Electrochemical-Mediated Regenerable FeII Active Sites for Efficient Uranium Extraction at Ultra-Low Cell Voltage
Corresponding Author
Prof. Yanyong Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yanjing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Minglei Song
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Siping Chen
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jianrong Wei
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jie You
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Bo Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shuangyin Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yanyong Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yanjing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Minglei Song
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Siping Chen
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jianrong Wei
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jie You
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Bo Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shuangyin Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Bio-Sensing and Chemometrics, Provincial Hunan Key Laboratory for Graphene Materials and Devices, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
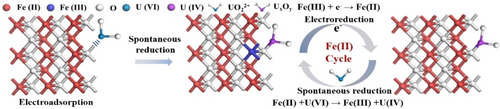
Nano-reduced iron (NRI) is a promising uranium adsorbent due to its strong reducibility and good selectivity, but it still faces the challenges of slow kinetics, limited and non-renewable active sites. In this work, we realized high efficiency uranium extraction under ultra-low cell voltage (−0.1 V) in seawater with 20 ppm UO2(NO3)2 solution by coupling electrochemical mediated FeII/FeIII redox and uranium extraction. The adsorption capacity and extraction efficiency of NRI after electrochemical uranium extraction (EUE) could reach 452 mg/g and 99.1 %, respectively. Combined with quasi-operando/operando characterization technologies, we clarified the mechanism of EUE and revealed that continuously regenerating FeII active sites by electroreduction could significantly enhance the property of EUE. This work here provides a new electrochemical mediated and low energy consumption uranium extraction strategy which also provides a reference for other metal resource recovery.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202217601-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.7 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1Z. Wan, M. Zhu, S. Chen, D. Sperling, Nature 2016, 530, 275–277.
- 2D. Wang, J. Song, J. Wen, Y. Yuan, Z. Liu, S. Lin, H. Wang, H. Wang, S. Zhao, X. Zhao, M. Fang, M. Lei, B. Li, N. Wang, X. Wang, H. Wu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802607.
- 3S. Kushwaha, M. Mane, S. Ravindranathan, A. Das, ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3254–3263.
- 4
- 4aS. Kushwaha, K. Patel, Chem 2021, 7, 271–274;
- 4bS. Zhao, Y. Yuan, Q. Yu, B. Niu, J. Liao, Z. Guo, N. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14979–14985;
- 4cR. I. Foster, K.-W. Kim, M.-K. Oh, K.-Y. Lee, Water Res. 2019, 158, 82–93.
- 5Y. Xie, Z. Y. Liu, Y. Y. Geng, H. Li, N. Wang, Y. P. Song, X. L. Wang, J. Chen, J. C. Wang, S. Q. Ma, G. Ye, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 97–162.
- 6L. Kong, Y. Ruan, Q. Zheng, M. Su, Z. Diao, D. Chen, L. Hou, X. Chang, K. Shih, J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120784.
- 7
- 7aZ. Wang, Q. Meng, R. Ma, Z. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Sha, X. Ma, X. Ruan, X. Zou, Y. Yuan, G. Zhu, Chem 2020, 6, 1683–1691;
- 7bZ. Chen, Y. Liang, D. Jia, W. Chen, Z. Cui, X. Wang, Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1851–1858.
- 8
- 8aN. Tang, J. Liang, C. Niu, H. Wang, Y. Luo, W. Xing, S. Ye, C. Liang, H. Guo, J. Guo, Y. Zhang, G. Zeng, J. Mater. Chem. 2020, 8, 7588–7625;
- 8bC. W. Abney, R. T. Mayes, T. Saito, S. Dai, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13935–14013;
- 8cL. Ling, W.-x. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788–2791;
- 8dB. Yan, C. Ma, J. Gao, Y. Yuan, N. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906615.
- 9
- 9aC. Ma, J. Gao, D. Wang, Y. Yuan, J. Wen, B. Yan, S. Zhao, X. Zhao, Y. Sun, X. Wang, N. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900085;
- 9bQ. Sun, B. Aguila, L. D. Earl, C. W. Abney, L. Wojtas, P. K. Thallapally, S. Ma, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705479;
- 9cH. Tang, W. Cheng, Y. Yi, C. Ding, X. Nie, Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130229.
- 10
- 10aF. Chi, S. Zhang, J. Wen, J. Xiong, S. Hu, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8078–8084;
- 10bH. Yang, X. Liu, M. Hao, Y. Xie, X. Wang, H. Tian, G. I. N. Waterhouse, P. E. Kruger, S. G. Telfer, S. Ma, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106621;
- 10cL. Lin, T. Liu, Y. Qie, W. Liu, Y. Meng, Q. Yuan, F. Luan, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13327–13337.
- 11
- 11aT. Liu, J. Yuan, B. Zhang, W. Liu, L. Lin, Y. Meng, S. Yin, C. Liu, F. Luan, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14612–14619;
- 11bC. Liu, P.-C. Hsu, J. Xie, J. Zhao, T. Wu, H. Wang, W. Liu, J. Zhang, S. Chu, Y. Cui, Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17007.
- 12
- 12aY. Zhou, G. Li, L. Xu, J. Liu, Z. Sun, W. Shi, Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105209;
- 12bS. Szenknect, A. Mesbah, M. Descostes, A. Maihatchi-Ahamed, L. Bonato, M. Massonnet, Y. Ziouane, E. Vors, T. Vercouter, N. Clavier, J. Lautru, N. Dacheux, J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122501.
- 13
- 13aY. Zhang, L. Tao, C. Xie, D. Wang, Y. Zou, R. Chen, Y. Wang, C. Jia, S. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905923;
- 13bJ. Vavra, T. H. Shen, D. Stoian, V. Tileli, R. Buonsanti, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1347–1354.
- 14
- 14aT. Wang, L. Tao, X. Zhu, C. Chen, W. Chen, S. Du, Y. Zhou, B. Zhou, D. Wang, C. Xie, P. Long, W. Li, Y. Wang, R. Chen, Y. Zou, X.-Z. Fu, Y. Li, X. Duan, S. Wang, Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 66–73;
- 14bY. Zhang, B. Zhou, Z. Wei, W. Zhou, D. Wang, J. Tian, T. Wang, S. Zhao, J. Liu, L. Tao, S. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104791.
- 15
- 15aX. Wang, P. Wang, J. Ma, H. Liu, P. Ning, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 57–66;
- 15bZ. Xiong, D. Zhao, G. Pan, Water Res. 2007, 41, 3497–3505.
- 16T. A. Darziyeva, E. S. Alekperov, S. H. Jabarov, M. N. Mirzayev, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2150125.
- 17C. F. Du, K. N. Dinh, Q. Liang, Y. Zheng, Y. Luo, J. Zhang, Q. Yan, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801127.
- 18A. Satpathy, J. G. Catalano, D. E. Giammar, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4111–4120.
- 19J. Huang, A. Jones, T. D. Waite, Y. Chen, X. Huang, K. M. Rosso, A. Kappler, M. Mansor, P. G. Tratnyek, H. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8161–8233.
- 20L. Cui, X. Zhao, H. Xie, Z. Zhang, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 13334–13348.
- 21Z. Chen, Z. Wei, Y. Chen, Y. Nong, C. Yi, Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 209, 111429.
- 22J. Wei, J. Wang, Z. Shao, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 53188.
- 23Z. Wang, R. Ma, Q. Meng, Y. Yang, X. Ma, X. Ruan, Y. Yuan, G. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14523–14529.
- 24Z. Li, Z. Zhang, Z. Dong, F. Yu, M. Ma, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Liu, X. Cao, Y. Liu, Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120195.
- 25G. J. Hutchings, C. S. Heneghan, I. D. Hudson, S. H. Taylor, Nature 1996, 384, 341–343.
- 26S. Lazareva, Z. Ismagilov, V. Kuznetsov, N. Shikina, M. Kerzhentsev, Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1881–1889.
- 27J. Leduc, Y. Gönüllü, T. P. Ruoko, T. Fischer, L. Mayrhofer, N. V. Tkachenko, C.-L. Dong, A. Held, M. Moseler, S. Mathur, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905005.