Z-Scheme Photocatalytic Systems for Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Where Are We Now?
Wenhao Zhang
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Selangor Darul Ehsan, 43900 Malaysia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Abdul Rahman Mohamed
Low Carbon Economy (LCE) Research Group, School of Chemical Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, 14300 Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wee-Jun Ong
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Selangor Darul Ehsan, 43900 Malaysia
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenhao Zhang
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Selangor Darul Ehsan, 43900 Malaysia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Abdul Rahman Mohamed
Low Carbon Economy (LCE) Research Group, School of Chemical Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Nibong Tebal, 14300 Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wee-Jun Ong
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University Malaysia, Selangor Darul Ehsan, 43900 Malaysia
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
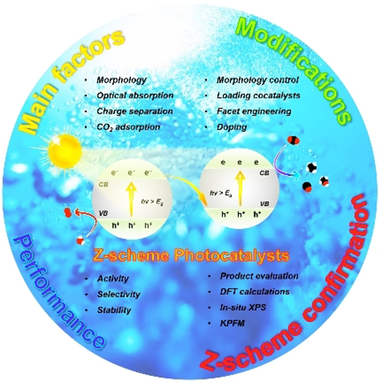
Mimicking natural photosynthesis: The latest progress on Z-scheme photocatalytic systems for CO2 reduction is comprehensively discussed in this Review. Particular attention is given to modification strategies that improve photocatalytic performance as well as confirmation methods to assess the Z-scheme charge transfer mechanism.
Abstract
Transforming CO2 into fuels by utilizing sunlight is promising to synchronously overcome global warming and energy-supply issues. It is crucial to design efficient photocatalysts with intriguing features such as robust light-harvesting ability, strong redox potential, high charge-separation, and excellent durability. Hitherto, a single-component photocatalyst is incapable to simultaneously meet all these criteria. Inspired by natural photosynthesis, constructing artificial Z-scheme photocatalysts provides a facile way to conquer these bottlenecks. In this review, we firstly introduce the fundamentals of photocatalytic CO2 reduction and Z-scheme systems. Thereafter we discuss state-of-the-art Z-scheme photocatalytic CO2 reduction, whereby special attention is placed on the predominant factors that affect photoactivity. Additionally, further modifications that are important for efficient photocatalysis are reviewed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201914925-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf497 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. Moreira, J. C. M. Pires, Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 371–379.
- 2F. Barzagli, C. Giorgi, F. Mani, M. Peruzzini, J. CO2 Util. 2017, 22, 346–354.
- 3C. W. W. Ng, R. Tasnim, J. L. Coo, Eng. Geol. 2018, 242, 108–120.
- 4T. P. Hughes, J. T. Kerry, M. Álvarez-Noriega, J. G. Álvarez-Romero, K. D. Anderson, A. H. Baird, R. C. Babcock, M. Beger, D. R. Bellwood, R. Berkelmans, T. C. Bridge, I. R. Butler, M. Byrne, N. E. Cantin, S. Comeau, S. R. Connolly, G. S. Cumming, S. J. Dalton, G. Diaz-Pulido, C. M. Eakin, W. F. Figueira, J. P. Gilmour, H. B. Harrison, S. F. Heron, A. S. Hoey, J.-P. A. Hobbs, M. O. Hoogenboom, E. V. Kennedy, C.-y. Kuo, J. M. Lough, R. J. Lowe, G. Liu, M. T. McCulloch, H. A. Malcolm, M. J. McWilliam, J. M. Pandolfi, R. J. Pears, M. S. Pratchett, V. Schoepf, T. Simpson, W. J. Skirving, B. Sommer, G. Torda, D. R. Wachenfeld, B. L. Willis, S. K. Wilson, Nature 2017, 543, 373.
- 5Y. Wang, D. He, H. Chen, D. Wang, J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2019, 40, 117–149.
- 6H. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Guo, X. Zhang, C. Ribeiro, T. He, Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 131–139.
- 7J. Xiao, W. Yang, S. Gao, C. Sun, Q. Li, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 2331–2336.
- 8W. Zhan, L. Sun, X. Han, Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 1.
- 9L. Liu, H. Zhao, J. M. Andino, Y. Li, ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1817–1828.
- 10J. Yu, J. Low, W. Xiao, P. Zhou, M. Jaroniec, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8839–8842.
- 11Z. Sun, N. Talreja, H. Tao, J. Texter, M. Muhler, J. Strunk, J. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7610–7627; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 7734–7752.
- 12J. Fu, B. Zhu, C. Jiang, B. Cheng, W. You, J. Yu, Small 2017, 13, 1603938.
- 13Z. Jiang, X. Liang, H. Zheng, Y. Liu, Z. Wang, P. Wang, X. Zhang, X. Qin, Y. Dai, M.-H. Whangbo, B. Huang, Appl. Catal. B 2017, 219, 209–215.
- 14F. Xu, J. Zhang, B. Zhu, J. Yu, J. Xu, Appl. Catal. B 2018, 230, 194–202.
- 15K. Qi, B. Cheng, J. Yu, W. Ho, Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1936–1955.
- 16D. Zeng, T. Zhou, W.-J. Ong, M. Wu, X. Duan, W. Xu, Y. Chen, Y.-A. Zhu, D.-L. Peng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5651–5660.
- 17D. Zeng, W.-J. Ong, H. Zheng, M. Wu, Y. Chen, D.-L. Peng, M.-Y. Han, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16171–16178.
- 18X. Dai, Y. Sun, Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16723–16732.
- 19D. Zeng, W. Xu, W.-J. Ong, J. Xu, H. Ren, Y. Chen, H. Zheng, D.-L. Peng, Appl. Catal. B 2018, 221, 47–55.
- 20X. Meng, S. Ouyang, T. Kako, P. Li, Q. Yu, T. Wang, J. Ye, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11517–11519.
- 21H. Zheng, Z. Jiang, H. Zhai, Z. Zheng, P. Wang, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, X. Qin, X. Zhang, B. Huang, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 243, 381–385.
- 22H. Nakanishi, K. Iizuka, T. Takayama, A. Iwase, A. Kudo, ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 112–118.
- 23S. Shoji, A. Yamaguchi, E. Sakai, M. Miyauchi, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20613–20619.
- 24B. Liu, L. Ye, R. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Zhang, R. Guan, L. Tian, X. Chen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4001–4009.
- 25P. Xia, M. Antonietti, B. Zhu, T. Heil, J. Yu, S. Cao, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900093.
- 26J. Di, C. Zhu, M. Ji, M. Duan, R. Long, C. Yan, K. Gu, J. Xiong, Y. She, J. Xia, H. Li, Z. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14847–14851; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15063–15067.
- 27C. Gao, Q. Meng, K. Zhao, H. Yin, D. Wang, J. Guo, S. Zhao, L. Chang, M. He, Q. Li, H. Zhao, X. Huang, Y. Gao, Z. Tang, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6485–6490.
- 28J. Liu, B. Liu, Y. Ren, Y. Yuan, H. Zhao, H. Yang, S. Liu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 14761–14775.
- 29F. Chen, H. Huang, L. Ye, T. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. Han, T. Ma, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804284.
- 30L. Ye, Y. Deng, L. Wang, H. Xie, F. Su, ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 3671–3701.
- 31J.-C. Wang, H.-C. Yao, Z.-Y. Fan, L. Zhang, J.-S. Wang, S.-Q. Zang, Z.-J. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3765–3775.
- 32F. Li, L. Zhang, J. Tong, Y. Liu, S. Xu, Y. Cao, S. Cao, Nano Energy 2016, 27, 320–329.
- 33J. Peng, X. Chen, W.-J. Ong, X. Zhao, N. Li, Chem 2019, 5, 18–50.
- 34J. Ke, M. Adnan Younis, Y. Kong, H. Zhou, J. Liu, L. Lei, Y. Hou, Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 69.
- 35W.-J. Ong, L.-L. Tan, S.-P. Chai, S.-T. Yong, A. R. Mohamed, Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1946–2008.
- 36W.-J. Ong, L.-L. Tan, S.-P. Chai, S.-T. Yong, A. R. Mohamed, ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 690–719.
- 37Y. Min, E. Im, G.-T. Hwang, J.-W. Kim, C.-W. Ahn, J.-J. Choi, B.-D. Hahn, J.-H. Choi, W.-H. Yoon, D.-S. Park, D. C. Hyun, G. D. Moon, Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1750–1769.
- 38Y. Tachibana, L. Vayssieres, J. R. Durrant, Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 511.
- 39P. Zhou, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec, Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4920–4935.
- 40D. Huang, S. Chen, G. Zeng, X. Gong, C. Zhou, M. Cheng, W. Xue, X. Yan, J. Li, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 385, 44–80.
- 41Y. Ren, D. Zeng, W.-J. Ong, Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 289–319.
- 42Y. Hong, Y. Jiang, C. Li, W. Fan, X. Yan, M. Yan, W. Shi, Appl. Catal. B 2016, 180, 663–673.
- 43F. Wu, X. Li, W. Liu, S. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 60–70.
- 44M. Jourshabani, Z. Shariatinia, A. Badiei, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1511–1525.
- 45Z. Li, J. Hou, B. Zhang, S. Cao, Y. Wu, Z. Gao, X. Nie, L. Sun, Nano Energy 2019, 59, 537–544.
- 46P. Wang, Y. Mao, L. Li, Z. Shen, X. Luo, K. Wu, P. An, H. Wang, L. Su, Y. Li, S. Zhan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11329–11334; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11451–11456.
- 47W. Yu, S. Zhang, J. Chen, P. Xia, M. H. Richter, L. Chen, W. Xu, J. Jin, S. Chen, T. Peng, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15668–15674.
- 48J. Qin, X. Hu, X. Li, Z. Yin, B. Liu, K.-h. Lam, Nano Energy 2019, 61, 27–35.
- 49X. Rong, H. Chen, J. Rong, X. Zhang, J. Wei, S. Liu, X. Zhou, J. Xu, F. Qiu, Z. Wu, Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 286–293.
- 50L. K.-S. Ng, E. J.-C. Tan, T. W. Goh, X. Zhao, Z. Chen, T. C. Sum, H. S. Soo, Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 192–202.
- 51X. Li, X. Song, C. Ma, Y. Cheng, D. Shen, S. Zhang, W. Liu, P. Huo, H. Wang, ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1298–1306.
- 52L. Zhu, H. Li, Q. Xu, D. Xiong, P. Xia, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 303–312.
- 53L. Zhang, Z.-J. Zhao, T. Wang, J. Gong, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5423–5443.
- 54J. H. Lee, S. Kattel, Z. Xie, B. M. Tackett, J. Wang, C.-J. Liu, J. G. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804762.
- 55J. Xie, X. Zhao, M. Wu, Q. Li, Y. Wang, J. Yao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9640–9644; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9788–9792.
- 56H. Yang, Y. Wu, Q. Lin, L. Fan, X. Chai, Q. Zhang, J. Liu, C. He, Z. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15476–15480; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15702–15706.
- 57S. N. Habisreutinger, L. Schmidt-Mende, J. K. Stolarczyk, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7372–7408; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 7516–7557.
- 58M. B. Ross, P. De Luna, Y. Li, C.-T. Dinh, D. Kim, P. Yang, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 648–658.
- 59S. Remiro-Buenamañana, H. García, ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 342–356.
- 60M. Ghoussoub, M. Xia, P. N. Duchesne, D. Segal, G. Ozin, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1122–1142.
- 61X. Chang, T. Wang, J. Gong, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2177–2196.
- 62S. Zhao, S. Li, T. Guo, S. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Wu, Y. Chen, Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 62.
- 63W.-J. Ong, L. K. Putri, Y.-C. Tan, L.-L. Tan, N. Li, Y. H. Ng, X. Wen, S.-P. Chai, Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1673–1696.
- 64X. Li, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec, X. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3962–4179.
- 65Y. Xia, Z. Tian, T. Heil, A. Meng, B. Cheng, S. Cao, J. Yu, M. Antonietti, Joule 2019, 3, 2792–2805.
- 66J. Ran, M. Jaroniec, S.-Z. Qiao, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704649.
- 67J. Wang, T. Xia, L. Wang, X. Zheng, Z. Qi, C. Gao, J. Zhu, Z. Li, H. Xu, Y. Xiong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16447–16451; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16685–16689.
- 68A. Li, Q. Cao, G. Zhou, B. V. K. J. Schmidt, W. Zhu, X. Yuan, H. Huo, J. Gong, M. Antonietti, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14549–14555; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 14691–14697.
- 69J. Tang, J. R. Durrant, D. R. Klug, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13885–13891.
- 70B. Zhu, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, S. Yang, Z. Tian, J. Yu, Catal. Today 2019, 335, 117–127.
- 71K. Li, B. Peng, T. Peng, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7485–7527.
- 72M. Li, L. Zhang, M. Wu, Y. Du, X. Fan, M. Wang, L. Zhang, Q. Kong, J. Shi, Nano Energy 2016, 19, 145–155.
- 73A. Meng, L. Zhang, B. Cheng, J. Yu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5581–5589.
- 74Y.-F. Xu, M.-Z. Yang, B.-X. Chen, X.-D. Wang, H.-Y. Chen, D.-B. Kuang, C.-Y. Su, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5660–5663.
- 75G. Zhang, L. Lin, G. Li, Y. Zhang, A. Savateev, S. Zafeiratos, X. Wang, M. Antonietti, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9372–9376; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9516–9520.
- 76B. C. Marepally, C. Ampelli, C. Genovese, T. Saboo, S. Perathoner, F. M. Wisser, L. Veyre, J. Canivet, E. A. Quadrelli, G. Centi, ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4442–4446.
- 77K. Kočí, L. Matějová, I. Troppová, M. Edelmannová, T. Prostějovský, P. Peikertová, T. Brunátová, J. Lang, L. Čapek, L. Obalová, Catal. Today 2017, 287, 52–58.
- 78L. Yuan, K.-Q. Lu, F. Zhang, X. Fu, Y.-J. Xu, Appl. Catal. B 2018, 237, 424–431.
- 79G. Yin, M. Nishikawa, Y. Nosaka, N. Srinivasan, D. Atarashi, E. Sakai, M. Miyauchi, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2111–2119.
- 80S. Shoji, G. Yin, M. Nishikawa, D. Atarashi, E. Sakai, M. Miyauchi, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 658, 309–314.
- 81Y. Lum, J. W. Ager, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 551–554; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 560–563.
- 82R. Shi, G. I. N. Waterhouse, T. Zhang, Sol. RRL 2017, 1, 1700126.
- 83Y. Wang, H. Suzuki, J. Xie, O. Tomita, D. J. Martin, M. Higashi, D. Kong, R. Abe, J. Tang, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5201–5241.
- 84T. M. Suzuki, S. Yoshino, T. Takayama, A. Iwase, A. Kudo, T. Morikawa, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10199–10202.
- 85Y. Bai, L. Ye, L. Wang, X. Shi, P. Wang, W. Bai, P. K. Wong, Appl. Catal. B 2016, 194, 98–104.
- 86Y. He, L. Zhang, B. Teng, M. Fan, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 649–656.
- 87L. Kuai, Y. Zhou, W. Tu, P. Li, H. Li, Q. Xu, L. Tang, X. Wang, M. Xiao, Z. Zou, RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88409–88413.
- 88P. Li, Y. Zhou, H. Li, Q. Xu, X. Meng, X. Wang, M. Xiao, Z. Zou, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 800–803.
- 89Y. Bai, T. Chen, P. Wang, L. Wang, L. Ye, X. Shi, W. Bai, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 406–414.
- 90H. Li, Y. Gao, Y. Zhou, F. Fan, Q. Han, Q. Xu, X. Wang, M. Xiao, C. Li, Z. Zou, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5547–5552.
- 91T. Takayama, K. Sato, T. Fujimura, Y. Kojima, A. Iwase, A. Kudo, Faraday Discuss. 2017, 198, 397–407.
- 92M. Wang, Q. Han, L. Li, L. Tang, H. Li, Y. Zhou, Z. Zou, Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 274002.
- 93W.-K. Jo, S. Kumar, S. Eslava, S. Tonda, Appl. Catal. B 2018, 239, 586–598.
- 94C. Kim, K. M. Cho, A. Al-Saggaf, I. Gereige, H.-T. Jung, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4170–4177.
- 95A. Bafaqeer, M. Tahir, A. Ali Khan, N. A. Saidina Amin, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8612–8624.
- 96J. Meng, Q. Chen, J. Lu, H. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 550–562.
- 97Y. Yang, J. Wu, T. Xiao, Z. Tang, J. Shen, H. Li, Y. Zhou, Z. Zou, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 255, 117771.
- 98J. Wu, Y. Feng, L. Bruce, C. Dai, X. Han, D. Li, J. Liu, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15289–15296.
- 99J. Wu, Y. Feng, D. Li, X. Han, J. Liu, Energy 2019, 178, 168–175.
- 100L. Zhou, H. Kamyab, A. Surendar, A. Maseleno, A. Z. Ibatova, S. Chelliapan, N. Karachi, Z. Parsaee, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 368, 30–40.
- 101X.-Y. Yu, L. Yu, X. W. Lou, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501333.
- 102J. Ran, G. Gao, F.-T. Li, T.-Y. Ma, A. Du, S.-Z. Qiao, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13907.
- 103T. Di, Q. Xu, W. Ho, H. Tang, Q. Xiang, J. Yu, ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1394–1411.
- 104M. F. Kuehnel, K. L. Orchard, K. E. Dalle, E. Reisner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7217–7223.
- 105A. Ryu, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 1000–1030.
- 106H. Tada, T. Mitsui, T. Kiyonaga, T. Akita, K. Tanaka, Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 782–786.
- 107H. Zhao, X. Ding, B. Zhang, Y. Li, C. Wang, Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 602–609.
- 108Z. Jiang, J. Pan, B. Wang, C. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 519–526.
- 109W.-K. Jo, N. C. S. Selvam, Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 913–924.
- 110A. Kumar, P. K. Prajapati, U. Pal, S. L. Jain, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8201–8211.
- 111X.-J. Wen, C.-G. Niu, L. Zhang, C. Liang, H. Guo, G.-M. Zeng, J. Catal. 2018, 358, 141–154.
- 112Y. Zou, J.-W. Shi, D. Ma, Z. Fan, C. Niu, L. Wang, ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3752–3761.
- 113X. Li, J. Yu, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, J. Xie, Small 2016, 12, 6640–6696.
- 114L. Ye, X. Jin, C. Liu, C. Ding, H. Xie, K. H. Chu, P. K. Wong, Appl. Catal. B 2016, 187, 281–290.
- 115K. Wada, C. S. K. Ranasinghe, R. Kuriki, A. Yamakata, O. Ishitani, K. Maeda, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23869–23877.
- 116S. Tonda, S. Kumar, M. Bhardwaj, P. Yadav, S. Ogale, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2667–2678.
- 117H. Li, W. Tu, Y. Zhou, Z. Zou, Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500389.
- 118J. Low, C. Jiang, B. Cheng, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, J. Yu, Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700080.
- 119Q. Xu, L. Zhang, J. Yu, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, M. Jaroniec, Mater. Today 2018, 21, 1042–1063.
- 120S. Bai, J. Jiang, Q. Zhang, Y. Xiong, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2893–2939.
- 121J. Liu, B. Cheng, J. Yu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 31175–31183.
- 122Z. Wang, C. Li, K. Domen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2109–2125.
- 123R. He, D. Xu, B. Cheng, J. Yu, W. Ho, Nanoscale Horiz. 2018, 3, 464–504.
- 124G. Yang, D. Chen, H. Ding, J. Feng, J. Z. Zhang, Y. Zhu, S. Hamid, D. W. Bahnemann, Appl. Catal. B 2017, 219, 611–618.
- 125P. Murugesan, S. Narayanan, M. Manickam, P. K. Murugesan, R. Subbiah, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 516–526.
- 126Z. Jiang, W. Wan, H. Li, S. Yuan, H. Zhao, P. K. Wong, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706108.
- 127R. Sun, Q. Shi, M. Zhang, L. Xie, J. Chen, X. Yang, M. Chen, W. Zhao, J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 619–626.
- 128M. E. Aguirre, R. Zhou, A. J. Eugene, M. I. Guzman, M. A. Grela, Appl. Catal. B 2017, 217, 485–493.
- 129A. Meng, B. Zhu, B. Zhong, L. Zhang, B. Cheng, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 518–527.
- 130Y. Xia, B. Cheng, J. Fan, J. Yu, G. Liu, Small 2019, 15, 1902459.
- 131J. Chen, C. Hu, Z. Deng, X. Gong, Y. Su, Q. Yang, J. Zhong, J. Li, R. Duan, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 716, 134–141.
- 132J. Low, B. Dai, T. Tong, C. Jiang, J. Yu, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802981.
- 133S. Wang, B. Zhu, M. Liu, L. Zhang, J. Yu, M. Zhou, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 243, 19–26.
- 134W. Yu, D. Xu, T. Peng, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19936–19947.
- 135W. Yu, J. Chen, T. Shang, L. Chen, L. Gu, T. Peng, Appl. Catal. B 2017, 219, 693–704.
- 136J. Zhang, P. Zhou, J. Liu, J. Yu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20382–20386.
- 137A. N. Rudenko, S. Brener, M. I. Katsnelson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 246401.
- 138A. Miyata, A. Mitioglu, P. Plochocka, O. Portugall, J. T.-W. Wang, S. D. Stranks, H. J. Snaith, R. J. Nicholas, Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 582.
- 139N. T. Thanh Truc, N. T. Hanh, M. V. Nguyen, N. T. P. Le Chi, N. Van Noi, D. T. Tran, M. N. Ha, D. Q. Trung, T.-D. Pham, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 968–974.
- 140N. Nie, L. Zhang, J. Fu, B. Cheng, J. Yu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 12–22.
- 141J. Jin, J. Yu, D. Guo, C. Cui, W. Ho, Small 2015, 11, 5262–5271.
- 142L. Wang, P. Jin, J. Huang, H. She, Q. Wang, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15660–15670.
- 143Y. Wang, Z. Zhang, L. Zhang, Z. Luo, J. Shen, H. Lin, J. Long, J. C. S. Wu, X. Fu, X. Wang, C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14595–14598.
- 144A. Nakada, R. Kuriki, K. Sekizawa, S. Nishioka, J. J. M. Vequizo, T. Uchiyama, N. Kawakami, D. Lu, A. Yamakata, Y. Uchimoto, O. Ishitani, K. Maeda, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9744–9754.
- 145H. Qin, R. T. Guo, X. Y. Liu, W. G. Pan, Z. Y. Wang, X. Shi, J. Y. Tang, C. Y. Huang, Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 15155–15163.
- 146R. Bhosale, S. Jain, C. P. Vinod, S. Kumar, S. Ogale, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6174–6183.
- 147Y. Huo, J. Zhang, K. Dai, Q. Li, J. Lv, G. Zhu, C. Liang, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 241, 528–538.
- 148N. T. Thanh Truc, L. Giang Bach, N. Thi Hanh, T. D. Pham, N. Thi Phuong Le Chi, D. T. Tran, M. V. Nguyen, V. N. Nguyen, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 1–8.
- 149J. Bian, J. Feng, Z. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, S. Ali, Y. Qu, L. Bai, J. Xie, D. Tang, X. Li, F. Bai, J. Tang, L. Jing, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10873–10878; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 10989–10994.
- 150W. Shi, X. Guo, C. Cui, K. Jiang, Z. Li, L. Qu, J.-C. Wang, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 243, 236–242.
- 151J. Yang, J. Hao, S. Xu, Q. Wang, J. Dai, A. Zhang, X. Pang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32025–32037.
- 152R.-G. Ciocarlan, N. Hoeven, E. Irtem, V. Van Acker, M. Mertens, E. M. Seftel, T. Breugelmans, P. Cool, J. CO2 Util. 2020, 36, 177–186.
- 153J. Tian, Z. Zhao, A. Kumar, R. I. Boughton, H. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6920–6937.
- 154T. Di, B. Zhu, B. Cheng, J. Yu, J. Xu, J. Catal. 2017, 352, 532–541.
- 155S. Liang, B. Han, X. Liu, W. Chen, M. Peng, G. Guan, H. Deng, Z. Lin, J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 754, 105–113.
- 156M. Thommes, K. Katsumi, A. V. Neimark, J. P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol, K. S. W. Sing, Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051.
- 157S. Cao, Y. Li, B. Zhu, M. Jaroniec, J. Yu, J. Catal. 2017, 349, 208–217.
- 158Y.-X. Pan, Y. You, S. Xin, Y. Li, G. Fu, Z. Cui, Y.-L. Men, F.-F. Cao, S.-H. Yu, J. B. Goodenough, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4123–4129.
- 159Q. Wang, T. Hisatomi, S. S. K. Ma, Y. Li, K. Domen, Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4144–4150.
- 160H. Xu, S. Ouyang, P. Li, T. Kako, J. Ye, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1348–1354.
- 161L. Ye, X. Jin, X. Ji, C. Liu, Y. Su, H. Xie, C. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 291, 39–46.
- 162S. Selcuk, A. Selloni, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1107.
- 163R. Li, F. Zhang, D. Wang, J. Yang, M. Li, J. Zhu, X. Zhou, H. Han, C. Li, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1432.
- 164J. Pan, G. Liu, G. Q. Lu, H.-M. Cheng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2133–2137; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 2181–2185.
- 165G.-Z. Yuan, C.-F. Hsia, Z.-W. Lin, C. Chiang, Y.-W. Chiang, M. H. Huang, Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12548–12556.
- 166M. Tahir, N. S. Amin, Appl. Catal. B 2015, 162, 98–109.
- 167X. Li, J. Xiong, Y. Xu, Z. Feng, J. Huang, Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 424–433.
- 168Y.-L. Wang, Y. Tian, Z.-L. Lang, W. Guan, L.-K. Yan, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21056–21063.
- 169Y. He, L. Zhang, M. Fan, X. Wang, M. L. Walbridge, Q. Nong, Y. Wu, L. Zhao, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 137, 175–184.
- 170S. Sato, T. Arai, T. Morikawa, K. Uemura, T. M. Suzuki, H. Tanaka, T. Kajino, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15240–15243.
- 171T. Arai, S. Sato, T. Kajino, T. Morikawa, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1274–1282.
- 172T. M. Suzuki, A. Iwase, H. Tanaka, S. Sato, A. Kudo, T. Morikawa, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13283–13290.
- 173K. Muraoka, H. Kumagai, M. Eguchi, O. Ishitani, K. Maeda, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7886–7889.
- 174K. Sekizawa, K. Maeda, K. Domen, K. Koike, O. Ishitani, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4596–4599.
- 175K. Muraoka, T. Uchiyama, D. Lu, Y. Uchimoto, O. Ishitani, K. Maeda, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 124–126.
- 176K. Muraoka, J. J. M. Vequizo, R. Kuriki, A. Yamakata, T. Uchiyama, L. Daling, Y. Uchimoto, O. Ishitani, K. Maeda, ChemPhotoChem 2019, 3, 1027–1033.
- 177J. Zhang, Y. Chen, X. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3092–3108.
- 178K. Maeda, K. Domen, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 627–648.
- 179J. Fu, K. Jiang, X. Qiu, J. Yu, M. Liu, Mater. Today 2020, 32, 222–243.
- 180X. Wang, C. Liow, A. Bisht, X. Liu, T. C. Sum, X. Chen, S. Li, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2207–2214.
- 181C. Liu, B. C. Colón, M. Ziesack, P. A. Silver, D. G. Nocera, Science 2016, 352, 1210–1213.
- 182Y. W. Lee, P. Boonmongkolras, E. J. Son, J. Kim, S. H. Lee, S. K. Kuk, J. W. Ko, B. Shin, C. B. Park, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4208.
- 183C. Han, Q. Quan, H. M. Chen, Y. Sun, Y.-J. Xu, Small 2017, 13, 1602947.
- 184S. K. Cushing, A. D. Bristow, N. Wu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 30013–30022.
- 185S. Zhang, Y. Zhao, R. Shi, G. I. N. Waterhouse, T. Zhang, EnergyChem 2019, 1, 100013.
10.1016/j.enchem.2019.100013 Google Scholar
- 186K. Sivula, R. van de Krol, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15010.
- 187Y. Shiraishi, T. Takii, T. Hagi, S. Mori, Y. Kofuji, Y. Kitagawa, S. Tanaka, S. Ichikawa, T. Hirai, Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 985–993.
- 188W.-J. Ong, L.-L. Tan, Y. H. Ng, S.-T. Yong, S.-P. Chai, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7159–7329.
- 189W.-J. Ong, Z. Lin, K. Domen, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1700451.
- 190W.-J. Ong, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5579–5580.