Assemblies of Peptides in a Complex Environment and their Applications
Dr. Huaimin Wang
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZhaoqianqi Feng
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing Xu
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Huaimin Wang
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZhaoqianqi Feng
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing Xu
Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, 415 South St, Waltham, MA, 02454 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
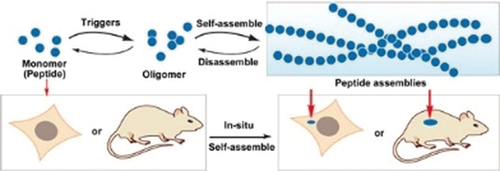
The rational design of peptide assemblies to achieve complex functions in a cellular environment has attracted increasing attention in recent years. In this Minireview, selected examples of peptide assemblies are highlighted, with a focus on instructed assembly for the spatiotemporal control of peptide assemblies in cells.
Abstract
Using peptide assemblies with emergent properties to achieve elaborate functions has attracted increasing attention in recent years. Besides tailoring the self-assembly of peptides in vitro, peptide research is advancing into a new and exciting frontier: the rational design of peptide assemblies (or their derivatives) for biological functions in a complex environment. This Minireview highlights recent developments in peptide assemblies and their applications in biological systems. After introducing the unique merits of peptide assemblies, we discuss the recent progress in designing peptides (or peptide derivatives) for self-assembly with conformational control. Then, we describe biological functions of peptide assemblies, with an emphasis on approach-instructed assembly for spatiotemporal control of peptide assemblies, in the cellular context. Finally, we discuss the future promises and challenges of this exciting area of chemistry.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1K. Siddle, J. Hutton, Peptide Hormones Secretion/Peptide Hormones Action, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991.
- 2
- 2aM. Ludwig, G. Leng, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 126;
- 2bM. Aspé-Sánchez, M. Moreno, M. I. Rivera, A. Rossi, J. Ewer, Front. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 510.
- 3J. L. Lau, M. K. Dunn, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707.
- 4
- 4aJ. L. Jiménez, J. I. Guijarro, E. Orlova, J. Zurdo, C. M. Dobson, M. Sunde, H. R. Saibil, EMBO J. 1999, 18, 815–821;
- 4bD. W. Choo, J. P. Schneider, N. R. Graciani, J. W. Kelly, Macromolecules 1996, 29, 355–366;
- 4cJ. P. Schneider, D. J. Pochan, B. Ozbas, K. Rajagopal, L. Pakstis, J. Kretsinger, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 15030–15037;
- 4dN. L. Ogihara, M. S. Weiss, D. Eisenberg, W. F. Degrado, Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 80–88;
- 4eT. Kunitake, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1992, 31, 709–726; Angew. Chem. 1992, 104, 692–710;
- 4fS. Zhang, T. Holmes, C. Lockshin, A. Rich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3334–3338;
- 4gM. R. Ghadiri, C. Soares, C. Choi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 825–831;
- 4hD. M. Gregory, T. L. Benzinger, T. S. Burkoth, H. Miller-Auer, D. G. Lynn, S. C. Meredith, R. E. Botto, Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 1998, 13, 149–166;
- 4iY. Qu, S. C. Payne, R. P. Apkarian, V. P. Conticello, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5014–5015;
- 4jM. J. Pandya, G. M. Spooner, M. Sunde, J. R. Thorpe, A. Rodger, D. N. Woolfson, Biochemistry 2000, 39, 8728–8734;
- 4kB. Xing, C.-W. Yu, K.-H. Chow, P.-L. Ho, D. Fu, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14846–14847;
- 4lJ. D. Hartgerink, E. Beniash, S. I. Stupp, Science 2001, 294, 1684–1688;
- 4mY.-C. Yu, P. Berndt, M. Tirrell, G. B. Fields, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 12515–12520.
- 5
- 5aS. Zhang, T. C. Holmes, C. M. DiPersio, R. O. Hynes, X. Su, A. Rich, Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1385–1393;
- 5bD. J. Pochan, J. P. Schneider, J. Kretsinger, B. Ozbas, K. Rajagopal, L. Haines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11802–11803;
- 5cJ. H. Collier, B. H. Hu, J. W. Ruberti, J. Zhang, P. Shum, D. H. Thompson, P. B. Messersmith, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9463–9464;
- 5dY. Zhang, H. Gu, Z. Yang, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13680–13681.
- 6G. A. Silva, C. Czeisler, K. L. Niece, E. Beniash, D. A. Harrington, J. A. Kessler, S. I. Stupp, Science 2004, 303, 1352–1355.
- 7T. C. Holmes, S. de Lacalle, X. Su, G. Liu, A. Rich, S. Zhang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6728–6733.
- 8
- 8aJ. Boekhoven, S. I. Stupp, Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1642–1659;
- 8bM. P. Hendricks, K. Sato, L. C. Palmer, S. I. Stupp, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2440–2448;
- 8cR. V. Ulijn, A. M. Smith, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 664–675;
- 8dM. C. Branco, D. M. Sigano, J. P. Schneider, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 427–434;
- 8eE. Gazit, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1263–1269;
- 8fL. Adler-Abramovich, E. Gazit, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6881–6893;
- 8gR. Langer, D. A. Tirrell, Nature 2004, 428, 487;
- 8hH. Shigemitsu, I. Hamachi, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 740–750;
- 8iA. G. Cheetham, R. W. Chakroun, W. Ma, H. Cui, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6638–6663;
- 8jH. Cui, M. J. Webber, S. I. Stupp, Biopolymers 2010, 94, 1–18.
- 9H. Wang, J. Shi, Z. Feng, R. Zhou, S. Wang, A. A. Rodal, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16297–16301; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 16515–16519.
- 10Z. Yang, H. Gu, D. Fu, P. Gao, J. K. Lam, B. Xu, Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1440–1444.
- 11S. Toledano, R. J. Williams, V. Jayawarna, R. V. Ulijn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1070–1071.
- 12
- 12aZ. Yang, G. Liang, B. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 315–326;
- 12bJ. Zhou, B. Xu, Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 987–999.
- 13X. Du, J. Zhou, J. Shi, B. Xu, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307.
- 14
- 14aZ. Yang, K. Xu, Z. Guo, Z. Guo, B. Xu, Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3152–3156;
- 14bZ. Yang, G. Liang, Z. Guo, Z. Guo, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8216–8219; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 8364–8367.
- 15
- 15aR. A. Pires, Y. M. Abul-Haija, D. S. Costa, R. Novoa-Carballal, R. L. Reis, R. V. Ulijn, I. Pashkuleva, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 576–579;
- 15bA. Tanaka, Y. Fukuoka, Y. Morimoto, T. Honjo, D. Koda, M. Goto, T. Maruyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 770–775;
- 15cJ. Zhan, Y. Cai, S. He, L. Wang, Z. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1813–1816; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 1831–1834;
- 15dG. B. Qi, Y. J. Gao, L. Wang, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703444;
- 15eJ. Wu, Z. Zheng, Y. Chong, X. Li, L. Pu, Q. Tang, L. Yang, X. Wang, F. Wang, G. Liang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1805018;
- 15fZ. Feng, T. Zhang, H. Wang, B. Xu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6470–6479;
- 15gD. Ye, G. Liang, M. L. Ma, J. Rao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2275–2279; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 2323–2327;
- 15hG. Liang, H. Ren, J. Rao, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 54–60.
- 16H. Wang, Z. Feng, A. Lu, Y. Jiang, H. Wu, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7579–7583; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 7687–7691.
- 17Y. Zhang, Y. Kuang, Y. Gao, B. Xu, Langmuir 2011, 27, 529–537.
- 18A. Lu, V. G. Magupalli, J. Ruan, Q. Yin, M. K. Atianand, M. R. Vos, G. F. Schröder, K. A. Fitzgerald, H. Wu, E. H. Egelman, Cell 2014, 156, 1193–1206.
- 19S. Burley, G. A. Petsko, Science 1985, 229, 23–28.
- 20J. Li, X. Du, S. Hashim, A. Shy, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 71–74.
- 21M. A. Schumacher, N. Chinnam, T. Ohashi, R. S. Shah, H. P. Erickson, J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33738–33744.
- 22D. Yuan, X. Du, J. Shi, N. Zhou, J. Zhou, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5705–5708; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 5797–5800.
- 23E. G. Krebs, E. H. Fischer, Vitam. Horm. 1964, 22, 399–410.
- 24J. Li, Z. Zhan, X. Du, J. Wang, B. Hong, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11716–11721; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11890–11895.
- 25
- 25aJ. Shi, G. Fichman, J. P. Schneider, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11188–11192; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11358–11362;
- 25bC. Liang, D. Zheng, F. Shi, T. Xu, C. Yang, J. Liu, L. Wang, Z. Yang, Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11987–11993.
- 26M. Kato, S. L. McKnight, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 351.
- 27T. Aida, E. Meijer, S. Stupp, Science 2012, 335, 813–817.
- 28H. He, B. Xu, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 900–906.
- 29Y. Kuang, J. Shi, J. Li, D. Yuan, K. A. Alberti, Q. Xu, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8104–8107; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 8242–8245.
- 30R. Zhou, Y. Kuang, J. Zhou, X. Du, J. Li, J. Shi, R. Haburcak, B. Xu, PloS One 2016, 11, e 0154126.
- 31X. Du, J. Zhou, H. Wang, J. Shi, Y. Kuang, W. Zeng, Z. Yang, B. Xu, Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e 2614.
- 32Y. Kuang, K. Miki, C. J. Parr, K. Hayashi, I. Takei, J. Li, M. Iwasaki, M. Nakagawa, Y. Yoshida, H. Saito, Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 685–694.
- 33J. Zhou, X. Du, J. Li, N. Yamagata, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10040–10043.
- 34J. Li, Y. Kuang, J. Shi, J. Zhou, J. E. Medina, R. Zhou, D. Yuan, C. Yang, H. Wang, Z. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13307–13311; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 13505–13509.
- 35H. Wang, Z. Feng, Y. Qin, J. Wang, B. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4931–4935; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5025–5029.
- 36
- 36aS. Vyas, E. Zaganjor, M. C. Haigis, Cell 2016, 166, 555–566;
- 36bD. R. Green, L. Galluzzi, G. Kroemer, Science 2011, 333, 1109–1112.
- 37H. Wang, Z. Feng, Y. Wang, R. Zhou, Z. Yang, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16046–16055.
- 38H. He, J. Wang, H. Wang, N. Zhou, D. Yang, D. R. Green, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1215–1218.
- 39T. P. Hopp, K. S. Prickett, V. L. Price, R. T. Libby, C. J. March, D. P. Cerretti, D. L. Urdal, P. J. Conlon, Nat. Biotechnol. 1988, 6, 1204–1210.
- 40J. R. Cubillos-Ruiz, S. E. Bettigole, L. H. Glimcher, Cell 2017, 168, 692–706.
- 41Z. Feng, H. Wang, S. Wang, Q. Zhang, X. Zhang, A. A. Rodal, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9566–9573.
- 42F. Foufelle, B. Fromenty, Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2016, 4, e 00211.
- 43Z. Feng, H. Wang, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16433–16437.
- 44
- 44aM. J. Powers, R. E. Rodriguez, L. G. Griffith, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 53, 415–426;
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19970220)53:4<415::AID-BIT10>3.0.CO;2-F CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 44bT. D. Sargeant, M. S. Rao, C.-Y. Koh, S. I. Stupp, Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1085–1098.
- 45I. R. Epstein, J. A. Pojman, An introduction to nonlinear chemical dynamics: oscillations, waves, patterns, and chaos, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1998.
10.1093/oso/9780195096705.001.0001 Google Scholar
- 46B. Rubinov, N. Wagner, H. Rapaport, G. Ashkenasy, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6683–6686; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6811–6814.
- 47S. Mann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 155–162; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 166–173.
- 48K. Petkau-Milroy, L. Brunsveld, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 219–232.
- 49
- 49aG. Ashkenasy, T. M. Hermans, S. Otto, A. F. Taylor, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2543–2554;
- 49bR. F. Ludlow, S. Otto, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 101–108;
- 49cJ. Boekhoven, A. M. Brizard, K. N. Kowlgi, G. J. Koper, R. Eelkema, J. H. van Esch, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4825–4828; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4935–4938.
- 50
- 50aF. Zhao, M. L. Ma, B. Xu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 883–891;
- 50bY. Gao, Y. Kuang, Z.-F. Guo, Z. Guo, I. J. Krauss, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13576–13577;
- 50cA. G. Cheetham, P. Zhang, Y.-a. Lin, L. L. Lock, H. Cui, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2907–2910.
- 51
- 51aA. Razgulin, N. Ma, J. Rao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4186–4216;
- 51bY. Takaoka, T. Sakamoto, S. Tsukiji, M. Narazaki, T. Matsuda, H. Tochio, M. Shirakawa, I. Hamachi, Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 557;
- 51cK. Mizusawa, Y. Takaoka, I. Hamachi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13386–13395.
- 52E. Sezgin, I. Levental, S. Mayor, C. Eggeling, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361.
- 53H. Wang, Z. Feng, B. Xu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2421–2436.
- 54J. Li, D. Bullara, X. Du, H. He, S. Sofou, I. G. Kevrekidis, I. R. Epstein, B. Xu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3804–3815.
- 55Z. Zheng, P. Chen, M. Xie, C. Wu, Y. Luo, W. Wang, J. Jiang, G. Liang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11128–11131.