Methanol Conversion into Dimethyl Ether on the Anatase TiO2(001) Surface
Feng Xiong
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYan-Yan Yu
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZongfang Wu
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorGuanghui Sun
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorLiangbing Ding
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorYuekang Jin
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Xue-Qing Gong
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Xue-Qing Gong, Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Weixin Huang, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Weixin Huang
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Xue-Qing Gong, Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Weixin Huang, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorFeng Xiong
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYan-Yan Yu
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZongfang Wu
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorGuanghui Sun
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorLiangbing Ding
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorYuekang Jin
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Xue-Qing Gong
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Xue-Qing Gong, Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Weixin Huang, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Weixin Huang
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Xue-Qing Gong, Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials, Centre for Computational Chemistry and Research Institute of Industrial Catalysis, East China University of Science and Technology, Meilong Road 130, Shanghai 200237 (P. R. China)
Weixin Huang, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, and Department of Chemical Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Jinzhai Road 96, Hefei 230026 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
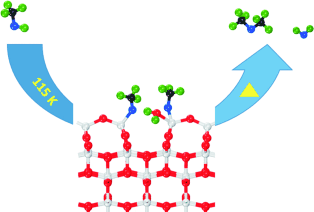
Let's face't: The methanol-to-dimethyl ether (DME) reaction was unambiguously identified to occur by the dehydration coupling of methoxy species at the fourfold-coordinated Ti4+ sites (Ti4c) on a mineral anatase TiO2(001)-(1×4) surface. The results show, for the first time, the predicted higher reactivity of this facet relative to other reported TiO2 facets.
Abstract
Exploring reactions of methanol on TiO2 surfaces is of great importance in both C1 chemistry and photocatalysis. Reported herein is a combined experimental and theoretical calculation study of methanol adsorption and reaction on a mineral anatase TiO2(001)-(1×4) surface. The methanol-to-dimethyl ether (DME) reaction was unambiguously identified to occur by the dehydration coupling of methoxy species at the fourfold-coordinated Ti4+ sites (Ti4c), and for the first time confirms the predicted higher reactivity of this facet compared to other reported TiO2 facets. Surface chemistry of methanol on the anatase TiO2(001)-(1×4) surface is seldom affected by co-chemisorbed water. These results not only greatly deepen the fundamental understanding of elementary surface reactions of methanol on TiO2 surfaces but also show that TiO2 with a high density of Ti4c sites is a potentially active and selective catalyst for the important methanol-to-DME reaction.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201509021_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf2 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Sun, G. Yang, Y. Yoneyama, N. Tsubaki, ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3346–3356.
- 2G. A. Olah, A. Goeppert, G. K. S. Prakash, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 487–498.
- 3W. Song, D. M. Marcus, H. Fu, J. O. Ehresmann, J. F. Haw, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3844–3845.
- 4P. Tian, Y. Wei, M. Ye, Z. Liu, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1922–1938.
- 5M. Xu, J. H. Lunsford, D. W. Goodman, A. Bhattacharyya, Appl. Catal. A 1997, 149, 289–301.
- 6R. M. Ladera, J. L. G. Fierro, M. Ojeda, S. Rojas, J. Catal. 2014, 312, 195–203.
- 7M. A. Henderson, I. Lyubinetsky, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4428–4455.
- 8U. Diebold, Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–226.
- 9M. A. Henderson, Surf. Sci. Rep. 2011, 66, 185–297.
- 10C. L. Pang, R. Lindsay, G. Thornton, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3887–3948.
- 11K. S. Kim, M. A. Barteau, Surf. Sci. 1989, 223, 13–32.
- 12M. A. Henderson, S. Otero-Tapia, M. E. Castro, Faraday Discuss. 1999, 114, 313–329.
- 13B. Li, J. Zhao, K. Onda, K. D. Jordan, J. Yang, H. Petek, Science 2006, 311, 1436.
- 14Q. Guo, C. Xu, Z. Ren, W. Yang, Z. Ma, D. Dai, H. Fan, T. K. Minton, X. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13366.
- 15K. R. Phillips, S. C. Jensen, M. Baron, S. C. Li, C. M. Friend, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 574–577.
- 16Q. Yuan, Z. Wu, Y. Jin, L. Xu, F. Xiong, Y. Ma, W. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5215–5219.
- 17C. Xu, W. Yang, Q. Guo, D. Dai, M. Chen, X. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 602–605.
- 18X. Mao, Z. Wang, X. Lang, Q. Hao, B. Wen, D. Dai, C. Zhou, L. M. Liu, X. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 6121–6127.
- 19M. Lazzeri, A. Vittadini, A. Selloni, Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 155409.
- 20M. Lazzeri, A. Selloni, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 266105.
- 21X. Q. Gong, A. Selloni, J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 19560–19562.
- 22X. Q. Gong, A. Selloni, A. Vittadini, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2804–2811.
- 23A. Vittadini, M. Casarin, A. Selloni, Theor. Chem. Acc. 2007, 117, 663–671.
- 24G. S. Herman, M. R. Sievers, Y. Gao, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3354–3357.
- 25Y. Liang, S. Gan, S. Chambers, E. Altman, Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 235402.
- 26T. Ohsawa, I. V. Lyubinetsky, M. A. Henderson, S. A. Chambers, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 20050–20056.
- 27Y. Wang, H. Sun, S. Tan, H. Feng, Z. Cheng, J. Zhao, A. Zhao, B. Wang, Y. Luo, J. Yang, J. G. Hou, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2214.
- 28G. Durinck, H. Poelman, P. Clauws, L. Fiermans, J. Vennik, G. Dalmai, Solid State Commun. 1991, 80, 579.
- 29K. S. Kim, M. A. Barteau, W. E. Farneth, Langmuir 1988, 4, 533–543.
- 30E. A. Taylor, G. L. Griffin, J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 477–481.
- 31J. M. Vohs, M. A. Barteau, Surf. Sci. 1989, 221, 590–608.
- 32M. B. Hugenschmidt, L. Gamble, C. T. Campbell, Surf. Sci. 1994, 302, 329–340.
- 33G. S. Herman, Z. Dohnalek, N. Ruzycki, U. Diebold, J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2788–2795.
- 34J. Blomquist, L. E. Walle, P. Uvdal, A. Borg, A. Sandell, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16616–16621.
- 35I. Carrizosa, G. Munuera, S. Castanar, J. Catal. 1977, 49, 265–277.
- 36Y. Suda, T. Morimoto, M. Nagao, Langmuir 1987, 3, 99–104.
- 37G. A. M. Hussein, N. Sheppard, M. I. Zaki, R. B. Fahim, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1991, 87, 2655–2659.
- 38C.-y. Wang, H. Groenzin, M. J. Shultz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8094–8095.