Enantioselective Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Intramolecular Aminoarylation of Alkenes by Dual N−H and Aryl C−H Bond Cleavage
Wen Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pinhong Chen
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Key Laboratory of Functional Small Organic Molecules, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi Normal University, 99 Ziyang Road, Nanchang, Jiangxi, 330022 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guosheng Liu
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorWen Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pinhong Chen
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Key Laboratory of Functional Small Organic Molecules, Ministry of Education, Jiangxi Normal University, 99 Ziyang Road, Nanchang, Jiangxi, 330022 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guosheng Liu
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
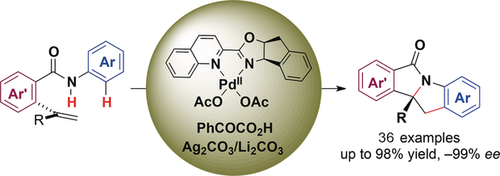
A neighborhood action group: In an asymmetric palladium-catalyzed intramolecular oxidative aminoarylation of alkenes in the presence of a quinolone–oxazoline chiral ligand and Ag2CO3 as the oxidant, the amide N−H bond of the substrate and a neighboring aryl C−H bond were both activated to react with the alkene (see scheme). Various indolines with a quaternary stereogenic center were synthesized in high yield with excellent enantioselectivity.
Abstract
An asymmetric palladium-catalyzed intramolecular oxidative aminoarylation of alkenes has been developed with quinoline–oxazoline chiral ligands and Ag2CO3 as the oxidant. Various indolines containing a quaternary stereogenic center were synthesized in high yield with excellent enantioselectivity. Preliminary mechanistic studies suggest that the addition of a catalytic amount of phenylglyoxylic acid significantly accelerates the reaction and slightly enhances the enantioselectivity.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201700889-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf9.9 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aE. J. Negishi, Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis, Vol. 2, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002;
10.1002/0471212466 Google Scholar
- 1bL. S. Hegedus, J. Mol. Catal. 1983, 19, 201–211;
- 1cG. Zeni, R. C. Larock, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4644–4680;
- 1dL. F. Tietze, K. M. Sommer, J. Zinngrebe, F. Stecker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 257–259; Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 262–264.
- 2For reviews, see:
- 2aS. S. Stahl, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3400–3420; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3480–3501;
- 2bE. M. Beccalli, G. Broggini, M. Martinelli, S. Sottocornola, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5318–5365;
- 2cT. E. Müller, M. Beller, Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 675–704;
- 2dV. Kotov, C. C. Scarborough, S. S. Stahl, Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1910–1923.
- 3For reviews of the Wacker process, see:
- 3aJ. M. Takacs, X. Jiang, Curr. Org. Chem. 2003, 7, 369–396;
- 3bC. N. Cornell, M. S. Sigman, Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1903–1909;
- 3cJ. Muzart, Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 7505–7521.
- 4
- 4aL. S. Hegedus, G. F. Allen, D. J. Olsen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 3583–3587;
- 4bE.-J. Negishi, C. Copéret, S. Ma, S.-Y. Liou, F. Liu, Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 365–394.
- 5For reviews, see:
- 5aK. Muñiz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9412–9423; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9576–9588;
- 5bK. M. Engle, T.-S. Mei, X. Wang, J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1478–1491; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 1514–1528;
- 5cG. Yin, X. Mu, G. Liu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2413–2423.
- 6For selected examples, see:
- 6aY. Liu, Y. Xie, H. Wang, H. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4314–4317;
- 6bD. R. White, J. T. Hutt, J. P. Wolfe, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11246–11249;
- 6cD. N. Mai, J. P. Wolfe, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12157–12159;
- 6dB. A. Hopkins, J. P. Wolfe, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9886–9890; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10024–10028;
- 6eH. Du, B. Zhao, Y. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8590–8591.
- 7R. I. McDonald, G. Liu, S. S. Stahl, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2981–3019.
- 8X. Liu, P. Chen, F. Wu, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1797–1804.
- 9
- 9aR. I. McDonald, P. B. White, A. B. Weinstein, C. P. Tam, S. S. Stahl, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2830–2833;
- 9bA. B. Weinstein, S. S. Stahl, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11505–11509; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 11673–11677.
- 10
- 10aG. Yang, C. Shen, W. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9141–9145; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9275–9279;
- 10bF. Jiang, Z. Wu, W. Zhang, Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 5124–5126.
- 11
- 11aK.-T. Yip, M. Yang, K.-L. Law, N.-Y. Zhu, D. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3130–3131;
- 11bW. He, K.-T. Yip, N.-Y. Zhu, D. Yang, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5626–5628;
- 11cW. Du, Q. Gu, Y. Li, Z. Lin, D. Yang, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 316–319.
- 12E. L. Ingalls, P. A. Sibbald, W. Kaminsky, F. E. Michael, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8854–8856.
- 13For pioneering non-enantioselective aminoarylation reactions related to the cyclization reported by Yang and co-workers, see:
- 13aK.-T. Yip, D. Yang, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2134–2137;
- 13bW. Du, Q. Gu, Z. Li, D. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1130–1135;
- 13cC. F. Rosewall, P. A. Sibbald, D. V. Liskin, F. E. Michael, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9488–9489;
- 13dP. A. Sibbald, C. F. Rosewall, R. D. Swartz, F. E. Michael, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15945–15951.
- 14For enantioselective aminoarylation reactions that proceed through a radical process with a copper catalyst, see:
- 14aW. Zeng, S. R. Chemler, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12948–12949;
- 14bL. Miao, I. Haque, M. R. Manzoni, W. S. Tham, S. R. Chemler, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4739–4741.
- 15
- 15aRef. [5c];
- 15bT. Wu, G. Yin, G. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16354–16355;
- 15cT. Wu, J. Cheng, P. Chen, G. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8707–8709;
- 15dH. Zhu, P. Chen, G. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1766–1769;
- 15eH. Zhu, P. Chen, G. Liu, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1485–1488;
- 15fC. Chen, P. Chen, G. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15648–15651.
- 16F. Yu, P. Chen, G. Liu, Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 819–822.
- 17The reaction under aerobic oxidation with Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol %) and L9 (10 mol %) provided 2 a in 52 % yield with −75 % ee in the absence of PGA (conditions A) and in 62 % yield with −82 % ee in the presence of PGA (20 mol %).
- 18When CF3CO2H (20 mol %) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (20 mol %) were added, 2 a was obtained in 68 % yield (−74 % ee) and 47 % yield (−71 % ee), respectively, thus indicating that the effect of phenylglyoxylic acid might stem from coordination to generate a cationic palladium species (see Scheme 3), rather than its strong Brønsted acidity.
- 19CCDC 1535090 [(S)-2 q] contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre.
- 20In both cases, predominant (or exclusive) cis AP was observed, as the addition of an extraneous base favors the generation of an amido–palladium complex, thus resulting in cis aminopalladation; for details, see: G. Liu, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6328–6335.
- 21In this case, the cis-AP process leads to excellent ee values (higher than 83 %) in the presence of PGA. The ee values observed in this study are much higher than those in Ref. [9b], thus revealing a significant difference between the two reactions.
- 22When PGA (2 equiv) was added to a solution of [(L9)Pd(OAc)2] in CDCl3 according to the standard conditions, [(L9)Pd(PGA)2] was formed immediately, with the release of HOAc (see the Supporting Information for details).