Reduced N6-Methyladenosine Mediated by METTL3 Acetylation Promotes MTF1 Expression and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Growth
Abstract
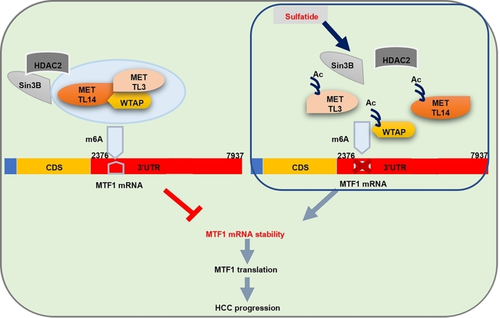
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A), one of the post-transcriptional modifications of RNA, is important in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanism of its regulation remains elusive. We here show that exposure of HCC cells to sulfatide significantly reduced the total mRNA m6A modification. Interestingly, METTL3 protein was robustly acetylated and the binding of METTL3 to MTF1 mRNA, METTL14 or WTAP was weakened in cells treated with sulfatide. Further investigation of the METTL3 complex revealed recruitment of the deacetylase scaffold SIN3B, but a diminished level of histone deacetylase HDAC2, which might enhance the acetylation of METTL3. The m6A abundance in MTF1 mRNA was markedly decreased in cells after sulfatide treatment. The expression of MTF1, a zinc-dependent transcription factor, was significantly strengthened with reduced m6A modification. Sulfatide prolonged the half-life of MTF1 mRNA, while the mutation (A to C) on 7 methylation sites in the 3’UTR of MTF1 mRNA enhanced MTF1 mRNA stability. 3-deaza-adenosine, an m6A methylation inhibitor, significantly reduced the m6A modification of MTF1 mRNA but extended its half-life time. Importantly, overexpression of MTF1 prompted HCC cell proliferation and was associated with poor prognosis. In conclusion, the METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex was regulated by acetylation induced by sulfatide to control MTF1 m6A methylation and its mRNA transcription, which was important for the tumor growth and migration of HCC.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests with regard to this article.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.