Chemical Composition of Volatiles of Eight Geranium L. Species from Vlasina Plateau (South Eastern Serbia)
Abstract
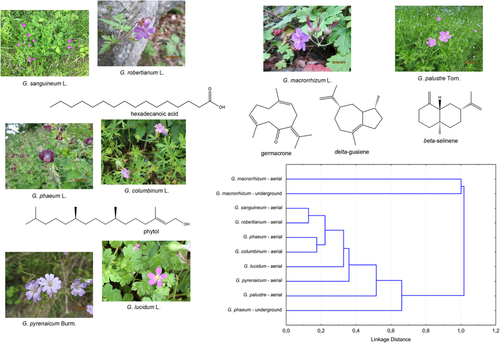
Geranium species are widely used in traditional medicine of Balkan. The aim of this work was to investigate and compare chemical composition of volatile fractions obtained by hydrodistillation from aerial parts of G. macrorrhizum, G. phaeum, G. sanguineum, G. robertianum, G. palustre, G. pyrenaicum, G. columbinum and G. lucidum as well as from underground parts of G. macrorrhizum and G. phaeum, originated from Vlasina plateau in South Eastern Serbia. The volatiles were analyzed using GC/MS and GC-FID. G. palustre volatiles have been studied for the first time with β-selinene (18.6 %) as a characteristic compound. The cluster analysis revealed separation of volatiles into two main groups. Volatile fractions of G. macrorrhizum were separated from all other samples due to high sesquiterpene content (92.3 % in aerial and 94.6 % in underground parts). The volatile fractions of other samples were mainly composed of sesquiterpenes (10.8–61.8 %), diterpenes (12.9–43.0 %) and fatty acids and their derivatives (6.6–21.6 %) with the exception of volatile fraction of G. phaeum underground parts which was dominated only by fatty acids and their derivatives (76.6 %). The results presented in this article contribute to the knowledge on the chemistry of this genus and advances the knowledge on flora of southeast Serbia.