Perfluoroalkyl-Decorated Noble-Metal-Free MOFs for the Highly Efficient One-Pot Four-Component Coupling between Aldehydes, Amines, Alkynes, and Flue Gas CO2
Fan Yang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJiajia Wang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYou Wang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBenling Yu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYiwen Cao
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Jiawei Li
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Linlin Wu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jianhan Huang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. You-Nian Liu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorFan Yang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJiajia Wang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYou Wang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorBenling Yu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYiwen Cao
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Jiawei Li
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Linlin Wu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jianhan Huang
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. You-Nian Liu
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Material Interface Science, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 Hunan, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
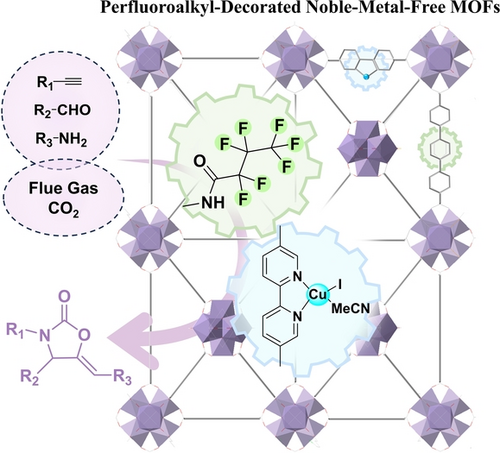
A series of perfluoroalkyl-decorated noble-metal-free metal–organic frameworks [PCN-(BPY-CuI)-(TPDC-Fx), x=3, 5, 7, 11] are rationally fabricated through the stepwise solvent-assisted linker installation, post-synthetic fluorination and metalation, which showed excellent performance in catalyzing the one-pot four-component tandem reaction between alkyne, aldehyde, amine and flue gas CO2 for the facile preparation of 2-oxazolidinones.
Abstract
The non-noble-metal catalysed-multicomponent reactions between flue gas CO2 and cheap industrial raw stocks into high value-added fine chemicals is a promising manner for the ideal CO2 utilization route. To achieve this, the key fundamental challenge is the rational development of highly efficient and facile reaction pathway while establishing compatible catalytic system. Herein, through the stepwise solvent-assisted linker installation, post-synthetic fluorination and metalation, we report the construction of a series of perfluoroalkyl-decorated noble-metal-free metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) PCN-(BPY-CuI)-(TPDC-Fx) [BPY=2,2′-bipyridine-5,5′-dicarboxylate, TPDC-NH2=2′-amino-[1,1′:4′,1′′-terphenyl]-4,4′′-dicarboxylic acid] that can catalyze the one-pot four-component reaction between alkyne, aldehyde, amine and flue gas CO2 for the preparation of 2-oxazolidinones. Such assembly endows the MOFs with superhydrophobic microenvironment, superior water resistance and highly stable catalytic site, leading to 21 times higher turnover numbers than that of homogeneous counterparts. Mechanism investigation implied that the substrates can be efficiently enriched by the MOF wall and then the adsorbed amine species act as an extrinsic binding site towards dilute CO2 through their strong preferential formation to carbamate acid. Moreover, density functional theory calculations suggest the tetrahedral geometry of Cu in MOF offers special resistance towards amine poisoning, thus maintaining its high efficiency during the catalytic process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202318115-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.2 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aB. B. Touré, D. G. Hall, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4439–4486;
- 1bA. Dömling, I. Ugi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3168–3210;
10.1002/1521-3773(20000915)39:18<3168::AID-ANIE3168>3.0.CO;2-U CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 1cE. Ruijter, R. Scheffelaar, R. V. A. Orru, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6234–6246;
- 1dB. H. Rotstein, S. Zaretsky, V. Rai, A. K. Yudin, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8323–8359.
- 2
- 2aD. J. Diekema, R. N. Jones, Lancet 2001, 358, 1975–1982;
- 2bM. R. Barbachyn, C. W. Ford, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2010–2023;
- 2cQ. Zhao, L. Xin, Y. Liu, C. Liang, J. Li, Y. Jian, H. Li, Z. Shi, H. Liu, W. Cao, J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10557–10580.
- 3S. Farshbaf, L. Z. Fekrib, M. Nikpassandc, R. Mohammadib, E. Vessally, J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 194–204.
- 4
- 4aR. Das, C. M. Nagaraja, Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5195–5204;
- 4bX.-D. Li, Y. Cao, R. Ma, L.-N. He, J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 338–345;
- 4cG. Zhang, H. Yang, H. Fei, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2519–2525;
- 4dM. Du, Y. Gong, C. Bu, J. Hu, Y. Zhang, C. Chen, S. Chaemchuen, Y. Yuan, F. Verpoort, J. Catal. 2021, 393, 70–82;
- 4eJ. Zhou, S. Yang, W. Wan, L. Chen, J. Chen, J. Catal. 2023, 418, 178–189.
- 5
- 5aY.-Z. Pan, Q. Xia, J.-X. Zhu, Y.-C. Wang, Y. Liang, H. Wang, H.-T. Tang, Y.-M. Pan, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 8239–8243;
- 5bJ.-H. Ye, L. Song, W.-J. Zhou, T. Ju, Z.-B. Yin, S.-S. Yan, Z. Zhang, J. Li, D.-G. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10022–10026;
- 5cM.-Y. Wang, Y. Cao, X. Liu, N. Wang, L.-N. He, S.-H. Li, Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1240–1244;
- 5dK. Yamashita, S. Hase, Y. Kayaki, T. Ikariya, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2334–2337.
- 6
- 6aN. Qiao, X.-Y. Xin, W.-M. Wang, Z.-L. Wu, J.-Z. Cui, Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 10725–10736;
- 6bX.-R. Tian, X.-L. Jiang, S.-L. Hou, Z.-H. Jiao, J. Han, B. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200123;
- 6cX. Wang, W.-Y. Gao, Z. Niu, L. Wojtas, J. A. Perman, Y.-S. Chen, Z. Li, B. Aguila, S. Ma, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1170–1173;
- 6dM. Cavalleri, C. Damiano, G. Manca, E. Gallo, Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202202729.
- 7
- 7aZ.-G. Zhou, P. He, J. Li, J. Zhang, G.-H. Xu, S.-Y. Zhang, X.-X. Deng, Z.-Y. Du, G.-T. Luo, H.-Y. Zhen, Y.-W. Chen, C.-T. He, Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 2045–2053;
- 7bA.-L. Gu, Y.-X. Zhang, Z.-L. Wu, H.-Y. Cui, T.-D. Hu, B. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114817;
- 7cA.-L. Gu, W.-T. Wang, X.-Y. Cheng, T.-D. Hu, Z.-L. Wu, Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 13425–13433;
- 7dC.-S. Cao, S.-M. Xia, Z.-J. Song, H. Xu, Y. Shi, L.-N. He, P. Cheng, B. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8586–8593;
- 7eM. Zhao, S. Huang, Q. Fu, W. Li, R. Guo, Q. Yao, F. Wang, P. Cui, C.-H. Tung, D. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20031–20036;
- 7fZ. Chang, X. Jing, C. He, X. Liu, C. Duan, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1384–1391;
- 7gH. Yang, X. Zhang, G. Zhang, H. Fei, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4469–4472.
- 8
- 8aL. Wang, C. Qi, W. Xiong, H. Jiang, Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 1598–1617;
- 8bY.-T. Liu, C.-W. Cheng, H.-C. Lu, T.-Y. Chang, C.-Y. Chen, H.-C. Yang, S.-H. Yu, S. Zehra, S.-H. Liu, M.-K. Leung, K.-M. Lee, H.-H. Chen, J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 13655–13663;
- 8cB. Yu, B.-B. Cheng, W.-Q. Liu, W. Li, S.-S. Wang, J. Cao, C.-W. Hu, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 90–97;
- 8dJ. Zhao, H. Huang, C. Qi, H. Jiang, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 5665–5667.
- 9
- 9aH. Zheng, Y. Fan, Y. Song, J. S. Chen, E. You, S. Labalme, W. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 10694–10699;
- 9bG. Yang, W. Shi, Y. Qian, X. Zheng, Z. Meng, H.-L. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308089;
- 9cZ. H. Syed, M. R. Mian, R. Patel, H. Xie, Z. Pengmei, Z. Chen, F. A. Son, T. A. Goetjen, A. Chapovetsky, K. M. Fahy, F. Sha, X. Wang, S. Alayoglu, D. M. Kaphan, K. W. Chapman, M. Neurock, L. Gagliardi, M. Delferro, O. K. Farha, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 16883–16897;
- 9dJ. Chen, Y. Wang, F. Wang, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202218115;
- 9eX. Zhao, R. Fang, F. Wang, X. Kong, Y. Li, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7873;
- 9fJ. Li, J. Liao, Y. Ren, C. Liu, C. Yue, J. Lu, H. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17148–17152;
- 9gJ. Li, L. He, Q. Liu, Y. Ren, H. Jiang, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 928;
- 9hD. Wang, Y. Zhao, Chem. 2021, 7, 2635–2671.
- 10
- 10aL. Y. Li, Z. X. Li, W. J. Yang, Y. M. Huang, G. Huang, Q. Q. Guan, Y. M. Dong, J. L. Lu, S.-H. Yu, H.-L. Jiang, Chem 2021, 7, 686–698;
- 10bY. Wang, T. Li, L. B. Li, R.-B. Lin, X. X. Jia, Z. Y. Chang, H.-M. Wen, X.-M. Chen, J. P. Li, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207955;
- 10cJ. Krautwurst, D. Smets, R. Lamann, U. Ruschewitz, Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8622–8632;
- 10dP. G. M. Mileo, K. Adil, L. Davis, A. Cadiau, Y. Belmabkhout, H. Aggarwal, G. Maurin, M. Eddaoudi, S. D. -Vinot, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13156–13160;
- 10eM. R. Tchalala, P. M. Bhatt, K. N. Chappanda, S. R. Tavares, K. Adil, Y. Belmabkhout, A. Shkurenko, A. Cadiau, N. Heymans, G. De Weireld, G. Maurin, K. N. Salama, M. Eddaoudi, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1328.
- 11
- 11aW. F. Xiong, C. R. Qi, H. T. He, L. Ouyang, M. Zhang, H. F. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3084–3087;
- 11bR. W. Flaig, T. M. Osborn Popp, A. M. Fracaroli, E. A. Kapustin, M. J. Kalmutzki, R. M. Altamimi, F. Fathieh, J. A. Reimer, O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12125–12128;
- 11cL. Wang, F. X Shi, C. R. Qi, W. J. Xu, W. F. Xiong, B. X. Kang, H. F. Jiang, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11821–11830.
- 12
- 12aS. Yuan, L. Feng, K. C. Wang, J. D. Pang, M. Bosch, C. Lollar, Y. J Sun, J. S. Qin, X. Y. Yang, P. Zhang, Q. Wang, L. F. Zou, Y. M. Zhang, L. L. Zhang, Y. Fang, J. L. Li, H.-C. Zhou, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704303;
- 12bV. Pascanu, G. G. Miera, A. K. Inge, B. Martín-Matute, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7223–7234;
- 12cT. Drake, P. F. Ji, W. B. Lin, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2129–2138;
- 12dT. He, X.-J. Kong, J.-R. Li, Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3083–3094.
- 13
- 13aS. Yuan, W. Lu, Y.-P. Chen, Q. Zhang, T.-F. Liu, D. Feng, X. Wang, J. Qin, H.-C. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3177–3180;
- 13bS. Yuan, Y.-P. Chen, J.-S. Qin, W. Lu, L. Zou, Q. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Sun, H.-C. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8912–8919;
- 13cC.-C. Cao, C.-X. Chen, Z.-W. Wei, Q.-F. Qiu, N.-X. Zhu, Y.-Y. Xiong, J.-J. Jiang, D. Wang, C.-Y. Su, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2589–2593.
- 14K. Artyushkova, B. Kiefer, B. Halevi, A. Knop-Gericke, R. Schlogl, P. Atanassov, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2539–2541.
- 15Y.-P. Wei, S. Yang, P. Wang, J.-H. Guo, J. Huang, W.-Y. Sun, Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 384–390.
- 16M. C. Biesinger, L. W. M. Lau, A. R. Gerson, R. S. C. Smart, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898.
- 17
- 17aB. Li, Z. Ju, M. Zhou, K. Su, D. Yuan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7687–7691;
- 17bS. Carniato, F. Rochet, J. J. Gallet, F. Bournel, G. Dufour, C. Mathieu, S. Rangan, Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 5515–5525.
- 18T. Yang, H. Lu, R. Qiu, L. Hong, S.-F. Yin, N. Kambe, Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 1436–1442.
- 19
- 19aT.-D. Hu, Y.-H. Ding, Organometallics 2020, 39, 505–515;
- 19bN. Heidary, M. Morency, D. Chartrand, K. H. Ly, R. Iftimie, N. Kornienko, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12382–12393;
- 19cJ. Z. Zhang, B. An, Z. Li, Y. H. Cao, Y. H. Dai, W. Y. Wang, L. Z. Zeng, W. B. Lin, C. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8829–8837;
- 19dL. Zhang, X.-X. Li, Z.-L. Lang, Y. Liu, J. Liu, L. Yuan, W.-Y. Lu, Y.-S. Xia, L.-Z. Dong, D.-Q. Yuan, Y.-Q. Lan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 3808–3816;
- 19eQ.-Y. Guo, Z. T. Wang, X. Y. Feng, Y. J. Fan, W. B. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306905;
- 19fS. R. V. Parambil, S. Karmakar, F. A. Rahimi, T. K. Maji, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 27821–27831.