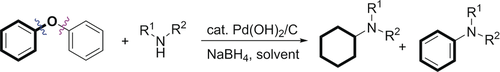Palladium-Catalyzed Formal Cross-Coupling of Diaryl Ethers with Amines: Slicing the 4-O-5 Linkage in Lignin Models
Corresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Huiying Zeng
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDawei Cao
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZihang Qiu
Department of Chemistry and FQRNT Centre for Green Chemistry and Catalysis, McGill University, 801 Sherbrooke St. West, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 0B8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chao-Jun Li
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry and FQRNT Centre for Green Chemistry and Catalysis, McGill University, 801 Sherbrooke St. West, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 0B8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Huiying Zeng
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDawei Cao
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZihang Qiu
Department of Chemistry and FQRNT Centre for Green Chemistry and Catalysis, McGill University, 801 Sherbrooke St. West, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 0B8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chao-Jun Li
The State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, 222 Tianshui Road, Lanzhou, 730000 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry and FQRNT Centre for Green Chemistry and Catalysis, McGill University, 801 Sherbrooke St. West, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 0B8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
Lignin is the second most abundant organic matter on Earth, and is an underutilized renewable source for valuable aromatic chemicals. For future sustainable production of aromatic compounds, it is highly desirable to convert lignin into value-added platform chemicals instead of using fossil-based resources. Lignins are aromatic polymers linked by three types of ether bonds (α-O-4, β-O-4, and 4-O-5 linkages) and other C−C bonds. Among the ether bonds, the bond dissociation energy of the 4-O-5 linkage is the highest and the most challenging to cleave. To date, 4-O-5 ether linkage model compounds have been cleaved to obtain phenol, cyclohexane, cyclohexanone, and cyclohexanol. The first example of direct formal cross-coupling of diaryl ether 4-O-5 linkage models with amines is reported, in which dual C(Ar)−O bond cleavages form valuable nitrogen-containing derivatives.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201712211-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aK. Sanderson, Nature 2011, 474, S 12–S14;
- 1bM. Carrier, A. Loppinet-Serani, D. Denux, J.-M. Lasnier, F. Ham-Pichavant, F. Cansell, C. Aymonier, Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 298–307.
- 2J. Ralph, G. Brunow, W. Boerjan, “Lignins” in: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, Wiley, New York, 2001.
- 3
- 3aG. W. Huber, S. Iborra, A. Corma, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098;
- 3bC. Xu, R. A. D. Arancon, J. Labidi, R. Luque, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7485–7500;
- 3cR. Sun, Cereal Straw as a Resource for Sustainable Biomaterials and Biofuels Chemistry, Extractives, Lignins, Hemicelluloses and Cellulose, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2010.
- 4
- 4aC. O. Tuck, E. Pérez, I. T. Horváth, R. A. Sheldon, M. Poliakoff, Science 2012, 337, 695–699;
- 4bJ. Zakzeski, P. C. A. Bruijnincx, A. L. Jongerius, B. M. Weckhuysen, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599.
- 5M. Stöcker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9200–9211; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 9340–9351.
- 6
- 6aJ. R. Regalbuto, Science 2009, 325, 822–824;
- 6bN. Yan, C. Zhao, P. J. Dyson, C. Wang, L. T. Liu, Y. Kou, ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 626–629.
- 7
- 7aA. J. Ragauskas, G. T. Beckham, M. J. Biddy, R. Chandra, F. Chen, M. F. Davis, B. H. Davison, R. A. Dixon, P. Gilna, M. Keller, P. Langan, A. K. Naskar, J. N. Saddler, T. J. Tschaplinski, G. A. Tuskan, C. E. Wyman, Science 2014, 344, 1246843;
- 7bE. Furimsky, Appl. Catal. A 2000, 199, 147–190.
- 8
- 8aV. M. Roberts, R. T. Knapp, X. Li, J. A. Lercher, ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 1407–1410;
- 8bA. G. Sergeev, J. F. Hartwig, Science 2011, 332, 439–443;
- 8cA. G. Sergeev, J. D. Webb, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20226–20229;
- 8dJ. He, C. Zhao, J. A. Lercher, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20768–20775;
- 8eC. Zhao, J. A. Lercher, ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 64–68;
- 8fF. Gao, J. D. Webb, J. F. Hartwig, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1474–1478; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 1496–1500;
- 8gQ. Meng, M. Hou, H. Liu, J. Song, B. Han, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14190;
- 8hM. Wang, H. Shi, D. M. Camaioni, J. A. Lercher, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2110–2114; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 2142–2146;
- 8iN. I.Saper, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, https://doi.org/10.1021/jasc.7b10537.
- 9
- 9aY.-R. Luo, Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2007;
10.1201/9781420007282 Google Scholar
- 9bM. W. Jarvis, J. W. Daily, H.-H. Carstensen, A. M. Dean, S. Sharma, D. C. Dayton, D. J. Robichaud, M. R. Nimlos, J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 428–438.
- 10
- 10aP. C. A. Bruijnincx, B. M. Weckhuysen, Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1035–1036;
- 10bS. K. Hanson, R. Wu, L. A. P. Silks, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3410–3413; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 3466–3469;
- 10cA. Rahimi, A. Azarpira, H. Kim, J. Ralph, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6415–6418.
- 11
- 11aJ. M. Nichols, L. M. Bishop, R. G. Bergman, J. A. Ellman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12554–12555;
- 11bP. Ferrini, R. Rinaldi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8634–8639; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 8778–8783;
- 11cJ. Zhang, J. Teo, X. Chen, H. Asakura, T. Tanaka, K. Teramura, N. Yan, ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1574–1583.
- 12M. Chatterjee, A. Chatterjee, T. Ishizaka, H. Kawanami, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1532–1539.
- 13
- 13aS. Son, F. D. Toste, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3791–3794; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 3879–3882;
- 13bA. Fedorov, A. A. Toutov, N. A. Swisher, R. H. Grubbs, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1640;
- 13cC. Li, X. Zhao, A. Wang, G. W. Huber, T. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11559–11624;
- 13dA. Rahimi, A. Ulbrich, J. J. Coon, S. S. Stahl, Nature 2014, 515, 249–252.
- 14
- 14aY.-L. Ren, M. Tian, X.-Z. Tian, Q. Wang, H. Shang, J. Wang, Z. C. Zhang, Catal. Commun. 2014, 52, 36–39;
- 14bL. Yang, Y. Li, P. E. Savage, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2633–2639;
- 14cY. Ren, M. Yan, J. Wang, Z. C. Zhang, K. Yao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12674–12678; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12906–12910;
- 14dW. B. Wu, J. M. Huang, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 10189–10195;
- 14eV. Stavila, R. Parthasarathi, R. W. Davis, F. El Gabaly, K. L. Sale, B. A. Simmons, S. Singh, M. D. Allendorf, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 55–59.
- 15
- 15aX. Liu, L. Xu, G. Xu, W. Jia, Y. Ma, Y. Zhang, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7611–7620;
- 15bY. Shao, Q. Xia, X. Liu, G. Lu, Y. Wang, ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1761–1767.
- 16N. A. McGrath, M. Brichacek, J. T. Njardarson, J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1348–1349.
- 17
- 17aZ. Chen, H. Zeng, S. A. Girard, F. Wang, N. Chen, C.-J. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14487–14491; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 14695–14699;
- 17bZ. Qiu, J.-S. Li, C.-J. Li, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6954–6958;
- 17cH. Zeng, Z. Qiu, A. Domínguez-Huerta, Z. Hearne, Z. Chen, C.-J. Li, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 510–519;
- 17dJ.-S. Li, Z. Qiu, C.-J. Li, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 3648–3653.
- 18
- 18aS. A. Lawrence, Amines Synthesis Properties and Applications, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2004;
- 18bK. Schofield, Hetero-Aromatic Nitrogen Compounds–Pyrroles and Pyridines, Springer, Berlin, 1967.
10.1007/978-1-4899-5892-1 Google Scholar
- 19
- 19aZ. Chen, H. Zeng, H. Gong, H. Wang, C.-J. Li, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4174–4178;
- 19bY. Ono, H. Ishida, J. Catal. 1981, 72, 121–128.
- 20
- 20aX. Wang, R. Rinaldi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11499–11503; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 11713–11717;
- 20bR. Rinaldi, R. Jastrzebski, M. T. Clough, J. Ralph, M. Kennema, P. C. A. Bruijnincx, B. M. Weckhuysen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8164–8215; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 8296–8354.
- 21It is well-known that palladium can catalyze the hydrogenation of the phenol (9) to cyclohexanone (14), see: H. Liu, T. Jiang, B. Han, S. Liang, Y. Zhou, Science 2009, 326, 1250–1252, and references therein.
- 22A. G. Cook, A. S. Karen, A. C. Kenneth, M. W. Allison, Lett. Org. Chem. 2004, 1, 1–5.