Spectroscopic Measurement of a Halogen Bond Energy
Dedicated to the 100th anniversary of Nankai University
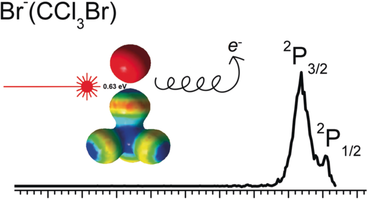
Graphical Abstract
Strong noncovalent interaction: While halogen bonding has been widely recognized in many fields of chemistry, a benchmark spectroscopic measurement of its strength is still absent. Here, the strength of a poster child halogen bond between Br− and CCl3Br using anion photoelectron spectroscopy is reported.
Abstract
Halogen bonding (XB) has emerged as an important bonding motif in supramolecules and biological systems. Although regarded as a strong noncovalent interaction, benchmark measurements of the halogen bond energy are scarce. Here, a combined anion photoelectron spectroscopy and density functional theory (DFT) study of XB in solvated Br− anions is reported. The XB strength between the positively-charged σ-hole on the Br atom of the bromotrichloromethane (CCl3Br) molecule and the Br− anion was found to be 0.63 eV (14.5 kcal mol−1). In the neutral complexes, Br(CCl3Br)1,2, the attraction between the free Br atom and the negatively charged equatorial belt on the Br atom of CCl3Br, which is a second type of halogen bonding, was estimated to have interaction strengths of 0.15 eV (3.5 kcal mol−1) and 0.12 eV (2.8 kcal mol−1).