Concomitant Near-Infrared Photothermy and Photoluminescence of Rod-Shaped Au52(PET)32 and Au66(PET)38 Synthesized Concurrently
Dr. Wanmiao Gu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yue Zhou
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenying Wang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qing You
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wentao Fan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yan Zhao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorGuoqing Bian
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Runguo Wang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Liang Fang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nan Yan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nan Xia
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lingwen Liao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhikun Wu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wanmiao Gu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yue Zhou
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenying Wang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qing You
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wentao Fan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yan Zhao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorGuoqing Bian
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Runguo Wang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Liang Fang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nan Yan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nan Xia
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lingwen Liao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhikun Wu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230031 Hefei, P. R.China
Key Laboratory of Precision and Intelligent Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026 Hefei, P. R.China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, 230601 Hefei, P. R.China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
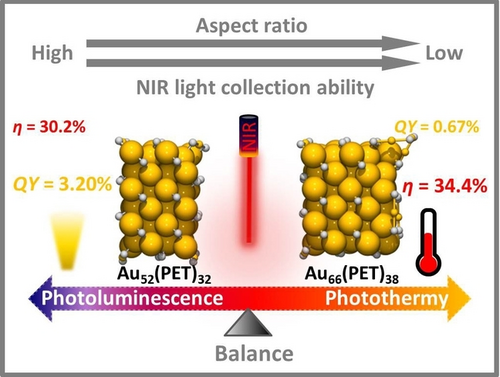
Two rod-shaped Au52(PET)32-G and Au66(PET)38 are synthesized and precisely characterized. Basing on the unreported transverse growth mode from Au52(PET)32-G to Au66(PET)38, six novel nanoclusters are predicted. Although the two nanoclusters have different aspect ratios and near-infrared (NIR) light collection abilities, they have concomitant photothermy (PT) and photoluminescence (PL) under NIR irradiation, and the PT and PL are in balance.
Abstract
Gold nanoclusters exhibiting concomitant photothermy (PT) and photoluminescence (PL) under near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation are rarely reported, and some fundamental issues remain unresolved for such materials. Herein, we concurrently synthesized two novel rod-shaped Au nanoclusters, Au52(PET)32 and Au66(PET)38 (PET = 2-phenylethanethiolate), and precisely revealed that their kernels were 4 × 4 × 6 and 5 × 4 × 6 face-centered cubic (fcc) structures, respectively, based on the numbers of Au layers in the [100], [010], and [001] directions. Following the structural growth mode from Au52(PET)32 to Au66(PET)38, we predicted six more novel nanoclusters. The concurrent synthesis provides rational comparison of the two nanoclusters on the stability, absorption, emission and photothermy, and reveals the aspect ratio-related properties. An interesting finding is that the two nanoclusters exhibit concomitant PT and PL under 785 nm light irradiation, and the PT and PL are in balance, which was explained by the qualitative evaluation of the radiative and non-radiative rates. The ligand effects on PT and PL were also investigated.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202407518-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Weissleder, V. Ntziachristos, Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 123–128;
- 1bY. Yang, Q. Jiang, F. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 554–628.
- 2
- 2aX. Cui, Q. Ruan, X. Zhuo, X. Xia, J. Hu, R. Fu, Y. Li, J. Wang, H. Xu, Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 6891–6952;
- 2bX. Huang, W. Zhang, G. Guan, G. Song, R. Zou, J. Hu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2529–2538.
- 3Y. Cai, P. Liang, Q. Tang, X. Yang, W. Si, W. Huang, Q. Zhang, X. Dong, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1054–1063.
- 4
- 4aH. Chen, L. Shao, Q. Li, J. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2679–2724;
- 4bC. J. Murphy, H.-H. Chang, P. Falagan-Lotsch, M. T. Gole, D. M. Hofmann, K. N. L. Hoang, S. M. McClain, S. M. Meyer, J. G. Turner, M. Unnikrishnan, M. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2124–2135.
- 5
- 5aX. Huang, I. H. El-Sayed, W. Qian, M. A. El-Sayed, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120;
- 5bN. S. Abadeer, M. R. Brennan, W. L. Wilson, C. J. Murphy, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8392–8406.
- 6B. Du, M. Yu, J. Zheng, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 358–374.
- 7
- 7aA. Tlahuice, I. L. Garzón, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 3737–3740;
- 7bI. Chakraborty, T. Pradeep, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8208–8271;
- 7cX.-M. Luo, C.-H. Gong, F. Pan, Y. Si, J.-W. Yuan, M. Asad, X.-Y. Dong, S.-Q. Zang, T. C. W. Mak, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1177;
- 7dS. Zhuang, D. Chen, W. Fan, J. Yuan, L. Liao, Y. Zhao, J. Li, H. Deng, J. Yang, J. Yang, Z. Wu, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7144–7150;
- 7eG. Yang, Z. Wang, F. Du, F. Jiang, X. Yuan, J. Y. Ying, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11879–11898.
- 8
- 8aI. D. Anderson, Y. Wang, C. M. Aikens, C. J. Ackerson, Nanoscale 2022, 14, 9134–9141;
- 8bA. Ambreen, Y. Zhou, W. Gu, Q. You, L. Fang, G. Bian, N. Yan, N. Xia, Z. Wu, Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 523–528.
- 9
- 9aP. D. Jadzinsky, G. Calero, C. J. Ackerson, D. A. Bushnell, R. D. Kornberg, Science 2007, 318, 430–433;
- 9bN. A. Sakthivel, M. Shabaninezhad, L. Sementa, B. Yoon, M. Stener, R. L. Whetten, G. Ramakrishna, A. Fortunelli, U. Landman, A. Dass, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15799–15814;
- 9cJ.-J. Li, Z. Liu, Z.-J. Guan, X.-S. Han, W.-Q. Shi, Q.-M. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 690–694;
- 9dX. Wang, B. Yin, L. Jiang, C. Yang, Y. Liu, G. Zou, S. Chen, M. Zhu, Science 2023, 381, 784–790.
- 10
- 10aH. Liu, G. Hong, Z. Luo, J. Chen, J. Chang, M. Gong, H. He, J. Yang, X. Yuan, L. Li, X. Mu, J. Wang, W. Mi, J. Luo, J. Xie, X.-D. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901015;
- 10bS. M. van de Looij, E. R. Hebels, M. Viola, M. Hembury, S. Oliveira, T. Vermonden, Bioconjugate Chem. 2022, 33, 4–23.
- 11
- 11aY. Li, Y. Song, X. Zhang, T. Liu, T. Xu, H. Wang, D.-e. Jiang, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12381–12389;
- 11bZ. Yang, X. Yang, Y. Guo, H. Kawasaki, ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 4504–4517.
- 12G. Yang, X. Pan, W. Feng, Q. Yao, F. Jiang, F. Du, X. Zhou, J. Xie, X. Yuan, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15605–15614.
- 13
- 13aY. Shichibu, Y. Negishi, T. Watanabe, N. K. Chaki, H. Kawaguchi, T. Tsukuda, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7845–7847;
- 13bH. Qian, W. T. Eckenhoff, Y. Zhu, T. Pintauer, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8280–8281;
- 13cR. Jin, C. Liu, S. Zhao, A. Das, H. Xing, C. Gayathri, Y. Xing, N. L. Rosi, R. R. Gil, R. Jin, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8530–8536;
- 13dQ. Li, C. J. Zeman IV, Z. Ma, G. C. Schatz, X. W. Gu, Small 2021, 17, 2007992;
- 13eS. Takano, S. Yamazoe, K. Koyasu, T. Tsukuda, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7027–7030;
- 13fZ. Ma, P. Wang, G. Zhou, J. Tang, H. Li, Y. Pei, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13739–13748;
- 13gL. Luo, Z. Liu, J. Kong, C. G. Gianopoulos, I. Coburn, K. Kirschbaum, M. Zhou, R. Jin, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2024, 121, e2318537121.
- 14
- 14aJ. B. Tracy, M. C. Crowe, J. F. Parker, O. Hampe, C. A. Fields-Zinna, A. Dass, R. W. Murray, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16209–16215;
- 14bK.-G. Liu, X.-M. Gao, T. Liu, M.-L. Hu, D.-e. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16905–16909;
- 14cT. Dainese, S. Antonello, S. Bonacchi, D. Morales-Martinez, A. Venzo, D. M. Black, M. Mozammel Hoque, R. L. Whetten, F. Maran, Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15394–15402;
- 14dJ. Zhao, A. Ziarati, A. Rosspeintner, Y. Wang, T. Bürgi, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7665–7674.
- 15Z. Liu, X. Meng, W. Gu, J. Zha, N. Yan, Q. You, N. Xia, H. Wang, Z. Wu, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2023, 39, 2212064.
- 16W. Gu, Y. Zhao, S. Zhuang, J. Zha, J. Dong, Q. You, Z. Gan, N. Xia, J. Li, H. Deng, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11184–11189.
- 17
- 17aS. Nematulloev, R.-W. Huang, J. Yin, A. Shkurenko, C. Dong, A. Ghosh, B. Alamer, R. Naphade, M. N. Hedhili, P. Maity, M. Eddaoudi, O. F. Mohammed, O. M. Bakr, Small 2021, 17, 2006839;
- 17bR. W. Y. Man, H. Yi, S. Malola, S. Takano, T. Tsukuda, H. Häkkinen, M. Nambo, C. M. Crudden, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2056–2061;
- 17cR. P. Brocha Silalahi, Y. Jo, J.-H. Liao, T.-H. Chiu, E. Park, W. Choi, H. Liang, S. Kahlal, J.-Y. Saillard, D. Lee, C. W. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301272;
- 17dL. Feng, Z.-M. Zhu, Y. Yang, Z. He, J. Zou, M.-B. Li, Y. Zhao, Z. Wu, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2024, 40, 2305029.
- 18S. Zhuang, L. Liao, M.-B. Li, C. Yao, Y. Zhao, H. Dong, J. Li, H. Deng, L. Li, Z. Wu, Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14809–14813.
- 19
- 19aS. Tian, Y.-Z. Li, M.-B. Li, J. Yuan, J. Yang, Z. Wu, R. Jin, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8667;
- 19bT. Higaki, C. Liu, C. Zeng, R. Jin, Y. Chen, N. L. Rosi, R. Jin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6694–6697;
- 19cS. Zhuang, L. Liao, J. Yuan, N. Xia, Y. Zhao, C. Wang, Z. Gan, N. Yan, L. He, J. Li, H. Deng, Z. Guan, J. Yang, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4510–4514;
- 19dN. Xia, J. Yuan, L. Liao, W. Zhang, J. Li, H. Deng, J. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12140–12145;
- 19eX. Liu, W. W. Xu, X. Huang, E. Wang, X. Cai, Y. Zhao, J. Li, M. Xiao, C. Zhang, Y. Gao, W. Ding, Y. Zhu, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3349;
- 19fZ.-J. Guan, F. Hu, J.-J. Li, Z.-R. Wen, Y.-M. Lin, Q.-M. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2995–3001;
- 19gY. Li, M. Zhou, Y. Song, T. Higaki, H. Wang, R. Jin, Nature 2021, 594, 380–384.
- 20
- 20aY. Wang, Z. Liu, A. Mazumder, C. G. Gianopoulos, K. Kirschbaum, L. A. Peteanu, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 26328–26338;
- 20bC. Zeng, Y. Chen, C. Liu, K. Nobusada, N. L. Rosi, R. Jin, Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500425;
- 20cL. Liao, C. Wang, S. Zhuang, N. Yan, Y. Zhao, Y. Yang, J. Li, H. Deng, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 731–734.
- 21W. W. Xu, B. Zhu, X. C. Zeng, Y. Gao, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13574.
- 22M. Walter, J. Akola, O. Lopez-Acevedo, P. D. Jadzinsky, G. Calero, C. J. Ackerson, R. L. Whetten, H. Grönbeck, H. Häkkinen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9157–9162.
- 23L. Yang, P. Wang, Z. Yang, Y. Pei, Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5554–5566.
- 24C. Zeng, Y. Chen, K. Iida, K. Nobusada, K. Kirschbaum, K. J. Lambright, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3950–3953.
- 25C. M. Aikens, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3065–3073.
- 26S. Link, M. B. Mohamed, M. A. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 3073–3077.
- 27
- 27aF. Jin, H. Dong, Y. Zhao, s. Zhuang, L. Liao, N. Yan, W. Gu, J. Zha, J. Yuan, J. Li, H. Deng, Z. Gan, J. Yang, Z. Wu, Acta Chim. Sin. 2020, 78, 407–411;
- 27bQ. You, X.-L. Jiang, W. Fan, Y.-S. Cui, Y. Zhao, S. Zhuang, W. Gu, L. Liao, C.-Q. Xu, J. Li, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202313491.
- 28K. Sheng, Z. Wang, L. Li, Z.-Y. Gao, C.-H. Tung, D. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10595–10603.
- 29
- 29aL. Zhao, Y. Liu, R. Xing, X. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3793–3801;
- 29bB. Chang, J. Chen, J. Bao, T. Sun, Z. Cheng, Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 13966–14037.
- 30S. Gao, G. Wei, S. Zhang, B. Zheng, J. Xu, G. Chen, M. Li, S. Song, W. Fu, Z. Xiao, W. Lu, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2206.
- 31
- 31aT. D. Green, C. Yi, C. Zeng, R. Jin, S. McGill, K. L. Knappenberger, Jr., J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 10611–10621;
- 31bQ. Li, C. J. Zeman, G. C. Schatz, X. W. Gu, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16095–16105.
- 32Deposition Numbers 2355084 (for Au52(PET)32-G) and 2355094 (for Au66(PET)38) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.