Synthesis of Cationic Biphen[4, 5]arenes as Biofilm Disruptors
Xinbei Du
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMengke Ma
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYahan Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Yu
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLongming Chen
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHan Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao Meng
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueshun Jia
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Junyi Chen
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Key Laboratory of Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Functional Material Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Structure and Performance for Functional Molecules, College of Chemistry, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qingbin Meng
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chunju Li
Key Laboratory of Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Functional Material Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Structure and Performance for Functional Molecules, College of Chemistry, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXinbei Du
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMengke Ma
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYahan Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Yu
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLongming Chen
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHan Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZhao Meng
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueshun Jia
Department of Chemistry, Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200444 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Junyi Chen
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Key Laboratory of Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Functional Material Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Structure and Performance for Functional Molecules, College of Chemistry, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qingbin Meng
State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing, 100850 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chunju Li
Key Laboratory of Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Functional Material Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Structure and Performance for Functional Molecules, College of Chemistry, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, 300387 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
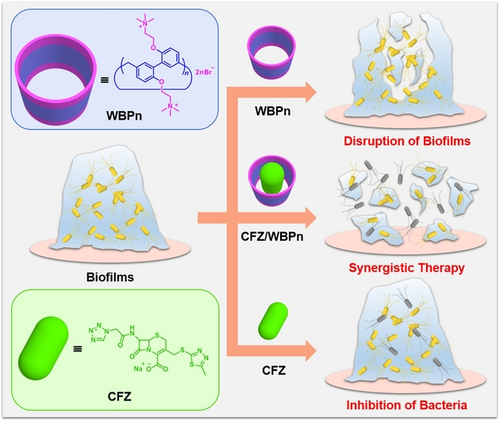
Cationic biphen[n]arenes were designed and synthesized, which could inhibit biofilm formation and eradicate stubborn mature biofilms. Moreover, their effective complexation with the conventional antibiotic cefazolin sodium could further enhance the biofilm disruption efficacy in vitro and synergistically improve the healing effect in E. coli-infected mice.
Abstract
Since bacteria in biofilms are inherently resistant to antibiotics and biofilm-associated infections pose a serious threat to global public health, new therapeutic agents and schemes are urgently needed to meet clinical requirements. Here two quaternary ammonium-functionalized biphen[n]arenes (WBPn, n=4, 5) were designed and synthesized with excellent anti-biofilm potency. Not only could they inhibit the assembly of biofilms, but also eradicate intractable mature biofilms formed by Gram-positive S. aureus and Gram-negative E. coli bacterial strains. Moreover, they could strongly complex a conventional antibiotic, cefazolin sodium (CFZ) with complex stability constants of (7.41±0.29)×104 M−1 for CFZ/WBP4 and (4.98±0.49)×103 M−1 for CFZ/WBP5. Combination of CFZ by WBP4 and WBP5 synergistically enhanced biofilm eradication performance in vitro and statistically improved healing efficacy on E. coli-infected mice models, providing a novel supramolecular strategy for combating biofilm-associated infections.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Research data are not shared.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202301857-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1B. Qin, C. Fei, A. A. Bridges, A. A. Mashruwala, H. A. Stone, N. S. Wingreen, B. L. Bassler, Science 2020, 369, 71–77.
- 2H. Flemming, J. Wingender, U. Szewzyk, P. Steinberg, S. A. Rice, S. Kjelleberg, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–578.
- 3W. M. Dunne, Jr., Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 155–166.
- 4I. Vacca, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 513.
- 5H. Flemming, J. Wingender, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633.
- 6T. R. Neu, J. R. Lawrence, Trends Microbiol. 2014, 23, 233–242.
- 7K. P. Rumbaugh, K. Sauer, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 571–586.
- 8K. M. G. O'Connell, J. T. Hodgkinson, H. F. Sore, M. Welch, G. P. C. Salmond, D. R. Spring, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10706–10733.
- 9Q. He, Z. Yang, Z. Zou, M. Qian, X. Wang, X. Zhang, Z. Yin, J. Wang, X. Ye, D. Liu, M. Guo, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205301.
- 10P. R. Judzewitsch, N. Corrigan, E. H. H. Wong, C. Boyer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24248–24256.
- 11T. N. Siriwardena, A. Capecchi, B.-H. Gan, X. Jin, R. He, D. Wei, L. Ma, T. Kçhler, C. Delden, S. Javor, J.-L. Reymond, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8483–8487.
- 12R. Zhao, H. Wang, T. Ji, G. Anderson, G. Nie, Y. Zhao, Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 216–226.
- 13J. Du, Y. Li, J. Wang, C. Wang, D. Liu, G. Wang, S. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26966–26972.
- 14J. J. Li, Y. Hu, B. Hu, W. Wang, H. Xu, X. Hu, F. Ding, H. Li, K. Wang, X. Zhang, D. Guo, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6279–6290.
- 15L. Chen, Y. Chen, R. Zhang, Q. Yu, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9929–9937.
- 16J. Ma, H. Deng, S. Ma, J. Li, X. Jia, C. Li, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6221–6624.
- 17L. Zhao, J. Chen, L. Tian, Y. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Du, M. Ma, J. Li, Q. Meng, C. Li, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2022, 11, 2200270.
- 18J. Chen, Q. Meng, Y. Zhang, M. Dong, L. Zhao, Y. Zhang, L. Chen, Y. Chai, Z. Meng, C. Wang, X. Jia, C. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11288–11293.
- 19R. Joseph, A. Naugolny, M. Feldman, I. M. Herzog, M. Fridman, Y. Cohen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 754–757.
- 20R. Liu, R. Huo, Y. Bi, Z. Zhao, Q. Liu, Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1037–1040.
- 21Q. Guo, Y. Zhao, X. Dai, T. Zhang, Y. Yu, X. Zhang, C. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16834–16847.
- 22A. Vishwakarma, F. Dang, A. Ferrell, H. A. Barton, A. Joy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 9440–9449.
- 23M. Müsken, S. D. Fiore, U. Römling, S. Häussler, Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1460–1469.
- 24M. C. Jennings, L. E. Ator, T. J. Paniak, K. P. C. Minbiole, W. M. Wuest, ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 2211–2215.
- 25E. Bar-Zeev, I. Berman-Frank, O. Girshevitz, T. Berman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9119–9124.
- 26M. Tiecco, L. Roscini, L. Corte, C. Colabella, R. Germani, G. Cardinali, Langmuir 2016, 32, 1101–1110.
- 27Q. Z. Jaber, R. I. Benhamou, I. M. Herzog, B. B. Baruch, M. Fridman, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16391–16395.
- 28K. R. Purdy Drew, L. K. Sanders, Z. W. Culumber, O. Zribi, G. C. L. Wong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 486–493.
- 29K. Ries, M. E. Levison, D. Kaye, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1973, 3, 168–174.
- 30G. Yu, J. Zhou, J. Shen, G. Tang, F. Huang, Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4073–4078.
- 31Y. Sun, H. Li, J. Huang, Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 5, 387–400.
- 32S. Guo, Q. Huang, Y. Chen, J. Wei, J. Zheng, L. Wang, Y. Wang, R. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 618–623.
- 33L. Grassi, G. Batoni, L. Ostyn, P. Rigole, S. V. Bossche, A. C. Rinaldi, G. Maisetta, S. Esin, T. Coenye, A. Crabbé, Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 198.
- 34J. M. Parrish, M. Soni, R. Mittal, J. Leukocyte Biol. 2019, 106, 943–956.