A Size-Reducible Nanodrug with an Aggregation-Enhanced Photodynamic Effect for Deep Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy
Chendong Ji
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorQin Gao
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorXinghua Dong
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wenyan Yin
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhanjun Gu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhihua Gan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuliang Zhao
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Meizhen Yin
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorChendong Ji
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorQin Gao
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorXinghua Dong
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wenyan Yin
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhanjun Gu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhihua Gan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuliang Zhao
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Meizhen Yin
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
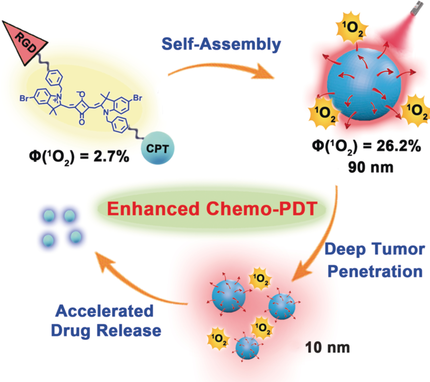
A size-reducible nanodrug with an enhanced photodynamic effect is constructed by self-assembly of a multifunctional indocyanine dye. Owing to the aggregation-enhanced photodynamic effect of the dye, the nanodrug exhibits a distinct singlet oxygen quantum yield. The generated singlet oxygen self-triggers the size reduction of the nanodrug, which facilitates deep tumor penetration of the nanodrug and accelerates chemodrug CPT release.
Abstract
Fluorescent dyes with multi-functionality are of great interest for photo-based cancer theranostics. However, their low singlet oxygen quantum yield impedes their potential applications for photodynamic therapy (PDT). Now, a molecular self-assembly strategy is presented for a nanodrug with a remarkably enhanced photodynamic effect based on a dye-chemodrug conjugate. The self-assembled nanodrug possesses an increased intersystem crossing rate owing to the aggregation of dye, leading to a distinct singlet oxygen quantum yield (Φ(1O2)). Subsequently, upon red light irradiation, the generated singlet oxygen reduces the size of the nanodrug from 90 to 10 nm, which facilitates deep tumor penetration of the nanodrug and release of chemodrug. The nanodrug achieved in situ tumor imaging and potent tumor inhibition by deep chemo-PDT. Our work verifies a facile and effective self-assembly strategy to construct nanodrugs with enhanced performance for cancer theranostics.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201807602-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.1 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. E. J. G. J. Dolmans, D. Fukumura, R. K. Jain, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380;
- 1bW. Fan, P. Huang, X. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6488;
- 1cC. Qian, J. Yu, Y. Chen, Q. Hu, X. Xiao, W. Sun, C. Wang, P. Feng, Q.-D. Shen, Z. Gu, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3313.
- 2
- 2aX. He, X. Wu, K. Wang, B. Shi, L. Hai, Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5601;
- 2bB. Wang, J. H. Wang, Q. Liu, H. Huang, M. Chen, K. Li, C. Li, X.-F. Yu, P. K. Chu, Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1954;
- 2cM. Ethirajan, Y. H. Chen, P. Joshi, R. K. Pandey, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 340;
- 2dD. W. Zheng, B. Li, C. X. Li, J. X. Fan, Q. Lei, C. Li, Z. Xu, X.-Z. Zhang, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8715;
- 2eW. Sun, S. Li, B. Häupler, J. Liu, S. Jin, W. Steffen, U. S. Schubert, H.-J. Butt, X.-J. Liang, S. Wu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603702.
- 3
- 3aT. Yogo, Y. Urano, Y. Ishitsuka, F. Maniwa, T. Nagano, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12162;
- 3bM. Schulze, A. Steffen, F. Würthner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1570; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1590.
- 4
- 4aW. Sun, S. Guo, C. Hu, J. Fan, X. Peng, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7768;
- 4bR. Kumar, W. S. Shin, K. Sunwoo, W. Y. Kim, S. Koo, S. Bhuniya, J. S. Kim, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6670;
- 4cR. R. Nani, A. P. Gorka, T. Nagaya, H. Kobayashi, M. J. Schnermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13635; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 13839;
- 4dY. Zhang, Q. Yin, J. Yen, J. Li, H. Ying, H. Wang, J. Cheng, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6948.
- 5
- 5aE. Delaey, F. van Laar, D. De Vos, A. Kamuhabwa, P. Jacobs, P. de Witte, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 55, 27;
- 5bA. J. Gomes, L. O. Lunardi, J. M. Marchetti, C. N. Lunardi, A. C. Tedesco, Photomed. Laser Surg. 2006, 24, 514.
- 6
- 6aK. K. Ng, G. Zheng, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11012;
- 6bQ. Chen, C. Liang, C. Wang, Z. Liu, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 903;
- 6cH. He, S. Ji, Y. He, A. Zhu, Y. Zou, Y. Deng, H. Ke, H. Yang, Y. Zhao, Z. Guo, H. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606690.
- 7
- 7aS. Kim, T. Y. Ohulchanskyy, H. E. Pudavar, R. K. Pandey, P. N. Prasad, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2669;
- 7bY. Yuan, C. J. Zhang, M. Gao, R. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1780; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 1800;
- 7cD. Zhang, G. B. Qi, Y. X. Zhao, S. L. Qiao, C. Yang, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6125.
- 8L. Yang, X. Wang, G. Zhang, X. Chen, G. Zhang, J. Jiang, Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17422.
- 9
- 9aY. Cakmak, S. Kolemen, S. Duman, Y. Dede, Y. Dolen, B. Kilic, Z. Kostereli, L. T. Yildirim, A. L. Dogan, Di. Guc, E. U. Akkaya, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11937; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 12143;
- 9bW. Wu, D. Mao, F. Hu, S. Xu, C. Chen, C. J. Zhang, X. Cheng, Y. Yuan, D. Ding, D. Kong, B. Liu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700548.
- 10
- 10aF. Danhier, A. Breton, V. Préat, Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2961;
- 10bQ. Hu, W. Sun, C. Qian, H. N. Bomba, H. Xin, Z. Gu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605803.
- 11
- 11aK. Cai, X. He, Z. Song, Q. Yin, Y. Zhang, F. M. Uckun, C. Jiang, J. Cheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3458;
- 11bA. G. Cheetham, P. Zhang, Y. A. Lin, L. L. Lock, H. Cui, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2907.
- 12C. Ji, Y. Zheng, J. Li, J. Shen, W. Yang, M. Yin, J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7494.
- 13R. Bao, B. Tan, S. Liang, N. Zhang, W. Wang, W. Liu, Biomaterials 2017, 122, 63.
- 14P. Huang, D. Wang, Y. Su, W. Huang, Y. Zhou, D. Cui, X. Zhu, D. Yan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11748.
- 15A. M. Smith, M. C. Mancini, S. Nie, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710.
- 16M. Mirenda, C. A. Strassert, L. E. Dicelio, E. S. Román, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1556.
- 17A. P. Gorka, M. J. Schnermann, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2016, 33, 117.
- 18K. Liu, R. Xing, Q. Zou, G. Ma, H. Möhwald, X. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3036; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 3088.
- 19
- 19aJ. Wang, W. Mao, L. Lock, J. Tang, M. Sui, W. Sun, H. Cui, D. Xu, Y. Shen, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7195;
- 19bY. Liu, D. Zhang, Z. Qiao, G. Qi, X.-J. Liang, X. Chen, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5034;
- 19cH. Chen, W. Zhang, G. Zhu, J. Xie, X. Chen, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17024.
- 20H. Xiang, Q. Deng, L. An, M. Guo, S. Yang, J. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 148.
- 21
- 21aS. Zhang, W. Guo, J. Wei, C. Li, X.-J. Liang, M. Yin, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3797;
- 21bS. Zhang, J. Li, J. Wei, M. Yin, Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 101.
- 22H. Wang, X. He, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhao, W. Feng, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 761.