A Radio-Pharmaceutical Fluorescent Probe for Synergistic Cancer Radiotherapy and Ratiometric Imaging of Tumor Reactive Oxygen Species
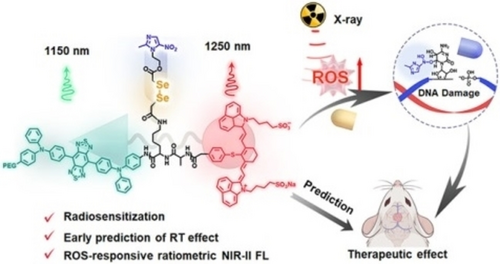
Graphical Abstract
An optical imaging agent and radiosensitized pharmaceutical containing diselenide and metronidazole was developed to realize the radiosensitizing effect and report the ROS levels through ratiometric NIR-II fluorescence imaging. This molecule exhibited synergetic radiosensitization and could monitor the radiotherapy response for both hypoxic tumors and orthotopic glioma.
Abstract
Radiotherapy (RT) is an effective and widely applied cancer treatment strategy in clinic. However, it usually suffers from radioresistance of tumor cells and severs side effects of excessive radiation dose. Therefore, it is highly significant to improve radiotherapeutic performance and monitor real-time tumor response, achieving precise and safe RT. Herein, an X-ray responsive radio-pharmaceutical molecule containing chemical radiosensitizers of diselenide and nitroimidazole (BBT-IR/Se-MN) is reported. BBT-IR/Se-MN exhibits enhanced radiotherapeutic effect via a multifaceted mechanisms and self-monitoring ROS levels in tumors during RT. Under X-ray irradiation, the diselenide produces high levels of ROS, leading to enhanced DNA damage of cancer cell. Afterwards, the nitroimidazole in the molecule inhibits the damaged DNA repair, offering a synergetic radiosensitization effect of cancer. Moreover, the probe shows low and high NIR-II fluorescence ratios in the absence and presence of ROS, which is suitable for precise and quantitative monitoring of ROS during sensitized RT. The integrated system is successfully applied for radiosensitization and the early prediction of in vitro and in vivo RT efficacy.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.