpenoids from the whole plants of Leptopus lolonum induced cell apoptosis via MAPK and Akt pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells’, Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104886.