Practical Organocatalytic Synthesis of Functionalized Non-C2-Symmetrical Atropisomeric Biaryls
Dr. Hongyin Gao
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Qing-Long Xu
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Current address: Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Drug Discovery for Metabolic Disease and State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines China Pharmaceutical University, 24 Tongjia Xiang, Nanjing 210009 (P.R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCraig Keene
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Muhammed Yousufuddin
Life and Health Sciences Department, The University of North Texas at Dallas, Dallas, TX 75241 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Daniel H. Ess
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT 84602 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. László Kürti
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hongyin Gao
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Qing-Long Xu
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Current address: Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Drug Discovery for Metabolic Disease and State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines China Pharmaceutical University, 24 Tongjia Xiang, Nanjing 210009 (P.R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCraig Keene
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Muhammed Yousufuddin
Life and Health Sciences Department, The University of North Texas at Dallas, Dallas, TX 75241 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Daniel H. Ess
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT 84602 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. László Kürti
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)
Department of Chemistry, Rice University, BioScience Research Collaborative, 6500 Main Street, Rm 380, Houston, TX 77030 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
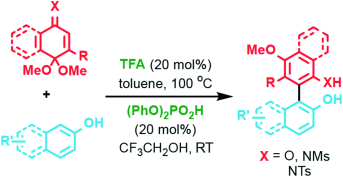
An organic acid catalyzed direct arylation of aromatic C(sp2)H bonds in phenols and naphthols was developed. This transformation is operationally simple, does not require an external oxidant, is readily scaled up, and the structurally diverse biaryls are formed with complete regioselectivity. Density functional calculations suggest a mechanism involving a mixed-acetal formation/[3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement sequence.
Abstract
An organic acid catalyzed direct arylation of aromatic C(sp2)H bonds in phenols and naphthols for the preparation of 1,1′-linked functionalized biaryls was developed. The products are non-C2-symmetrical, atropoisomeric, and represent previously untapped chemical space. Overall this transformation is operationally simple, does not require an external oxidant, is readily scaled up (up to 98 mmol), and the structurally diverse 2,2′-dihydroxy biaryl (i.e., BINOL-type), as well as 2-amino-2′-hydroxy products (i.e., NOBIN-type) are formed with complete regioselectivity. Density-functional calculations suggest that the quinone and imino-quinone monoacetal coupling partners are exclusively arylated at their α-position by an asynchronous [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of a mixed acetal species which is formed in situ under the reaction conditions.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201508419_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf4.5 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aG. Bringmann, A. J. P. Mortimer, P. A. Keller, M. J. Gresser, J. Garner, M. Breuning, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5384–5427; Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 5518–5563;
- 1bC. Wolf in Dynamic Stereochemistry of Chiral Compounds: Principles and Applications, RSC, 2007, pp. 29–135;
- 1cG. Bringmann, T. Gulder, T. A. M. Gulder, M. Breuning, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 563–639;
- 1dA. Zask, J. Murphy, G. A. Ellestad, Chirality 2013, 25, 265–274.
- 2
- 2aJ. Clayden, W. J. Moran, P. J. Edwards, S. R. LaPlante, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6398–6401; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6516–6520;
- 2bS. R. LaPlante, P. J. Edwards, L. D. Fader, A. Jakalian, O. Hucke, ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 505–513;
- 2cS. R. LaPlante, L. D. Fader, K. R. Fandrick, D. R. Fandrick, O. Hucke, R. Kemper, S. P. F. Miller, P. J. Edwards, J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7005–7022.
- 3
- 3aY. Chen, S. Yekta, A. K. Yudin, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3155–3211;
- 3bP. Kočovský, S. Vyskočil, M. Smrčina, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3213–3245;
- 3cE. N. Jacobsen, A. Pfaltz, H. Yamamoto, Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis, Springer, New York, 2004;
- 3dT. Akiyama, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5744–5758;
- 3eH.-U. Blaser, H.-J. Federsel, Asymmetric Catalysis On Industrial Scale: Challenges, Approaches, And Solutions, 2nd ed., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010;
10.1002/9783527630639 Google Scholar
- 3fE. J. Corey, L. Kürti, Enantioselective Chemical Synthesis: Methods, Logic and Practice, Direct Book Publishing, Dallas, 2010;
- 3gI. Ojima, Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis, 3rd ed., Wiley, 2010;
10.1002/9780470584248 Google Scholar
- 3hC. A. Busacca, D. R. Fandrick, J. J. Song, C. H. Senanayake, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1825–1864;
- 3iJ. Magano, J. R. Dunetz, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2177–2250;
- 3jQ.-L. Zhou, Privileged Chiral Ligands and Catalysts, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011.
10.1002/9783527635207 Google Scholar
- 4
- 4aL. Anastasia, E.-I. Negishi, Handb. Organopalladium Chem. Org. Synth. 2002, 1, 311–334;
- 4bJ. Hassan, M. Sevignon, C. Gozzi, E. Schulz, M. Lemaire, Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1359–1469;
- 4cD. Alberico, M. E. Scott, M. Lautens, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 174–238;
- 4dL. Ackermann, Modern Arylation Methods, Wiley, New York, 2009;
10.1002/9783527627325 Google Scholar
- 4eG. P. McGlacken, L. M. Bateman, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2447–2464;
- 4fJ. A. Ashenhurst, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 540–548;
- 4gS. Quideau, D. Deffieux, L. Pouysegu, Comprehensive Organic Synthesis, Vol. 3, 2nd ed. 2014, pp. 656–740;
10.1016/B978-0-08-097742-3.00318-9 Google Scholar
- 4hG. Bencivenni, Synlett 2015, 1915–1922;
- 4iG. Ma, M. P. Sibi, Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11644–11657.
- 5H. Gao, D. H. Ess, M. Yousufuddin, L. Kürti, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7086–7089.
- 6
- 6aT. Dohi, M. Ito, I. Itani, N. Yamaoka, K. Morimoto, H. Fujioka, Y. Kita, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6208–6211;
- 6bM. Terada, K. Dan, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5781–5783;
- 6cM. Holtz-Mulholland, M. de Leseleuc, S. K. Collins, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1835–1837;
- 6dS. K. Reddy Parumala, R. K. Peddinti, Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3546–3549.
- 7C. C. C. Johansson Seechurn, M. O. Kitching, T. J. Colacot, V. Snieckus, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5062–5085; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 5150–5174.
- 8
- 8aA. Lei, W. Liu, C. Liu, M. Chen, Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 10352–10361;
- 8bY.-X. Su, L.-P. Sun, Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2012, 9, 87–117.
- 9C. S. Yeung, V. M. Dong, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1215–1292.
- 10
- 10aC. K. De, F. Pesciaioli, B. List, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9293–9295; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 9463–9465;
- 10bG.-Q. Li, H. Gao, C. Keene, M. Devonas, D. H. Ess, L. Kürti, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7414–7417.
- 11S. Quideau, L. Pouysegu, Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 1999, 31, 617–680.
- 12
- 12aT. Dohi, N. Washimi, T. Kamitanaka, K.-i. Fukushima, Y. Kita, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6142–6146; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 6266–6270;
- 12bT. Dohi, T. Kamitanaka, S. Watanabe, Y. Hu, N. Washimi, Y. Kita, Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13614–13618.
- 13A great advantage of this approach is that in the case of the BINOL-type products the OH substituents in the 2- and 2′-positions are directly obtained in their unprotected form and no extra deprotection step is needed. If the biaryl product contains more than one protected OH group (i.e., OMe), selective deprotection of these groups becomes very challenging. Therefore it is desirable to have only the 2- and 2′-hydroxy groups in their unprotected form as it allows the most flexibility with regard to coordination with metals and further transformations (e.g., conversion of phosphoramidites and phosphoric acids).
- 14M. Ito, H. Kubo, I. Itani, K. Morimoto, T. Dohi, Y. Kita, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14078–14081.
- 15A model system was used in which the methyl (Me) groups of the quinone monoacetal (1) were replaced with hydrogen (H) atoms.
- 16
- 16aM. J. Frisch, et al. Gaussian 09, revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, 2009;
- 16bY. Zhao, D. G. Truhlar, Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241;
- 16cY. Zhao, D. G. Truhlar, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157–167;
- 16dA. V. Marenich, C. J. Cramer, D. G. Truhlar, J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396.
- 17
- 17aO. Wiest, K. A. Black, K. N. Houk, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 10336–10337;
- 17bM. M. Davidson, I. H. Hillier, M. A. Vincent, Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 246, 536–540;
- 17cV. Aviyente, H. Y. Yoo, K. N. Houk, J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 6121–6128;
- 17dH. Y. Yoo, K. N. Houk, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 2877–2884;
- 17eB. Gómez, P. K. Chattaraj, R. Contreras, P. Fuentealba, J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 11227–11233;
- 17fM. M. Khaledy, M. Y. S. Kalani, K. S. Khuong, K. N. Houk, V. Aviyente, R. Neier, N. Soldermann, J. Velker, J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 572–577.
- 18The M06-2X functional has approximately 3 kcal mol−1 error in the activation barrier for the uncatalyzed reaction. See: T. R. Ramadhar, R. A. Batey, Comput. Theor. Chem. 2011, 976, 167–182.
- 19We were unable to isolate mixed-acetal intermediates from the reaction mixtures. This is not surprising given the highly acid-sensitive nature of quinone monoacetals.
- 20
- 20aM. Kirsten, J. Rehbein, M. Hiersemann, T. Strassner, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4001–4011;
- 20bC. Uyeda, E. N. Jacobsen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5062–5075.
- 21CCDC 1436770 (5 c) and 1436773 (5 s) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre.