In Vivo Solid-Phase Microextraction for Sampling of Oxylipins in Brain of Awake, Moving Rats
Alexander Napylov
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nathaly Reyes-Garces
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Restek Corporation, Bellefonte, PA, 16823 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. German Gomez-Rios
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Restek Corporation, Bellefonte, PA, 16823 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mariola Olkowicz
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorSofia Lendor
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCian Monnin
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Barbara Bojko
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Department of Pharmacodynamics and Molecular Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Poland
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Clement Hamani
Neuroimaging Research Section, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, 250 College Street, Toronto, ON, M5T 1R8 Canada
Harquail Centre for Neuromodulation, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, 2075, Bayview Avenue, Toronto, ON, M4N 3M5 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Janusz Pawliszyn
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dajana Vuckovic
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorAlexander Napylov
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Nathaly Reyes-Garces
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Restek Corporation, Bellefonte, PA, 16823 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. German Gomez-Rios
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Restek Corporation, Bellefonte, PA, 16823 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mariola Olkowicz
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorSofia Lendor
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCian Monnin
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Barbara Bojko
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Current address: Department of Pharmacodynamics and Molecular Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Poland
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Clement Hamani
Neuroimaging Research Section, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, 250 College Street, Toronto, ON, M5T 1R8 Canada
Harquail Centre for Neuromodulation, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, 2075, Bayview Avenue, Toronto, ON, M4N 3M5 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Janusz Pawliszyn
Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dajana Vuckovic
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Concordia University, 7141 Sherbrooke Street West, Montreal, QC, H4B 1R6 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
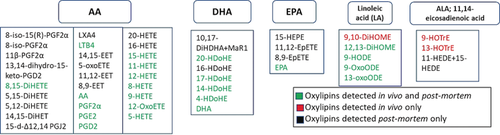
Biocompatible in vivo solid-phase microextraction was used to measure 52 eicosanoids and other oxylipins directly in brains of awake moving rats with high temporal and spatial resolution. In vivo profiles of extracellular brain fluid did not reflect oxylipin concentrations in post-mortem tissue and provide a novel tool to elucidate oxylipin pathways and function.
Abstract
Oxylipins are key lipid mediators of important brain processes, including pain, sleep, oxidative stress, and inflammation. For the first time, an in-depth profile of up to 52 oxylipins can be obtained from the brains of awake moving animals using in vivo solid-phase microextraction (SPME) chemical biopsy tool in combination with liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry. Among these, 23 oxylipins are detectable in the majority of healthy wildtype samples. This new approach successfully eliminates the changes in oxylipin concentrations routinely observed during the analysis of post-mortem samples, allows time-course monitoring of their concentrations with high spatial resolution in specific brain regions of interest, and can be performed using the same experimental set-up as in vivo microdialysis (MD) thus providing a new and exciting tool in neuroscience and drug discovery.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201909430-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1W. Smith, R. Murphy, In Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes: 6th ed. ), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016, pp. 259–296.
10.1016/B978-0-444-63438-2.00009-2 Google Scholar
- 2C. Wasternack, I. Feussner, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 363–386.
- 3M. W. Buczynski, D. S. Dumlao, E. A. Dennis, J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1015–1038.
- 4W. L. Smith, Biochem. J. 1989, 259, 315–324.
- 5J. W. Phillis, L. A. Horrocks, A. A. Farooqui, Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 52, 201–243.
- 6E. Ricciotti, G. A. FitzGerald, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000.
- 7C. M. Davis, X. Liu, N. J. Alkayed, Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 31–46.
- 8X. Liu, C. M. Davis, N. J. Alkayed, Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2017, https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7056.
- 9D. M. Aronoff, A. A. Romanovsky, Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 162, 15–25.
- 10O. Hayaishi, J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 863–868.
- 11C. Chen, N. G. Bazan, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediators 2005, 77, 65–76.
- 12S. Ito, E. Okuda-Ashitaka, T. Minami, Neurosci. Res. 2001, 41, 299–332.
- 13M. H. Shishehbor, R. Zhang, H. Medina, M.-L. Brennan, D. M. Brennan, S. G. Ellis, E. J. Topol, S. L. Hazen, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1678–1683.
- 14V. C. Tam, O. Quehenberger, C. M. Oshansky, R. Suen, A. M. Armando, P. M. Treuting, P. G. Thomas, E. A. Dennis, A. Aderem, Cell 2013, 154, 213–227.
- 15M. A. Sugimoto, L. P. Sousa, V. Pinho, M. Perretti, M. M. Teixeira, Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 160.
- 16M. Puppolo, D. Varma, S. A. Jansen, J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 964, 50–64.
- 17G. Astarita, A. C. Kendall, E. A. Dennis, A. Nicolaou, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 456–468.
- 18J. Folch, M. Lees, G. H. Sloane Stanley, J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509.
- 19E. G. Bligh, W. J. Dyer, Can. J. Biochem. Phys. 1959, 37, 911–917.
- 20R. D. Saunders, L. A. Horrocks, Anal. Biochem. 1984, 143, 71–75.
- 21M. Y. Golovko, E. J. Murphy, J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 893–902.
- 22M.-O. Trépanier, M. Eiden, D. Morin-Rivron, R. P. Bazinet, M. Masoodi, J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 766–775.
- 23M. Y. Golovko, E. J. Murphy, Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 432, 243–247.
- 24L. Sun, J. A. Stenken, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 1059–1071.
- 25H. Alfredson, K. Thorsen, R. Lorentzon, Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1999, 7, 378–381.
- 26M. Karamouzis, I. Karamouzis, E. Vamvakoudis, G. Ampatzidis, K. Christoulas, N. Angelopoulou, K. Mandroukas, Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent. Fatty Acids 2001, 64, 259–263.
- 27J. W. Łazarewicz, E. Salińska, A. Stafiej, A. Ziembowicz, E. Ziemińska, Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2000, 60, 427–435.
- 28O. Pepicelli, E. Fedele, M. Berardi, M. Raiteri, G. Levi, A. Greco, M. A. Ajmone-Cat, L. Minghetti, J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1561–1567.
- 29F. Kondo, M. Tachi, M. Gosho, M. Fukayama, K. Yoshikawa, S. Okada, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5261–5272.
- 30F. Clausen, N. Marklund, A. Lewén, P. Enblad, S. Basu, L. Hillered, J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 766–775.
- 31G. Ouyang, D. Vuckovic, J. Pawliszyn, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2784–2814.
- 32D. Vuckovic, S. Risticevic, J. Pawliszyn, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5618–5628; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 5734–5745.
- 33V. Bessonneau, Y. Zhan, I. A. M. De Lannoy, V. Saldivia, J. Pawliszyn, J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1424, 134–138.
- 34E. Cudjoe, B. Bojko, I. de Lannoy, V. Saldivia, J. Pawliszyn, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12124–12126; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12346–12348.
- 35N. Reyes-Garcés, M. Diwan, E. Boyacı, G. A. Gómez-Ríos, B. Bojko, J. N. Nobrega, F. R. Bambico, C. Hamani, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9875–9884.
- 36C. Monnin, P. Ramrup, C. Daigle-Young, D. Vuckovic, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 201–211.
- 37A. Napylov, MSc thesis, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, 2019.
- 38J. Chong, J. Xia, Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314.
- 39J. Chong, O. Soufan, C. Li, I. Caraus, S. Li, G. Bourque, D. S. Wishart, J. Xia, Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W 486–W494.
- 40Z.-X. Yuan, S. I. Rapoport, Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent. Fatty Acids 2015, 101, 9–14.
- 41M. Hennebelle, Z. Zhang, A. H. Metherel, A. P. Kitson, Y. Otoki, C. E. Richardson, J. Yang, K. S. S. Lee, B. D. Hammock, L. Zhang, et al., Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4342.
- 42A. Wong, D. R. Sagar, C. A. Ortori, D. A. Kendall, V. Chapman, D. A. Barrett, J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1902–1913.
- 43H. Yue, S. A. Jansen, K. I. Strauss, M. R. Borenstein, M. F. Barbe, L. J. Rossi, E. Murphy, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1122–1134.
- 44J. S. B. Shaik, T. M. Miller, S. H. Graham, M. D. Manole, S. M. Poloyac, J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 945–946, 207–216.
- 45E. A. Crago, B. P. Thampatty, P. R. Sherwood, C.-W. J. Kuo, C. Bender, J. Balzer, M. Horowitz, S. M. Poloyac, Stroke 2011, 42, 1872–1877.
- 46P. B. M. C. Derogis, F. P. Freitas, A. S. F. Marques, D. Cunha, P. P. Appolinário, F. de Paula, T. C. Lourenço, M. Murgu, P. Di Mascio, M. H. G. Medeiros, et al., PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77561.
- 47C. Jouvène, B. Fourmaux, A. Géloën, L. Balas, T. Durand, M. Lagarde, M. Létisse, M. Guichardant, Lipids 2018, 53, 103–116.
- 48S. A. Brose, A. G. Baker, M. Y. Golovko, Lipids 2013, 48, 411–419.
- 49A. Y. Taha, F. Gao, E. Ramadan, Y. Cheon, S. I. Rapoport, H.-W. Kim, BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 131.
- 50J. G. Devassy, S. Leng, M. Gabbs, M. Monirujjaman, H. M. Aukema, Adv. Nutr. Res. 2016, 7, 905–916.
- 51K. M. Nesbitt, A. Jaquins-Gerstl, E. M. Skoda, P. Wipf, A. C. Michael, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8173–8179.
- 52M. Huq, M. Tascon, E. Nazdrajic, A. Roszkowska, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7719–7728.
- 53D. Vuckovic, I. de Lannoy, B. Gien, Y. Yang, F. M. Musteata, R. Shirey, L. Sidisky, J. Pawliszyn, J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3367–3375.