The formation of a metallosupramolecular porous helicate through salicylaldehydethiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxic activity, DNA binding and DFT calculations
Elif Avcu Altiparmak
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorGuneş Ozen Eroglu
Department of Molecular Medicine, Aziz Sancar Institute of Experimental Medicine, Istanbul University, 34093 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorElif Ozcelik
Chemistry Department, Yildiz Technical University, Davutpasa Campus, 34220 Esenler, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorNamık Özdemir
Department of Mathematics and Science Education, Faculty of Education, Ondokuz Mayıs University, 55139 Samsun, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSerap Erdem Kuruca
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University, 34093 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorNergis Arsu
Chemistry Department, Yildiz Technical University, Davutpasa Campus, 34220 Esenler, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorBahri Ülküseven
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tulay Bal-Demirci
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
Tulay Bal-Demirci, Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, İstanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 İstanbul, Turkey.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorElif Avcu Altiparmak
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorGuneş Ozen Eroglu
Department of Molecular Medicine, Aziz Sancar Institute of Experimental Medicine, Istanbul University, 34093 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorElif Ozcelik
Chemistry Department, Yildiz Technical University, Davutpasa Campus, 34220 Esenler, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorNamık Özdemir
Department of Mathematics and Science Education, Faculty of Education, Ondokuz Mayıs University, 55139 Samsun, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorSerap Erdem Kuruca
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University, 34093 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorNergis Arsu
Chemistry Department, Yildiz Technical University, Davutpasa Campus, 34220 Esenler, Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorBahri Ülküseven
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tulay Bal-Demirci
Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
Tulay Bal-Demirci, Department of Chemistry, Engineering Faculty, İstanbul University-Cerrahpaşa, 34320 İstanbul, Turkey.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The reaction of salicylaldehyde-S-methylisothiosemicarbazone in the presence of ethylenediamine base and iron (III)chloride generated unforeseen homotopic dinuclear triple-stranded iron (III)helicate. The synthesized helicate was characterized by elemental analysis, IR, UV–Vis spectroscopy, magnetic moment measurement, and evaluated cytotoxic activities against K562, HL-60 and THP-1 leukemia cells. In addition, solid-state structure has been determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction technique. In the complex, three dinucleating O, N, N, O donor ligands provide three diazine (═N─N═) bridges between the metal ions and facial O3N3 coordination spheres around them. The ligands are folded about the N─N single bond and coordinated to the two metal ions in a helical fashion to form the triple helical structure. In the crystal lattice, chains of centrosymmetric
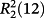 rings, which are connected to one another via π─π stacking interactions, are generated by C─H···O intermolecular interactions. The results are also confirmed by the density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The results obtained from the cytotoxicity test showed to be effective in low concentrations on the leukemia cells. An intercalative binding mode of helicate-DNA complex was confirmed with the high intrinsic binding constant (Kb = 8×106 M−1) and competitive displacement assay of Ethidium bromide with high Ksv value.
rings, which are connected to one another via π─π stacking interactions, are generated by C─H···O intermolecular interactions. The results are also confirmed by the density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The results obtained from the cytotoxicity test showed to be effective in low concentrations on the leukemia cells. An intercalative binding mode of helicate-DNA complex was confirmed with the high intrinsic binding constant (Kb = 8×106 M−1) and competitive displacement assay of Ethidium bromide with high Ksv value.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| aoc5023-sup-0001-Supplementary_figures_last.docxWord 2007 document , 802.4 KB |
FIGURE S1 Theoric IR spactra of Starting Material FIGURE S2 Theoric IR spectra of Helicate FIGURE S3 Experimental IR spectra of Starting Material FIGURE S4 Experimental IR spectra of Helicate FIGURE S5 Experimental UV–Vis. Spectra of Starting material FIGURE S6 Experimental UV–Vis. Spectra of Helicate FIGURE S7 The comparison of UV spectrum of starting material and Helicate FIGURE S8 Experimental 1H-NMR Spectra of Starting material |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1J. Bernstein, H. L. Yale, K. Losee, M. Holsing, J. Martins, W. A. Lott, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 906.
- 2R. Yanardag, T. Bal-Demirci, B. Ülküseven, S. Bolkent, S. Tunali, S. Bolkent, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 818.
- 3J. Patole, S. Padhye, M. S. Moodbidri, N. Shirsat, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 40, 1052.
- 4T. Bal-Demirci, G. Congur, A. Erdem, S. Erdem-Kuruca, N. Özdemir, K. Akgün-Dar, B. Varol, B. Ülküseven, New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 5643.
- 5A. Kumar Das, S. Goswami, Sens. Actuators B 2017, 245, 1062.
- 6T. Bal-Demirci, M. Akkurt, Ş. P. Yalçın, O. Büyükgüngör, Transition Met. Chem. 2010, 35, 95.
- 7D. X. West, A. E. Liberta, S. B. Padhye, R. C. Chikate, P. B. Sonawane, A. S. Kumbhar, R. G. Yerande, Coord. Chem. Rev. 1993, 123, 49.
- 8D. Palanimuthu, R. Poon, S. Sahni, R. Anjum, D. Hibbs, H.-Y. Lin, P. V. Bernhardt, D. S. Kalinowski, D. R. Richardson, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 612.
- 9M. Albrecht, Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 281.
- 10J. W. Steed, J. L. Atwood, Supramolecular Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons, Chichester 2000.
- 11(a)J.-M. Lehn, Supramolecular Chemistry: Concepts and Perspectives, VCH, Weinheim 1995.
10.1002/3527607439 Google Scholar(b)J.-M. Lehn, A. Rigault, J. Siegel, J. Harrowfield, B. Chevrier, D. Moras, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. a. 1987, 84, 2565.
- 12C. Piguet, M. Borkovec, J. Hamacek, K. Zeckert, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 705.
- 13T. R. Cook, V. Vajpayee, M. H. Lee, P. J. Stang, K. Chi, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2464.
- 14T. Miao, Q. Deng, H. Gao, X. Fu, S. Li, J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 859.
- 15A. Oleksy, A. G. Blanco, R. Boer, I. Usón, J. Aymamí, A. Rodger, M. J. Hannon, M. Coll, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1227.
- 16H. Furukawa, K. E. Cordova, M. O'Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
- 17Y. Haketa, H. Maeda, Chem. – Eur. J. 2011, 17, 1485.
- 18C. Pariya, C. R. Sparrow, C. K. Back, G. Sandi, F. R. Fronczek, A. W. Maverick, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6305.
- 19S. Ghosh, D. R. Turner, S. R. Batten, P. S. Mukherjee, Dalton Trans. 2007, 1869.
- 20Y. Okuno, K. Uoto, O. Yonemitsu, T. Tomohiro, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1987, 1018.
10.1039/C39870001018 Google Scholar
- 21R. D. Schnebeck, E. Freisinger, B. Lippert, Chem. Commun. 1999, 675.
- 22F. Gao, H. Chao, F. Zhou, Y.-X. Yuan, B. Peng, L.-N. Ji, J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1487.
- 23(a)J. Malina, M. J. Hannon, V. Brabec, Chem. – Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11189. (b)J. Malina, P. Scott, V. Brabec, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 14656. (c)S. E. Howson, A. Bolhuis, V. Brabec, G. J. Clarkson, J. Malina, A. Rodger, P. Scott, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 31. (d)R. A. Kaner, S. J. Allison, A. D. Faulkner, R. M. Phillips, D. I. Roper, S. L. Shepherd, D. H. Simpson, N. R. Waterfield, P. Scott, Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 951. (e)S. M. McNeill, D. Preston, J. E. M. Lewis, A. Robert, K. Knerr-Rupp, D. O. Graham, J. R. Wright, G. I. Giles, J. D. Crowley, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 11129.
- 24(a)A. D. Richards, A. Rodger, M. J. Hannon, A. Bolhuis, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 469. (b)S. V. Kumar, W. K. C. Lo, H. J. L. Brooks, J. D. Crowley, Inorg. Chim. Acta 2015, 425, 1.
- 25A. C. G. Hotze, N. J. Hodges, R. E. Hayden, C. Sanchez-Cano, C. Paines, N. Male, M. K. Tse, C. M. Bunce, J. K. Chipman, M. J. Hannon, Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 1258.
- 26A. C. G. Hotze, B. M. Kariuki, M. J. Hannon, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4839.
- 27V. Brabec, O. Hrabina, J. Kasparkova, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 351, 2.
- 28K. Nakamato, M. Tsuboi, G. D. Strahan, Drug-DNA Interactions: Structures and Spectra, John Wiley & Sons Inc., Hobojen, NJ 2008.
10.1002/9780470370612 Google Scholar
- 29S. U. Rehman, T. Sarwar, M. A. Husain, H. M. Ishqi, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 576, 49.
- 30M. Sirajuddin, S. Ali, A. Badshah, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2013, 124, 1.
- 31M. J. Hannon, V. Moreno, M. J. Prieto, E. Molderheim, E. Sletten, I. Meistermann, C. J. Isaac, K. J. Sanders, A. Rodger, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 879.
- 32A. D. Faulkner, R. A. Kaner, Q. M. A. Abdallah, G. Clarkson, D. J. Fox, P. Gurnani, S. E. Howson, R. M. Phillips, D. I. Roper, D. H. Simpson, P. Scott, Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 797.
- 33V. Brabec, S. E. Howson, R. A. Kaner, R. M. Lord, J. Malina, R. M. Phillips, Q. M. A. Abdallah, P. C. McGowan, A. Rodger, P. Scott, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4407.
- 34L. Cardo, V. Sadovnikova, S. Phongtongpasuk, N. J. Hodges, M. J. Hannon, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6575.
- 35J. Li, T. Murakami, M. Higuchi, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 2013, 23, 119.
- 36N. Ataci, E. Ozcelik, N. Arsu, Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 204, 281.
- 37N. Ataci, N. Arsu, Spectrochim. Acta A 2016, 169, 128.
- 38T. Bal-Demirci, Polyhedron 2008, 27, 440.
- 39 Stoe & Cie, X-AREA Version 1.18 and X-RED32 Version 1.04, Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany 2002.
- 40G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr. A 2015, 71, 3.
- 41G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3.
- 42L. J. Farrugia, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849.
- 43T. Mosmann, J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55.
- 44R. Dennington, T. A. Keith, J. M. Millam, GaussView, Version 5.0, Semichem, Inc., Shawnee Mission, KS 2009.
- 45M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J. L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J. A. Montgomery Jr., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, N. Rega, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, J. E. Knox, J. B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R. E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A. J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, V. G. Zakrzewski, G. A. Voth, P. Salvador, J. J. Dannenberg, S. Dapprich, A. D. Daniels, Ö. Farkas, J. B. Foresman, J. V. Ortiz, J. Cioslowski, D. J. Fox, Gaussian 09W, Revision C.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT 2009.
- 46A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648.
- 47C. Lee, W. Yang, R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785.
- 48R. Krishnan, J. S. Binkley, R. Seeger, J. A. Pople, J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650.
- 49M. J. Frisch, J. A. Pople, J. S. Binkley, J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265.
- 50P. J. Hay, W. R. Wadt, J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270.
- 51P. J. Hay, W. R. Wadt, J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 284.
- 52P. J. Hay, W. R. Wadt, J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299.
- 53M. P. Andersson, P. Uvdal, J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 2937.
- 54R. Shen, W. Wang, G. Yang, J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 959.
- 55S. Kashanian, M. M. Khodaei, P. Pakravan, DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 639.
- 56E. Tuite, U. Sehilstedt, P. Hagmar, B. Norden, M. Takahashi, Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 482.
- 57S. Kashanian, S. Heidary, H. Zeidali, K. Omidfar, N. Shahabadi, Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 10045.
- 58N. Shahabadi, M. Maghsudi, Dyes Pigm. 2013, 96, 377.
- 59M. Hong, F. Chen-jie, D. Chun-ying, L. Yu-ting, M. Qing-jin, Dalton Trans. 2003, 7, 1229.
- 60J. Wang, B. Liu, B. Yang, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. E: Struct. Rep. Online 2008, 64, m1210.
- 61F. -F. Jian, C. -Y. Zhu, H. -L. Xiao, L. -Z. Xu, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2005, 631, 769.
- 62J. Saroja, V. Manivannan, P. Chakraborty, S. Pa1, Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 3099.
- 63S. G. Sreerama, S. Pal, Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6299.
- 64C. Yamazaki, Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 610.
- 65L. Yan, S. Ding, Y. Ji, Z. Liu, C. Liu, J. Coord. Chem. 2011, 64, 3531.
- 66J. -W. Ran, S. -W. Liu, P. Wu, J. Pei, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 373.
- 67J. Bernstein, R. E. Davis, L. Shimoni, N. L. Chang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1555.
- 68Ş. Güveli, T. Bal-Demirci, B. Ülküseven, N. Özdemir, Polyhedron 2016, 110, 188.
- 69M. Şahin, A. Koca, N. Özdemir, M. Dinçer, O. Büyükgüngör, T. Bal-Demirci, Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 10228.
- 70C. R. Groom, I. J. Bruno, M. P. Lightfoot, S. C. Ward, Acta Crystallogr. B 2016, 72, 171.
- 71I. J. Bruno, J. C. Cole, P. R. Edgington, M. Kessler, C. F. Macrae, P. McCabe, J. Pearson, R. Taylor, Acta Crystallogr. B 2002, 58, 389.
- 72S. Pasayat, S. P. Dash, S. Majumder, R. Dinda, E. Sinn, H. Stoeckli-Evans, S. Mukhopadhyay, S. K. Bhutia, P. Mitra, Polyhedron 2014, 80, 198.
- 73R. K. Mishra, K. K. Upadhyay, S. Shukla, R. Mishra, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4238.
- 74M. J. Waring, J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 269.
- 75H. Chen, S. Li, Y. Yao, L. Zhou, J. Zhao, Y. Gu, K. Wang, X. Li, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4785.
- 76A. K. Williams, S. C. Dasilva, A. Bhatta, B. Rawal, M. Liu, Anal. Biochem. 2012, 422, 66.
- 77M. Cory, D. D. McKee, J. Kagan, D. W. Henry, J. A. Miller, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 2528.




