Vacancy Modulating Co3Sn2S2 Topological Semimetal for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
Dr. Yuwei Zhao
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yongbin Zhu
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Feng Jiang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yiyao Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. You Meng
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ying Guo
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qing Li
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhaodong Huang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shaoce Zhang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Rong Zhang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Johnny C. Ho
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qianfan Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Weishu Liu
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chunyi Zhi
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Centre for Functional Photonics, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yuwei Zhao
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yongbin Zhu
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Feng Jiang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yiyao Li
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. You Meng
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ying Guo
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Qing Li
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhaodong Huang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shaoce Zhang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Rong Zhang
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Johnny C. Ho
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qianfan Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Weishu Liu
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chunyi Zhi
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Centre for Functional Photonics, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
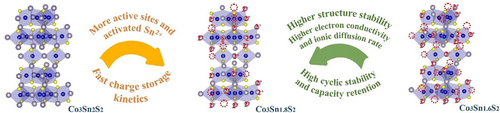
A Weyl semimetal Co3Sn2S2 cathode was applied in aqueous Zn-ion batteries with a discharge plateau around 1.5 V. Co3Sn1.8S2 activates Sn2+ and provides active sites with impressive charge-storage capabilities and fast kinetic processes. The material has high structural stability and conductivity, and an ionic diffusion rate that achieves appreciable cycling stability and capacity retention.
Abstract
Weyl semimetals (WSMs) with high electrical conductivity and suitable carrier density near the Fermi level are enticing candidates for aqueous Zn-ion batteries (AZIBs), meriting from topological surface states (TSSs). We propose a WSM Co3Sn2S2 cathode for AZIBs showing a discharge plateau around 1.5 V. By introducing Sn vacancies, extra redox peaks from the Sn4+/Sn2+ transition appear, which leads to more Zn2+ transfer channels and active sites promoting charge-storage kinetics and Zn2+ storage capability. Co3Sn1.8S2 achieves a specific energy of 305 Wh kg−1 (0.2 Ag−1) and a specific power of 4900 Wkg−1 (5 Ag−1). Co3Sn1.8S2 and ZnxCo3Sn1.8S2 benefit from better conductivity at lower temperatures; the quasi-solid Co3Sn1.8S2//Zn battery delivers 126 mAh g−1 (0.6 Ag−1) at −30 °C and a cycling stability over 3000 cycles (2 Ag−1) with 85 % capacity retention at −10 °C.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202111826-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.8 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. Chen, W. Zhu, D. Xiao, Z. Zhang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 056804.
- 2L. Müchler, H. Zhang, S. Chadov, B. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7221–7225; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 7333–7337.
- 3J. Liu, D. Vanderbilt, Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 155316.
- 4A. A. Burkov, M. D. Hook, L. Balents, Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 235126.
- 5Y. Xing, J. Shen, H. Chen, L. Huang, Y. Gao, Q. Zheng, Y. Zhang, G. Li, B. Hu, G. Qian, L. Cao, X. Zhang, P. Fan, R. Ma, Q. Wang, Q. Yin, H. Lei, W. Ji, S. Du, H. Yang, W. Wang, C. Shen, X. Lin, E. Liu, B. Shen, Z. Wang, H. Gao, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5613.
- 6E. Liu, Y. Sun, N. Kumar, L. Muechler, A. Sun, L. Jiao, S. Yang, D. Liu, A. Liang, Q. Xu, J. Kroder, V. Süß, H. Borrmann, C. Shekhar, Z. Wang, C. Xi, W. Wang, W. Schnelle, S. Wirth, Y. Chen, S. T. B. Goennenwein, C. Felser, Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 1125–1131.
- 7Q. Wang, Y. Xu, R. Lou, Z. Liu, M. Li, Y. Huang, D. Shen, H. Weng, S. Wang, H. Lei, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3681.
- 8M. Armand, J. M. Tarascon, Nature 2008, 451, 652–657.
- 9H. Li, C. Han, Y. Huang, Y. Huang, M. Zhu, Z. Pei, Q. Xue, Z. Wang, Z. Liu, Z. Tang, Y. Wang, F. Kang, B. Li, C. Zhi, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 941–951.
- 10N. Zhang, F. Cheng, J. Liu, L. Wang, X. Long, X. Liu, F. Li, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 405.
- 11F. Wan, L. Zhang, X. Dai, X. Wang, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1656.
- 12C. Liu, Z. Neale, J. Zheng, X. Jia, J. Huang, M. Yan, M. Tian, M. Wang, J. Yang, G. Cao, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2273–2285.
- 13G. Li, Z. Yang, Y. Jiang, C. Jin, W. Huang, X. Ding, Y. Huang, Nano Energy 2016, 25, 211–217.
- 14W. Li, K. Wang, S. Cheng, K. Jiang, Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 15, 14–21.
- 15C. Han, J. Zhu, C. Zhi, H. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15479–15512.
- 16Y. Lu, Q. Zhang, L. Li, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Chem 2018, 4, 2786–2813.
- 17W. Li, K. Wang, K. Jiang, Adv. Sci. 2020, 8, 3785–3794.
- 18X. Wu, A. Markir, L. Ma, Y. Xu, H. Jiang, D. P. Leonard, W. Shin, T. Wu, J. Lu, X. Ji, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12640–12645; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12770–12775.
- 19Y. Zhao, D. Wang, X. Li, Q. Yang, Y. Guo, F. Mo, Q. Li, C. Peng, H. Li, C. Zhi, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2003070.
- 20Y. Yang, Y. Tang, S. Liang, Z. Wu, G. Fang, X. Cao, C. Wang, T. Lin, A. Pan, J. Zhou, Nano Energy 2019, 61, 617–625.
- 21Y. Fu, Q. Wei, G. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Hu, D. Wang, L. Zuin, T. Zhou, Y. Wu, S. Sun, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801445.
- 22B. Wu, G. Zhang, M. Yan, T. Xiong, P. He, L. He, X. Xu, L. Mai, Small 2018, 14, e1703850.
- 23Y. Xu, M. Zhou, X. Wang, C. Wang, L. Liang, F. Grote, M. Wu, Y. Mi, Y. Lei, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8768–8771; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 8892–8895.
- 24W. Zou, J. Dong, Y. Luo, Q. Zhao, T. Xie, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606100.
- 25M. A. Kassem, Y. Tabata, T. Waki, H. Nakamura, Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 014429.
- 26G. Li, Q. Xu, W. Shi, C. Fu, L. Jiao, M. E. Kamminga, M. Q. Yu, H. Tueysuez, N. Kumar, V. Suess, R. Saha, A. K. Srivastava, S. Wirth, G. Auffermann, J. Gooth, S. Parkin, Y. Sun, E. K. Liu, C. Felser, Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw9867.
- 27M. Holder, Y. S. Dedkov, A. Kade, H. Rosner, W. Schnelle, A. Leithe-Jasper, R. Weihrich, S. L. Molodtsov, Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 205116.
- 28Z. Huang, T. Wang, H. Song, X. Li, G. Liang, D. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1011–1021; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 1024–1034.
- 29H. S. Kim, J. B. Cook, H. Lin, J. S. Ko, S. H. Tolbert, B. Dunn, Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 454–460.
- 30J. Wang, J. Polleux, J. Lim, B. Dunn, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14925–14931.
- 31A. J. Bard, L. R. Faulkner, Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Ed. , Wiley, 2001.
- 32Y. Zhao, L. Ma, Y. Zhu, P. Qin, H. Li, F. Mo, D. Wang, G. Liang, Q. Yang, W. Liu, C. Y. Zhi, ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7270–7280.
- 33Q. Li, Y. Wang, F. Mo, D. Wang, G. Liang, Y. W. Zhao, Q. Yang, Z. D. Huang, C. Y. Zhi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003931.
- 34Z. Li, Y. Ren, L. Mo, C. Liu, K. Hsu, Y. Ding, X. Zhang, X. Li, L. Hu, D. Ji, G. Cao, ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5581–5589.
- 35Z. Jian, W. Luo, X. Ji, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11566–11569.
- 36X. Li, N. Li, Z. Huang, Z. Chen, G. Liang, Q. Yang, M. Li, Y. Zhao, L. Ma, B. Dong, Q. F. Huang, J. Fan, C. Y. Zhi, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006897.
- 37W. Zhong, Z. Wang, N. Gao, L. Huang, Z. Lin, Y. Liu, F. Meng, J. Deng, S. Jin, Q. Zhang, L. Gu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22743–22748; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 22931–22936.
- 38Q. Zhang, K. Xia, Y. Ma, Y. Lu, L. Li, J. Liang, S. Chou, J. Chen, ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2704–2712.
- 39D. Reber, R. Kühnel, C. Battaglia, ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 44–51.
- 40N. Yesibolati, N. Umirov, A. Koishybay, M. Omarova, I. Kurmanbayeva, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Z. Bakenov, Electrochim. Acta 2015, 152, 505–511.
- 41M. H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, S. Kim, J. P. Duong, J. Jo, Z. Xiu, V. Mathew, J. Kim, Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 60, 121–125.
- 42R. Trócoli, F. La Mantia, ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 481–485.
- 43L. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Zhou, Z. Liu, Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18263.
- 44S. Yang, C. Li, Y. Wang, S. Chen, M. Cui, X. Bai, Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 33, 230–238.
- 45F. Mo, Y. Huang, Q. Li, Z. Wang, R. Jiang, W. Gai, C. Zhi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010830.
- 46Y. Zhao, Z. Chen, F. Mo, D. Wang, Y. Guo, Z. Liu, X. Li, Q. Li, G. Liang, C. Zhi, Adv. Sci. 2020, 8, 2002590.