Advances and Challenges for the Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to CO: From Fundamentals to Industrialization
Dr. Song Jin
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhimeng Hao
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kai Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhenhua Yan
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jun Chen
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Song Jin
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhimeng Hao
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kai Zhang
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhenhua Yan
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jun Chen
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 100th anniversary of Chemistry at Nankai University
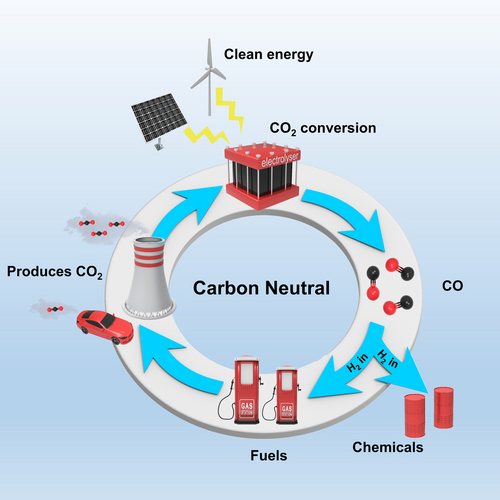
Graphical Abstract
The selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO provides a promising approach to realize a sustainable, carbon-neutral economy. This Review gives a comprehensive overview focusing on catalyst and electrolyte design, and their integration with electrolyzer technology towards industrial implementation. The current challenges in the commercial use of CO2 electrolysis to generate CO are also presented to enable future developments.
Abstract
The electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR) provides an attractive approach to convert renewable electricity into fuels and feedstocks in the form of chemical bonds. Among the different CO2RR pathways, the conversion of CO2 into CO is considered one of the most promising candidate reactions because of its high technological and economic feasibility. Integrating catalyst and electrolyte design with an understanding of the catalytic mechanism will yield scientific insights and promote this technology towards industrial implementation. Herein, we give an overview of recent advances and challenges for the selective conversion of CO2 into CO. Multidimensional catalyst and electrolyte engineering for the CO2RR are also summarized. Furthermore, recent studies on the large-scale production of CO are highlighted to facilitate industrialization of the electrochemical reduction of CO2. To conclude, the remaining technological challenges and future directions for the industrial application of the CO2RR to generate CO are highlighted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202101818-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf425.7 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Rogelj, M. den Elzen, N. Höhne, T. Fransen, H. Fekete, H. Winkler, R. Schaeffer, F. Sha, K. Riahi, M. Meinshausen, Nature 2016, 534, 631–639.
- 2J. D. Shakun, P. U. Clark, F. He, S. A. Marcott, A. C. Mix, Z. Liu, B. Otto-Bliesner, A. Schmittner, E. Bard, Nature 2012, 484, 49–54.
- 3K. Anderson, G. Peters, Science 2016, 354, 182–183.
- 4
- 4aH. Agustsson, G. H. Grinestaf, in The 13th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery 2005;
- 4bA. A. Espie, P. J. Brand, R. C. Skinner, R. A. Hubbard, H. I. Turan, in Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies-6th International Conference (Eds.: J. Gale, Y. Kaya), Pergamon, Oxford, 2003, pp. 213–218.
- 5S. Sultana, P. Chandra Sahoo, S. Martha, K. Parida, RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44170–44194.
- 6T. Zheng, K. Jiang, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802066.
- 7S. N. Habisreutinger, L. Schmidt-Mende, J. K. Stolarczyk, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7372–7408; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 7516–7557.
- 8J. Grodkowski, P. Neta, J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 4967–4972.
- 9W. Wang, S. Wang, X. Ma, J. Gong, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3703–3727.
- 10
- 10aM. G. Kibria, J. P. Edwards, C. M. Gabardo, C. T. Dinh, A. Seifitokaldani, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807166;
- 10bY. Ni, L. Miao, J. Wang, J. Liu, M. Yuan, J. Chen, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 1181–1186;
- 10cF. Y. Gao, R. C. Bao, M. R. Gao, S. H. Yu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15458–15478.
- 11G. Glockler, J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 1049–1054.
- 12
- 12aX. Tan, C. Yu, Y. Ren, S. Cui, W. Li, J. Qiu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 765–780;
- 12bN. Han, P. Ding, L. He, Y. Li, Y. Li, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902338;
- 12cY. Wei, J. Liu, F. Chen, J. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19651–19656.
- 13G. Wang, J. Chen, Y. Ding, P. Cai, L. Yi, Y. Li, C. Tu, Y. Hou, Z. Wen, L. Dai, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4993–5061.
- 14C. Chen, J. F. Khosrowabadi Kotyk, S. W. Sheehan, Chem 2018, 4, 2571–2586.
- 15L. V. Haynes, D. T. Sawyer, Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 332–338.
- 16S. Meshitsuka, M. Ichikawa, K. Tamaru, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1974, 158–159.
- 17T. Yamamoto, D. A. Tryk, A. Fujishima, H. Ohata, Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3327–3334.
- 18B. Kumar, M. Asadi, D. Pisasale, S. Sinha-Ray, B. A. Rosen, R. Haasch, J. Abiade, A. L. Yarin, A. Salehi-Khojin, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2819.
- 19M. Asadi, B. Kumar, A. Behranginia, B. A. Rosen, A. Baskin, N. Repnin, D. Pisasale, P. Phillips, W. Zhu, R. Haasch, R. F. Klie, P. Král, J. Abiade, A. Salehi-Khojin, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4470.
- 20S. Lin, C. S. Diercks, Y. B. Zhang, N. Kornienko, E. M. Nichols, Y. Zhao, A. R. Paris, D. Kim, P. Yang, O. M. Yaghi, C. J. Chang, Science 2015, 349, 1208–1213.
- 21N. Kornienko, Y. Zhao, C. S. Kley, C. Zhu, D. Kim, S. Lin, C. J. Chang, O. M. Yaghi, P. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14129–14135.
- 22C. Zhao, X. Dai, T. Yao, W. Chen, X. Wang, J. Wang, J. Yang, S. Wei, Y. Wu, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8078–8081.
- 23S. Verma, S. Lu, P. J. Kenis, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 466–474.
- 24Y. Hori, H. Wakebe, T. Tsukamoto, O. Koga, Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1833–1839.
- 25B. A. Rosen, A. Salehi-Khojin, M. R. Thorson, W. Zhu, D. T. Whipple, P. J. A. Kenis, R. I. Masel, Science 2011, 334, 643–644.
- 26
- 26aD. D. Zhu, J. L. Liu, S. Z. Qiao, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3423–3452;
- 26bW. Zhang, Y. Hu, L. Ma, G. Zhu, Y. Wang, X. Xue, R. Chen, S. Yang, Z. Jin, Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700275.
- 27
- 27aJ. Shen, R. Kortlever, R. Kas, Y. Y. Birdja, O. Diaz-Morales, Y. Kwon, I. Ledezma-Yanez, K. J. P. Schouten, G. Mul, M. T. M. Koper, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8177;
- 27bY. Y. Birdja, E. Pérez-Gallent, M. C. Figueiredo, A. J. Göttle, F. Calle-Vallejo, M. T. M. Koper, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 732–745.
- 28J. Shen, M. J. Kolb, A. J. Göttle, M. T. M. Koper, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 15714–15721.
- 29H. A. Schwarz, R. W. Dodson, J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 409–414.
- 30F. A. Armstrong, J. Hirst, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14049–14054.
- 31M. Zhong, K. Tran, Y. Min, C. Wang, Z. Wang, C. T. Dinh, P. De Luna, Z. Yu, A. S. Rasouli, P. Brodersen, S. Sun, O. Voznyy, C. S. Tan, M. Askerka, F. Che, M. Liu, A. Seifitokaldani, Y. Pang, S. C. Lo, A. Ip, Z. Ulissi, E. H. Sargent, Nature 2020, 581, 178–183.
- 32X. Wang, Z. Wang, F. P. García de Arquer, C. T. Dinh, A. Ozden, Y. C. Li, D. H. Nam, J. Li, Y. S. Liu, J. Wicks, Z. Chen, M. Chi, B. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Tam, J. Y. Howe, A. Proppe, P. Todorović, F. Li, T. T. Zhuang, C. M. Gabardo, A. R. Kirmani, C. McCallum, S. F. Hung, Y. Lum, M. Luo, Y. Min, A. Xu, C. P. O'Brien, B. Stephen, B. Sun, A. H. Ip, L. J. Richter, S. O. Kelley, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 478–486.
- 33R. A. Geioushy, M. M. Khaled, K. Alhooshani, A. S. Hakeem, A. Rinaldi, Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 456–462.
- 34R. Kortlever, J. Shen, K. J. P. Schouten, F. Calle-Vallejo, M. T. M. Koper, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4073–4082.
- 35S. Verma, B. Kim, H. R. M. Jhong, S. Ma, P. J. A. Kenis, ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1972–1979.
- 36M. Jouny, W. Luc, F. Jiao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2165–2177.
- 37R. M. Navarro, M. A. Peña, J. L. G. Fierro, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3952–3991.
- 38G. Centi, S. Perathoner, Catal. Today 2009, 148, 191–205.
- 39D. Voiry, H. S. Shin, K. P. Loh, M. Chhowalla, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0105.
- 40Y. Chen, C. W. Li, M. W. Kanan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19969–19972.
- 41M. Ma, B. J. Trześniewski, J. Xie, W. A. Smith, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9748–9752; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 9900–9904.
- 42D. Kim, C. Xie, N. Becknell, Y. Yu, M. Karamad, K. Chan, E. J. Crumlin, J. K. Nørskov, P. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8329–8336.
- 43R. Reske, H. Mistry, F. Behafarid, B. Roldan Cuenya, P. Strasser, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6978–6986.
- 44W. Zhu, R. Michalsky, Ö. Metin, H. Lv, S. Guo, C. J. Wright, X. Sun, A. A. Peterson, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16833–16836.
- 45H. Mistry, R. Reske, Z. Zeng, Z. J. Zhao, J. Greeley, P. Strasser, B. R. Cuenya, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16473–16476.
- 46J. A. Trindell, J. Clausmeyer, R. M. Crooks, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16161–16167.
- 47K. S. Kim, W. J. Kim, H. K. Lim, E. K. Lee, H. Kim, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4443–4448.
- 48X. Feng, K. Jiang, S. Fan, M. W. Kanan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4606–4609.
- 49R. G. Mariano, K. McKelvey, H. S. White, M. W. Kanan, Science 2017, 358, 1187–1192.
- 50M. Liu, M. Liu, X. Wang, S. M. Kozlov, Z. Cao, P. De Luna, H. Li, X. Qiu, K. Liu, J. Hu, C. Jia, P. Wang, H. Zhou, J. He, M. Zhong, X. Lan, Y. Zhou, Z. Wang, J. Li, A. Seifitokaldani, C. T. Dinh, H. Liang, C. Zou, D. Zhang, Y. Yang, T. S. Chan, Y. Han, L. Cavallo, T. K. Sham, B. J. Hwang, E. H. Sargent, Joule 2019, 3, 1703–1718.
- 51C. Kim, T. Eom, M. S. Jee, H. Jung, H. Kim, B. K. Min, Y. J. Hwang, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 779–785.
- 52Y. Fang, J. C. Flake, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3399–3405.
- 53A. Guan, C. Yang, Y. Quan, H. Shen, N. Cao, T. Li, Y. Ji, G. Zheng, Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3969–3980.
- 54W. Zhu, Y. J. Zhang, H. Zhang, H. Lv, Q. Li, R. Michalsky, A. A. Peterson, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16132–16135.
- 55S. Liu, X. Z. Wang, H. Tao, T. Li, Q. Liu, Z. Xu, X. Z. Fu, J. L. Luo, Nano Energy 2018, 45, 456–462.
- 56S. Back, M. S. Yeom, Y. Jung, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5089–5096.
- 57M. Liu, Y. Pang, B. Zhang, P. De Luna, O. Voznyy, J. Xu, X. Zheng, C. T. Dinh, F. Fan, C. Cao, F. P. G. de Arquer, T. S. Safaei, A. Mepham, A. Klinkova, E. Kumacheva, T. Filleter, D. Sinton, S. O. Kelley, E. H. Sargent, Nature 2016, 537, 382–386.
- 58T. Saberi Safaei, A. Mepham, X. Zheng, Y. Pang, C. T. Dinh, M. Liu, D. Sinton, S. O. Kelley, E. H. Sargent, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7224–7228.
- 59Y. Ma, J. Wang, J. Yu, J. Zhou, X. Zhou, H. Li, Z. He, H. Long, Y. Wang, P. Lu, J. Yin, H. Sun, Z. Zhang, Z. Fan, Matter 2021, 4, 888–926.
- 60C. W. Li, M. W. Kanan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7231–7234.
- 61
- 61aZ. Sun, T. Ma, H. Tao, Q. Fan, B. Han, Chem 2017, 3, 560–587;
- 61bW. Shao, X. Zhang, Nanoscale 2021, 13, 7081–7095.
- 62L. Dai, Q. Qin, P. Wang, X. Zhao, C. Hu, P. Liu, R. Qin, M. Chen, D. Ou, C. Xu, S. Mo, B. Wu, G. Fu, P. Zhang, N. Zheng, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701069.
- 63S. Liu, H. Tao, L. Zeng, Q. Liu, Z. Xu, Q. Liu, J. L. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2160–2163.
- 64C. Y. Lee, Y. Zhao, C. Wang, D. R. G. Mitchell, G. G. Wallace, Sustainable Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1023–1027.
- 65M. Asadi, K. Kim, C. Liu, A. V. Addepalli, P. Abbasi, P. Yasaei, P. Phillips, A. Behranginia, J. M. Cerrato, R. Haasch, P. Zapol, B. Kumar, R. F. Klie, J. Abiade, L. A. Curtiss, A. Salehi-Khojin, Science 2016, 353, 467–470.
- 66C. Tsai, K. Chan, J. K. Nørskov, F. Abild-Pedersen, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 3884–3889.
- 67C. Tsai, F. Abild-Pedersen, J. K. Nørskov, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1381–1387.
- 68X. Hong, K. Chan, C. Tsai, J. K. Nørskov, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4428–4437.
- 69P. Abbasi, M. Asadi, C. Liu, S. Sharifi-Asl, B. Sayahpour, A. Behranginia, P. Zapol, R. Shahbazian-Yassar, L. A. Curtiss, A. Salehi-Khojin, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 453–460.
- 70J. Xu, X. Li, W. Liu, Y. Sun, Z. Ju, T. Yao, C. Wang, H. Ju, J. Zhu, S. Wei, Y. Xie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9121–9125; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9249–9253.
- 71Q. Lu, J. Rosen, Y. Zhou, G. S. Hutchings, Y. C. Kimmel, J. G. Chen, F. Jiao, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3242.
- 72J. Rosen, G. S. Hutchings, Q. Lu, S. Rivera, Y. Zhou, D. G. Vlachos, F. Jiao, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4293–4299.
- 73R. Kas, K. K. Hummadi, R. Kortlever, P. de Wit, A. Milbrat, M. W. J. Luiten-Olieman, N. E. Benes, M. T. M. Koper, G. Mul, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10748.
- 74G. Hyun, J. T. Song, C. Ahn, Y. Ham, D. Cho, J. Oh, S. Jeon, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5680–5685.
- 75W. Luo, J. Zhang, M. Li, A. Züttel, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3783–3791.
- 76A. S. Hall, Y. Yoon, A. Wuttig, Y. Surendranath, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14834–14837.
- 77Y. Yoon, A. S. Hall, Y. Surendranath, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15282–15286; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15508–15512.
- 78
- 78aY. Chen, S. Ji, C. Chen, Q. Peng, D. Wang, Y. Li, Joule 2018, 2, 1242–1264;
- 78bL. Zhang, D. Liu, Z. Muhammad, F. Wan, W. Xie, Y. Wang, L. Song, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903955;
- 78cL. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800443.
- 79
- 79aY. Cheng, S. Yang, S. P. Jiang, S. Wang, Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800440;
- 79bQ. Qu, S. Ji, Y. Chen, D. Wang, Y. Li, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4201–4215;
- 79cD. Gao, T. Liu, G. Wang, X. Bao, ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 713–727;
- 79dY. Zhu, X. Yang, C. Peng, C. Priest, Y. Mei, G. Wu, Small 2021, 17, 2005148.
- 80K. Jiang, S. Siahrostami, A. J. Akey, Y. Li, Z. Lu, J. Lattimer, Y. Hu, C. Stokes, M. Gangishetty, G. Chen, Y. Zhou, W. Hill, W. B. Cai, D. Bell, K. Chan, J. K. Nørskov, Y. Cui, H. Wang, Chem 2017, 3, 950–960.
- 81X. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Sang, W. Zheng, S. Zhang, L. Shuai, B. Yang, Z. Li, J. Chen, L. Lei, N. M. Adli, M. K. H. Leung, M. Qiu, G. Wu, Y. Hou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4192–4198; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 4238–4244.
- 82Y. Cheng, S. Zhao, B. Johannessen, J.-P. Veder, M. Saunders, M. R. Rowles, M. Cheng, C. Liu, M. F. Chisholm, R. De Marco, H. M. Cheng, S. Z. Yang, S. P. Jiang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706287.
- 83S. Jin, Y. Ni, Z. Hao, K. Zhang, Y. Lu, Z. Yan, Y. Wei, Y. R. Lu, T. S. Chan, J. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21885–21889; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 22069–22073.
- 84C. Zhang, S. Yang, J. Wu, M. Liu, S. Yazdi, M. Ren, J. Sha, J. Zhong, K. Nie, A. S. Jalilov, Z. Li, H. Li, B. I. Yakobson, Q. Wu, E. Ringe, H. Xu, P. M. Ajayan, J. M. Tour, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703487.
- 85Y. Pan, R. Lin, Y. Chen, S. Liu, W. Zhu, X. Cao, W. Chen, K. Wu, W. C. Cheong, Y. Wang, L. Zheng, J. Luo, Y. Lin, Y. Liu, C. Liu, J. Li, Q. Lu, X. Chen, D. Wang, Q. Peng, C. Chen, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4218–4221.
- 86F. Yang, P. Song, X. Liu, B. Mei, W. Xing, Z. Jiang, L. Gu, W. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12303–12307; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12483–12487.
- 87X. Zu, X. Li, W. Liu, Y. Sun, J. Xu, T. Yao, W. Yan, S. Gao, C. Wang, S. Wei, Y. Xie, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808135.
- 88B. Zhang, J. Zhang, F. Zhang, L. Zheng, G. Mo, B. Han, G. Yang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906194.
- 89W. Ju, A. Bagger, G. P. Hao, A. S. Varela, I. Sinev, V. Bon, B. Roldan Cuenya, S. Kaskel, J. Rossmeisl, P. Strasser, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 944.
- 90J. Jiao, R. Lin, S. Liu, W. C. Cheong, C. Zhang, Z. Chen, Y. Pan, J. Tang, K. Wu, S. F. Hung, H. M. Chen, L. Zheng, Q. Lu, X. Yang, B. Xu, H. Xiao, J. Li, D. Wang, Q. Peng, C. Chen, Y. Li, Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 222–228.
- 91W. Ren, X. Tan, W. Yang, C. Jia, S. Xu, K. Wang, S. C. Smith, C. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6972–6976; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7046–7050.
- 92X. Duan, J. Xu, Z. Wei, J. Ma, S. Guo, S. Wang, H. Liu, S. Dou, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701784.
- 93T. Liu, S. Ali, Z. Lian, B. Li, D. S. Su, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21596–21603.
- 94J. Wu, R. M. Yadav, M. Liu, P. P. Sharma, C. S. Tiwary, L. Ma, X. Zou, X. D. Zhou, B. I. Yakobson, J. Lou, P. M. Ajayan, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5364–5371.
- 95P. P. Sharma, J. Wu, R. M. Yadav, M. Liu, C. J. Wright, C. S. Tiwary, B. I. Yakobson, J. Lou, P. M. Ajayan, X. D. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13701–13705; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 13905–13909.
- 96S. Liu, H. Yang, X. Huang, L. Liu, W. Cai, J. Gao, X. Li, T. Zhang, Y. Huang, B. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800499.
- 97J. Wu, M. Liu, P. P. Sharma, R. M. Yadav, L. Ma, Y. Yang, X. Zou, X.-D. Zhou, R. Vajtai, B. I. Yakobson, J. Lou, P. M. Ajayan, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 466–470.
- 98X. Cui, Z. Pan, L. Zhang, H. Peng, G. Zheng, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701456.
- 99G. L. Chai, Z. X. Guo, Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1268–1275.
- 100J. Xu, Y. Kan, R. Huang, B. Zhang, B. Wang, K. H. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Sun, Q. Li, G. Centi, D. Su, ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1085–1089.
- 101B. Qin, Y. Li, H. Wang, G. Yang, Y. Cao, H. Yu, Q. Zhang, H. Liang, F. Peng, Nano Energy 2019, 60, 43–51.
- 102J. Xie, X. Zhao, M. Wu, Q. Li, Y. Wang, J. Yao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9640–9644; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9788–9792.
- 103M. Francisco-Marquez, A. Galano, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 24476–24481.
- 104F. Pan, B. Li, X. Xiang, G. Wang, Y. Li, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2124–2133.
- 105W. Wang, L. Shang, G. Chang, C. Yan, R. Shi, Y. Zhao, G. I. N. Waterhouse, D. Yang, T. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808276.
- 106Y. Lum, Y. Kwon, P. Lobaccaro, L. Chen, E. L. Clark, A. T. Bell, J. W. Ager, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 202–209.
- 107L. Sun, V. Reddu, A. C. Fisher, X. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 374–403.
- 108J. C. Fontecilla-Camps, P. Amara, C. Cavazza, Y. Nicolet, A. Volbeda, Nature 2009, 460, 814–822.
- 109J. H. Jeoung, H. Dobbek, Science 2007, 318, 1461–1464.
- 110K. Torbensen, D. Joulié, S. Ren, M. Wang, D. Salvatore, C. P. Berlinguette, M. Robert, ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 1512–1518.
- 111M. Zhu, J. Chen, L. Huang, R. Ye, J. Xu, Y. F. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6595–6599; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 6667–6671.
- 112X. Zhang, Z. Wu, X. Zhang, L. Li, Y. Li, H. Xu, X. Li, X. Yu, Z. Zhang, Y. Liang, H. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14675.
- 113Y. Guo, Y. Wang, Y. Shen, Z. Cai, Z. Li, J. Liu, J. Chen, C. Xiao, H. Liu, W. Lin, C. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21493–21501.
- 114C. Costentin, S. Drouet, M. Robert, J. M. Savéant, Science 2012, 338, 90–94.
- 115J. A. Buss, D. G. VanderVelde, T. Agapie, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10121–10125.
- 116X. Ren, S. Liu, H. Li, J. Ding, L. Liu, Z. Kuang, L. Li, H. Yang, F. Bai, Y. Huang, T. Zhang, B. Liu, Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1727–1733.
- 117M. N. Jackson, S. Oh, C. J. Kaminsky, S. B. Chu, G. Zhang, J. T. Miller, Y. Surendranath, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1004–1010.
- 118C. S. Diercks, Y. Liu, K. E. Cordova, O. M. Yaghi, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 301–307.
- 119D. H. Nam, O. Shekhah, G. Lee, A. Mallick, H. Jiang, F. Li, B. Chen, J. Wicks, M. Eddaoudi, E. H. Sargent, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21513–21521.
- 120Q. Wu, M. J. Mao, Q. J. Wu, J. Liang, Y. B. Huang, R. Cao, Small 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202004933.
- 121I. Hod, O. K. Farha, J. T. Hupp, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1192–1193.
- 122R. R. Knowles, E. N. Jacobsen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20678–20685.
- 123H. Coskun, A. Aljabour, P. De Luna, D. Farka, T. Greunz, D. Stifter, M. Kus, X. Zheng, M. Liu, A. W. Hassel, W. Schöfberger, E. H. Sargent, N. S. Sariciftci, P. Stadler, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700686.
- 124
- 124aM. König, J. Vaes, E. Klemm, D. Pant, iScience 2019, 19, 135–160;
- 124bD. V. Vasilyev, P. J. Dyson, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 1392–1405.
- 125H. Zhong, K. Fujii, Y. Nakano, F. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 55–61.
- 126R. Kortlever, K. H. Tan, Y. Kwon, M. T. M. Koper, J. Solid State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 1843–1849.
- 127M. Dunwell, Q. Lu, J. M. Heyes, J. Rosen, J. G. Chen, Y. Yan, F. Jiao, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3774–3783.
- 128A. Wuttig, Y. Yoon, J. Ryu, Y. Surendranath, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17109–17113.
- 129D. Gao, J. Wang, H. Wu, X. Jiang, S. Miao, G. Wang, X. Bao, Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 55, 1–5.
- 130P. Bumroongsakulsawat, G. H. Kelsall, Electrochim. Acta 2014, 141, 216–225.
- 131A. S. Varela, M. Kroschel, T. Reier, P. Strasser, Catal. Today 2016, 260, 8–13.
- 132F. Zhang, A. C. Co, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1674–1681; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 1691–1698.
- 133A. Frumkin, Z. Phys. Chem. 1933, 164A, 121.
10.1515/zpch-1933-16411 Google Scholar
- 134A. Murata, Y. Hori, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 64, 123–127.
- 135O. Ayemoba, A. Cuesta, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27377–27382.
- 136M. R. Singh, Y. Kwon, Y. Lum, J. W. Ager, A. T. Bell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13006–13012.
- 137M. R. Thorson, K. I. Siil, P. J. A. Kenis, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F69–F74.
- 138S. Sato, K. Saita, K. Sekizawa, S. Maeda, T. Morikawa, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4452–4458.
- 139A. S. Varela, W. Ju, T. Reier, P. Strasser, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2136–2144.
- 140D. L. T. Nguyen, M. S. Jee, D. H. Won, H. S. Oh, B. K. Min, Y. J. Hwang, Catal. Commun. 2018, 114, 109–113.
- 141Y. Hori, A. Murata, R. Takahashi, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1989, 85, 2309–2326.
- 142J. Resasco, Y. Lum, E. Clark, J. Z. Zeledon, A. T. Bell, ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 1064–1072.
- 143R. J. Gilliam, J. W. Graydon, D. W. Kirk, S. J. Thorpe, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 359–364.
- 144D. Gao, R. M. Arán-Ais, H. S. Jeon, B. Roldan Cuenya, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 198–210.
- 145U. Kaiser, E. Heitz, Ber. Bunsen-Ges. 1973, 77, 818–823.
- 146Y. Oh, H. Vrubel, S. Guidoux, X. Hu, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3878–3881.
- 147Y. Tomita, S. Teruya, O. Koga, Y. Hori, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 4164.
- 148T. C. Berto, L. Zhang, R. J. Hamers, J. F. Berry, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 703–707.
- 149E. Lamy, L. Nadjo, J. M. Saveant, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfaces Electrochem. 1977, 78, 403–407.
- 150B. M. Setterfield-Price, R. A. W. Dryfe, J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 730, 48–58.
- 151J. Shi, F. X. Shen, F. Shi, N. Song, Y. J. Jia, Y. Q. Hu, Q. Y. Li, J. X. Liu, T. Y. Chen, Y. N. Dai, Electrochim. Acta 2017, 240, 114–121.
- 152A. V. Rudnev, U. E. Zhumaev, A. Kuzume, S. Vesztergom, J. Furrer, P. Broekmann, T. Wandlowski, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 38–44.
- 153S. Kaneco, K. Iiba, S. K. Suzuki, K. Ohta, T. Mizuno, J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 7456–7460.
- 154T. Saeki, K. Hashimoto, N. Kimura, K. Omata, A. Fujishima, J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 404, 299–302.
- 155T. Saeki, K. Hashimoto, N. Kimura, K. Omata, A. Fujishima, J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 390, 77–82.
- 156M. C. Corvo, J. Sardinha, S. C. Menezes, S. Einloft, M. Seferin, J. Dupont, T. Casimiro, E. J. Cabrita, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13024–13027; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 13262–13265.
- 157N. M. Simon, M. Zanatta, F. P. dos Santos, M. C. Corvo, E. J. Cabrita, J. Dupont, ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4927–4933.
- 158X. Tan, X. Sun, B. Han, Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab022.
- 159L. Sun, G. K. Ramesha, P. V. Kamat, J. F. Brennecke, Langmuir 2014, 30, 6302–6308.
- 160A. Khadhraoui, P. Gotico, B. Boitrel, W. Leibl, Z. Halime, A. Aukauloo, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11630–11633.
- 161J. Medina-Ramos, J. L. DiMeglio, J. Rosenthal, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8361–8367.
- 162M. Ramdin, T. W. de Loos, T. J. H. Vlugt, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8149–8177.
- 163T. Y. Chen, J. Shi, F. X. Shen, J. Z. Zhen, Y. F. Li, F. Shi, B. Yang, Y. J. Jia, Y. N. Dai, Y. Q. Hu, ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2295–2300.
- 164F. Zhou, S. Liu, B. Yang, P. Wang, A. S. Alshammari, Y. Deng, Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 46, 103–106.
- 165S. F. Zhao, M. Horne, A. M. Bond, J. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 23989–24001.
- 166E. E. L. Tanner, C. Batchelor-McAuley, R. G. Compton, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 26442–26447.
- 167K. Paduszyński, U. Domańska, J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1311–1324.
- 168I. Reche, I. Gallardo, G. Guirado, RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 65176–65183.
- 169B. A. Rosen, W. Zhu, G. Kaul, A. Salehi-Khojin, R. I. Masel, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, H138–H141.
- 170M. Petkovic, K. R. Seddon, L. P. N. Rebelo, C. Silva Pereira, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403.
- 171T. Burdyny, W. A. Smith, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1442–1453.
- 172S. Malkhandi, B. S. Yeo, Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 26, 112–121.
- 173B. Kim, F. Hillman, M. Ariyoshi, S. Fujikawa, P. J. A. Kenis, J. Power Sources 2016, 312, 192–198.
- 174N. P. Brandon, D. J. Brett, Philos. Trans. Ser. A 2006, 364, 147–159.
- 175C. Delacourt, P. L. Ridgway, J. B. Kerr, J. Newman, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B42.
- 176S. Verma, Y. Hamasaki, C. Kim, W. Huang, S. Lu, H. R. M. Jhong, A. A. Gewirth, T. Fujigaya, N. Nakashima, P. J. A. Kenis, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 193–198.
- 177S. Ren, D. Joulié, D. Salvatore, K. Torbensen, M. Wang, M. Robert, C. P. Berlinguette, Science 2019, 365, 367–369.
- 178P. Jeanty, C. Scherer, E. Magori, K. Wiesner-Fleischer, O. Hinrichsen, M. Fleischer, J. CO2 Util. 2018, 24, 454–462.
- 179D. Higgins, C. Hahn, C. Xiang, T. F. Jaramillo, A. Z. Weber, ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 317–324.
- 180D. A. Salvatore, C. M. Gabardo, A. Reyes, C. P. O'Brien, S. Holdcroft, P. Pintauro, B. Bahar, M. Hickner, C. Bae, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, C. P. Berlinguette, Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 339–348.
- 181G. Wang, J. Pan, S. P. Jiang, H. Yang, J. CO2 Util. 2018, 23, 152–158.
- 182K. Jiang, S. Siahrostami, T. Zheng, Y. Hu, S. Hwang, E. Stavitski, Y. Peng, J. Dynes, M. Gangisetty, D. Su, K. Attenkofer, H. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 893–903.
- 183R. S. Reiter, W. White, S. Ardo, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, H3132–H3134.
- 184D. A. Salvatore, D. M. Weekes, J. He, K. E. Dettelbach, Y. C. Li, T. E. Mallouk, C. P. Berlinguette, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 149–154.
- 185P. Millet, N. Mbemba, S. A. Grigoriev, V. N. Fateev, A. Aukauloo, C. Etiévant, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 4134–4142.
- 186Z. Yin, H. Peng, X. Wei, H. Zhou, J. Gong, M. Huai, L. Xiao, G. Wang, J. Lu, L. Zhuang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2455–2462.
- 187Y. Zou, S. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202003579.
- 188N. T. Suen, S. F. Hung, Q. Quan, N. Zhang, Y. J. Xu, H. M. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 337–365.
Citing Literature
September 13, 2021
Pages 20627-20648