Activation and Deactivation Strategies Promoted by Medium Effects for Selective Aliphatic C−H Bond Functionalization
Corresponding Author
Prof. Massimo Bietti
Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Chimiche, Università “Tor Vergata”, Via della Ricerca Scientifica, 1, I-00133 Rome, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Massimo Bietti
Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Chimiche, Università “Tor Vergata”, Via della Ricerca Scientifica, 1, I-00133 Rome, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
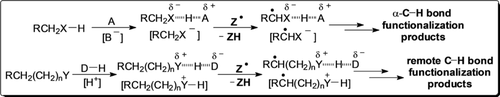
In the medium term: Effects of the reaction medium can be used to alter the reactivity and selectivity in synthetically useful procedures for the functionalization of aliphatic C−H bonds. This Review discusses the mechanistic features in terms of hydrogen bonding and acid–base interactions and shows that these effects can promote aliphatic C−H bond (de)activation toward hydrogen atom transfer reagents.
Abstract
Selective functionalization of unactivated aliphatic C−H bonds represents an important goal of modern synthetic chemistry. Differentiating between such bonds in organic molecules with high levels of selectivity remains a crucial issue, and a profound understanding of even the subtlest reactivity trends is needed. Among the methods that have been developed, those based on hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) have attracted considerable interest. Within this framework, medium effects have proved effective in altering the reactivity and site selectivity in synthetically useful C−H functionalization procedures. In this Review, the mechanistic features behind the available strategies are discussed. It is shown that hydrogen bonding and acid–base interactions can promote C−H bond activation or deactivation toward HAT reagents, thereby providing fine-control over the site selectivity and product chemoselectivity as well as useful guidelines for future development and applications.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1T. Cernak, K. D. Dykstra, S. Tyagarajan, P. Vachal, S. W. Krska, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 546–576.
- 2See, for example: R. R. Karimov, J. F. Hartwig, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4234–4241; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 4309–4317; H. M. L. Davies, D. Morton, ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 936–943; J. Yamaguchi, A. D. Yamaguchi, K. Itami, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8960–9009; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9092–9142; R. G. Bergman, Nature 2007, 446, 391–393; K. Godula, D. Sames, Science 2006, 312, 67–72.
- 3T. Newhouse, P. S. Baran, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3362–3374; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 3422–3435.
- 4J. M. Mayer, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 36–46.
- 5M. C. White, Science 2012, 335, 807–809.
- 6M. Salamone, M. Bietti, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2895–2903.
- 7D. Ravelli, M. Fagnoni, T. Fukuyama, T. Nishikawa, I. Ryu, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 701–713.
- 8T. Nanjo, E. C. de Lucca, Jr., M. C. White, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14586–14591.
- 9Y. Kawamata, M. Yan, Z. Liu, D.-H. Bao, J. Chen, J. T. Starr, P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7448–7451.
- 10R. K. Quinn, Z. A. Könst, S. E. Michalak, Y. Schmidt, A. R. Szklarski, A. R. Flores, S. Nam, D. A. Horne, C. D. Vanderwal, E. J. Alexanian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 696–702.
- 11M. K. Nielsen, B. J. Shields, J. Liu, M. J. Williams, M. J. Zacuto, A. G. Doyle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7191–7194; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 7297–7300.
- 12D. R. Heitz, J. C. Tellis, G. A. Molander, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12715–12718.
- 13H. Yi, G. Zhang, H. Wang, Z. Huang, J. Wang, A. K. Singh, A. Lei, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9016–9085.
- 14R. Zhou, Y. Y. Goh, H. Liu, H. Tao, L. Li, J. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16621–16625; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 16848–16852.
- 15M. Milan, M. Bietti, M. Costas, ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 196–204; D. Font, M. Canta, M. Milan, O. Cussó, X. Ribas, R. J. M. Klein Gebbink, M. Costas, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5776–5779; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 5870–5873; L. Gómez, I. Garcia-Bosch, A. Company, J. Benet-Buchholz, A. Polo, X. Sala, X. Ribas, M. Costas, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5720–5723; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 5830–5833.
- 16B. Qiu, D. Xu, Q. Sun, C. Miao, Y.-M. Lee, X.-X. Li, W. Nam, W. Sun, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2479–2487.
- 17W. Liu, J. T. Groves, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1727–1735.
- 18A. R. H. Narayan, G. Jiménez-Osés, P. Liu, S. Negretti, W. Zhao, M. M. Gilbert, R. O. Ramabhadran, Y.-F. Yang, L. R. Furan, Z. Li, L. M. Podust, J. Montgomery, K. N. Houk, D. H. Sherman, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 653–660.
- 19F. Liu, Z. Yang, Y. Yu, Y. Mei, K. N. Houk, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16650–16656.
- 20W. G. Shuler, S. L. Johnson, M. K. Hilinski, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4790–4793.
- 21B. P. Roberts, Chem. Soc. Rev. 1999, 28, 25–35.
- 22B. Chan, C. J. Easton, L. Radom, J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 3843–3847.
- 23M. Milan, G. Carboni, M. Salamone, M. Costas, M. Bietti, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5903–5911.
- 24K. Yamada, T. Fukuyama, S. Fujii, D. Ravelli, M. Fagnoni, I. Ryu, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8615–8618.
- 25A. Sharma, J. F. Hartwig, Nature 2015, 517, 600–604.
- 26I. Prat, L. Gómez, M. Canta, X. Ribas, M. Costas, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 1908–1913.
- 27S. A. Moteki, A. Usui, T. Zhang, C. R. Solorio Alvarado, K. Maruoka, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8657–8660; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 8819–8822.
- 28See, for example: G.-D. Roiban, M. T. Reetz, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2208–2224; W. Chang, Y. Guo, C. Wang, S. E. Butch, A. C. Rosenzweig, A. K. Boal, C. Krebs, J. M. Bollinger, Jr., Science 2014, 343, 1140–1144; R. Fasan, ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 647–666; J. C. Lewis, P. S. Coelho, F. H. Arnold, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2003–2021.
- 29See, for example: G. J. Choi, Q. Zhu, D. C. Miller, C. J. Gu, R. R. Knowles, Nature 2016, 539, 268–271; H. G. Yayla, H. Wang, K. T. Tarantino, H. S. Orbe, R. R. Knowles, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10794–10797; E. C. Gentry, R. R. Knowles, Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1546–1556.
- 30S. Mitroka, S. Zimmeck, D. Troya, J. M. Tanko, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2907–2913.
- 31M. Morris, B. Chan, L. Radom, J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 2810–2819.
- 32J. L. Jeffrey, J. A. Terrett, D. W. C. MacMillan, Science 2015, 349, 1532–1536.
- 33A. Dewanji, C. Mück-Lichtenfeld, A. Studer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6749–6752; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6861–6864.
- 34J. A. Cradlebaugh, L. Zhang, G. R. Shelton, G. Litwinienko, B. E. Smart, K. U. Ingold, W. R. Dolbier, Jr., Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2083–2086.
- 35J. W. Boyle, Jr., J. F. Bunnett, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 1418–1422.
- 36J. Twilton, M. Christensen, D. A. DiRocco, R. T. Ruck, I. W. Davies, D. W. C. MacMillan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5369–5373.
- 37B. Chan, C. J. Easton, L. Radom, J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 1741–1746.
- 38R. J. O'Reilly, B. Chan, M. S. Taylor, S. Ivanic, G. B. Bacskay, C. J. Easton, L. Radom, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16553–16559.
- 39L. M. Pipitone, G. Carboni, D. Sorrentino, M. Galeotti, M. Salamone, M. Bietti, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 808–811.
- 40M. Salamone, F. Basili, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 3643–3650.
- 41M. Bietti, R. Martella, M. Salamone, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6110–6113.
- 42M. Bietti, M. Salamone, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3654–3657.
- 43M. Salamone, I. Giammarioli, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 4645–4651.
- 44M. Salamone, L. Mangiacapra, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 1149–1154.
- 45M. Salamone, V. B. Ortega, T. Martin, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 5539–5545.
- 46E. Gaster, S. Kozuch, D. Pappo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5912–5915; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6006–6009.
- 47The HBD ability of the solvent can be quantified on the basis of Abraham's
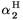 parameter:
parameter: 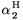 =0.771, 0.561, 0.550, and 0.367 for HFIP, TFE, AcOH, and MeOH, respectively, see Ref. [48].
=0.771, 0.561, 0.550, and 0.367 for HFIP, TFE, AcOH, and MeOH, respectively, see Ref. [48].
- 48M. H. Abraham, P. L. Grellier, D. V. Prior, P. P. Duce, J. J. Morris, P. J. Taylor, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1989, 699–711.
- 49V. Dantignana, M. Milan, O. Cussó, A. Company, M. Bietti, M. Costas, ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 1350–1358.
- 50D. Wang, W. G. Shuler, C. J. Pierce, M. K. Hilinski, Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3826–3829.
- 51M. Salamone, I. Giammarioli, M. Bietti, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3255–3262.
- 52M. Salamone, L. Mangiacapra, G. A. DiLabio, M. Bietti, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 415–423.
- 53K. Izutsu, Acid-Base Dissociation Constants in Dipolar Aprotic Solvents, Blackwell, Oxford, 1990.
- 54M. Milan, M. Salamone, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 5710–5716.
- 55M. Salamone, G. Carboni, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 9269–9278.
- 56A. Nova, D. Balcells, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 614–616.
- 57M. Salamone, G. Carboni, L. Mangiacapra, M. Bietti, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 9214–9223.
- 58M. Salamone, L. Mangiacapra, G. Carboni, M. Bietti, Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 7757–7763.
- 59M. Bietti, O. Lanzalunga, A. Lapi, T. Martin, M. Mazzonna, M. Salamone, J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 5761–5768.
- 60M. Bietti, V. Forcina, O. Lanzalunga, A. Lapi, T. Martin, M. Mazzonna, M. Polin, M. Salamone, J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11924–11931.
- 61G. A. DiLabio, P. Franchi, O. Lanzalunga, A. Lapi, F. Lucarini, M. Lucarini, M. Mazzonna, V. K. Prasad, B. Ticconi, J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 6133–6141.
- 62G. Asensio, M. E. González-Núñez, C. B. Bernardini, R. Mello, W. Adam, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7250–7253.
- 63J. M. Howell, K. Feng, J. R. Clark, L. J. Trzepkowski, M. C. White, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14590–14593.
- 64A. M. Adams, J. Du Bois, H. A. Malik, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 6066–6069.
- 65M. Lee, M. S. Sanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12796–12799.
- 66C. T. Mbofana, E. Chong, J. Lawniczak, M. S. Sanford, Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4258–4261.
- 67M. Lee, M. S. Sanford, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 572–575.
- 68V. Soulard, F. Dénès, P. Renaud, Free Radical Res. 2016, 50, S 2–S5.
- 69J. B. C. Mack, J. D. Gipson, J. Du Bois, M. S. Sigman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9503–9506.
- 70D. M. Schultz, F. Lévesque, D. A. DiRocco, M. Reibarkh, Y. Ji, L. A. Joyce, J. F. Dropinski, H. Sheng, B. D. Sherry, I. W. Davies, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15274–15278; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 15476–15480.
- 71G. Olivo, G. Farinelli, A. Barbieri, O. Lanzalunga, S. Di Stefano, M. Costas, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16347–16351; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 16565–16569.