Interfacial Design of Dendrite-Free Zinc Anodes for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
Qi Zhang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyi Luan
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yougen Tang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiaobo Ji
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haiyan Wang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorQi Zhang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJingyi Luan
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yougen Tang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiaobo Ji
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haiyan Wang
Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Power Sources, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
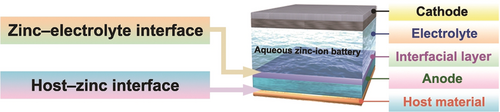
Electrons and ions: Aqueous zinc-ion batteries are promising candidates for the next-generation energy storage system. This Minireview summarizes the recent developments in the modification of the host–zinc and the zinc–electrolyte interfaces. Design strategies to fabricate dendrite-free zinc anodes by optimizing the interfacial electron and ion distribution are discussed.
Abstract
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries have rapidly developed recently as promising energy storage devices in large-scale energy storage systems owing to their low cost and high safety. Research on suppressing zinc dendrite growth has meanwhile attracted widespread attention to improve the lifespan and reversibility of batteries. Herein, design methods for dendrite-free zinc anodes and their internal mechanisms are reviewed from the perspective of optimizing the host–zinc interface and the zinc–electrolyte interface. Furthermore, a design strategy is proposed to homogenize zinc deposition by regulating the interfacial electric field and ion distribution during zinc nucleation and growth. This Minireview can offer potential directions for the rational design of dendrite-free zinc anodes employed in aqueous zinc-ion batteries.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1B. Obama, Science 2017, 355, 126–129.
- 2
- 2aT. M. Gür, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2696–2767;
- 2bX. Zeng, J. Hao, Z. Wang, J. Mao, Z. Guo, Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 410–437.
- 3
- 3aT. B. Schon, B. T. McAllister, P. F. Li, D. S. Seferos, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6345–6404;
- 3bZ. P. Cano, D. Banham, S. Ye, A. Hintennach, J. Lu, M. Fowler, Z. Chen, Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 279–289.
- 4H. Ao, Y. Zhao, J. Zhou, W. Cai, X. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Qian, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18708–18734.
- 5
- 5aC. Xie, Y. Liu, W. Lu, H. Zhang, X. Li, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1834–1839;
- 5bD. Chao, W. Zhou, C. Ye, Q. Zhang, Y. Chen, L. Gu, K. Davey, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7823–7828; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7905–7910.
- 6
- 6aS. D. Han, S. Kim, D. Li, V. Petkov, H. D. Yoo, P. J. Phillips, H. Wang, J. J. Kim, K. L. More, B. Key, R. F. Klie, J. Cabana, V. R. Stamenkovic, T. T. Fister, N. M. Markovic, A. K. Burrell, S. Tepavcevic, J. T. Vaughey, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4874–4884;
- 6bF. Wan, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16358–16367; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 16508–16517.
- 7G. Fang, J. Zhou, A. Pan, S. Liang, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2480–2501.
- 8R. Zhang, X. R. Chen, X. Chen, X. B. Cheng, X. Q. Zhang, C. Yan, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7764–7768; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 7872–7876.
- 9
- 9aK. Lu, H. Zhang, B. Song, W. Pan, H. Ma, J. Zhang, Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296, 755–761;
- 9bH. Glatz, E. Tervoort, D. Kundu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 3522–3530.
- 10
- 10aC. Shen, X. Li, N. Li, K. Xie, J. G. Wang, X. Liu, B. Wei, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25446–25453;
- 10bK. Zhao, C. Wang, Y. Yu, M. Yan, Q. Wei, P. He, Y. Dong, Z. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Mai, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800848.
- 11
- 11aW. Xu, K. Zhao, W. Huo, Y. Wang, G. Yao, X. Gu, H. Cheng, L. Mai, C. Hu, X. Wang, Nano Energy 2019, 62, 275–281;
- 11bA. Naveed, H. Yang, J. Yang, Y. Nuli, J. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2760–2764; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2786–2790;
- 11cK. E. Sun, T. K. Hoang, T. N. Doan, Y. Yu, X. Zhu, Y. Tian, P. Chen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9681–9687.
- 12H. Jia, Z. Wang, B. Tawiah, Y. Wang, C. Y. Chan, B. Fei, F. Pan, Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104523.
- 13G. Li, Z. Liu, Q. Huang, Y. Gao, M. Regula, D. Wang, L. Q. Chen, D. Wang, Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 1076–1083.
- 14R. Winand, J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 377–385.
- 15Z. Wang, J. Huang, Z. Guo, X. Dong, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Joule 2019, 3, 1289–1300.
- 16A. Pei, G. Zheng, F. Shi, Y. Li, Y. Cui, Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1132–1139.
- 17
- 17aQ. Zhang, J. Luan, Y. Tang, X. Ji, S. Wang, H. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18444–18448;
- 17bF. Sagane, K. I. Ikeda, K. Okita, H. Sano, H. Sakaebe, Y. Iriyama, J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 34–42.
- 18W. Dong, J. L. Shi, T. S. Wang, Y. X. Yin, C. R. Wang, Y. G. Guo, RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19157–19163.
- 19
- 19aQ. Yang, G. Liang, Y. Guo, Z. Liu, B. Yan, D. Wang, Z. Huang, X. Li, J. Fan, C. Zhi, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903778;
- 19bY. Yin, S. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Song, N. Chang, Y. Pan, H. Zhang, X. Li, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906803;
- 19cY. Zeng, X. Zhang, R. Qin, X. Liu, P. Fang, D. Zheng, Y. Tong, X. Lu, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903675.
- 20
- 20aR. Zhang, X. B. Cheng, C. Z. Zhao, H. J. Peng, J. L. Shi, J. Q. Huang, J. Wang, F. Wei, Q. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2155–2162;
- 20bL. L. Lu, J. Ge, J. N. Yang, S. M. Chen, H. B. Yao, F. Zhou, S. H. Yu, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4431–4437.
- 21Z. Zhao, J. Zhao, Z. Hu, J. Li, J. Li, Y. Zhang, C. Wang, G. Cui, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1938–1949.
- 22
- 22aX. Xie, S. Liang, J. Gao, S. Guo, J. Guo, C. Wang, G. Xu, X. Wu, G. Chen, J. Zhou, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 503–510;
- 22bC. Yan, H. R. Li, X. Chen, X. Q. Zhang, X. B. Cheng, R. Xu, J. Q. Huang, Q. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9422–9429.
- 23Q. Zhang, J. Luan, L. Fu, S. Wu, Y. Tang, X. Ji, H. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15841–15847; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 15988–15994.
- 24
- 24aY. Gu, H. Y. Xu, X. G. Zhang, W. W. Wang, J. W. He, S. Tang, J. W. Yan, D. Y. Wu, M. S. Zheng, Q. F. Dong, B. W. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3092–3096; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 3124–3128;
- 24bL. P. Wang, N. W. Li, T. S. Wang, Y. X. Yin, Y. G. Guo, C. R. Wang, Electrochim. Acta 2017, 244, 172–177.
- 25J. Luan, Q. Zhang, H. Yuan, D. Sun, Z. Peng, Y. Tang, X. Ji, H. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901433.
- 26C. P. Yang, Y. X. Yin, S. F. Zhang, N. W. Li, Y. G. Guo, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8058.
- 27C. Li, X. Shi, S. Liang, X. Ma, M. Han, X. Wu, J. Zhou, Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122248.
- 28Z. Kang, C. Wu, L. Dong, W. Liu, J. Mou, J. Zhang, Z. Chang, B. Jiang, G. Wang, F. Kang, C. Xu, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3364–3371.
- 29J. Zhao, H. Ren, Q. Liang, D. Yuan, S. Xi, C. Wu, W. Manalastas, J. Ma, W. Fang, Y. Zheng, C. F. Du, M. Srinivasan, Q. Yan, Nano Energy 2019, 62, 94–102.
- 30X. Chen, X. R. Chen, T. Z. Hou, B. Q. Li, X. B. Cheng, R. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau7728.
- 31Q. Zhang, J. Luan, D. Sun, Y. Tang, H. Wang, Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6551–6554.
- 32Y. Tian, Y. An, C. Wei, B. Xi, S. Xiong, J. Feng, Y. Qian, ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11676–11685.
- 33
- 33aL. Suo, D. Oh, Y. Lin, Z. Zhuo, O. Borodin, T. Gao, F. Wang, A. Kushima, Z. Wang, H. C. Kim, Y. Qi, W. Yang, F. Pan, J. Li, K. Xu, C. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18670–18680;
- 33bH. Qiu, X. Du, J. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Ju, Z. Chen, Z. Hu, D. Yan, X. Zhou, G. Cui, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5374.
- 34
- 34aM. Li, Q. He, Z. Li, Q. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Meng, X. Liu, S. Li, B. Wu, L. Chen, Z. Liu, W. Luo, C. Han, L. Mai, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901469;
- 34bA. Xia, X. Pu, Y. Tao, H. Liu, Y. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 852–859.
- 35R. Xu, X. B. Cheng, C. Yan, X. Q. Zhang, Y. Xiao, C. Z. Zhao, J. Q. Huang, Q. Zhang, Matter 2019, 1, 317–344.
- 36L. Fan, X. Li, Nano Energy 2018, 53, 630–642.
- 37L. Kang, M. Cui, F. Jiang, Y. Gao, H. Luo, J. Liu, W. Liang, C. Zhi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801090.
- 38
- 38aP. Liang, J. Yi, X. Liu, K. Wu, Z. Wang, J. Cui, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, J. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908528;
- 38bD. Wang, Z. Fan, D. Zhou, A. Khesro, S. Murakami, A. Feteira, Q. Zhao, X. Tan, I. M. Reaney, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4133–4144.
- 39M. Cui, Y. Xiao, L. Kang, W. Du, Y. Gao, X. Sun, Y. Zhou, X. Li, H. Li, F. Jiang, C. Zhi, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6490–6496.
- 40I. Jung, D. A. Dikin, R. D. Piner, R. S. Ruoff, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4283–4287.
- 41S. Wei, S. Choudhury, J. Xu, P. Nath, Z. Tu, L. A. Archer, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605512.
- 42M. Li, J. Meng, Q. Li, M. Huang, X. Liu, K. A. Owusu, Z. Liu, L. Mai, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802016.
- 43N. W. Li, Y. X. Yin, C. P. Yang, Y. G. Guo, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1853–1858.
- 44M. Bai, K. Xie, K. Yuan, K. Zhang, N. Li, C. Shen, Y. Lai, R. Vajtai, P. Ajayan, B. Wei, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801213.
- 45C. Li, S. Liu, C. Shi, G. Liang, Z. Lu, R. Fu, D. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1363.
- 46A. Mitha, A. Z. Yazdi, M. Ahmed, P. Chen, ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2409–2418.
- 47B. S. Lee, S. Cui, X. Xing, H. Liu, X. Yue, V. Petrova, H. D. Lim, R. Chen, P. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 38928–38935.
- 48N. Zhang, F. Cheng, Y. Liu, Q. Zhao, K. Lei, C. Chen, X. Liu, J. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12894–12901.
- 49F. Wan, L. Zhang, X. Dai, X. Wang, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1656.
- 50F. Wang, O. Borodin, T. Gao, X. Fan, W. Sun, F. Han, A. Faraone, J. A. Dura, K. Xu, C. Wang, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 543–549.
- 51C. Zhang, J. Holoubek, X. Wu, A. Daniyar, L. Zhu, C. Chen, D. P. Leonard, I. A. Rodriguez-Perez, J. X. Jiang, C. Fang, X. Ji, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 14097–14099.
- 52W. Li, K. Wang, M. Zhou, H. Zhan, S. Cheng, K. Jiang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22059–22066.
- 53G. M. Song, T. Vystavel, N. van der Pers, J. T. M. De Hosson, W. G. Sloof, Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2973–2981.
- 54L. Ma, S. Chen, N. Li, Z. Liu, Z. Tang, J. A. Zapien, S. Chen, J. Fan, C. Zhi, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908121.