Copper-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidative CC Bond Cleavage for CN Bond Formation: From Ketones to Amides†
Conghui Tang
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Ning Jiao
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)Search for more papers by this authorConghui Tang
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Ning Jiao
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China)Search for more papers by this authorFinancial support from the National Science Foundation of China (21325206, 21172006), the National Young Top-notch Talent Support Program, and the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (20120001110013) is greatly appreciated. We thank Yuchao Zhu in this group for reproducing the reactions of 2 f and 2 l.
Graphical Abstract
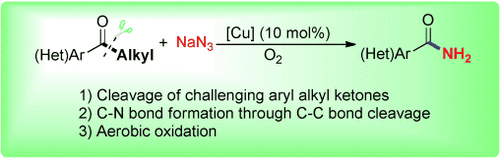
A copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative C(CO)C(alkyl) bond cleavage of aryl alkyl ketones for CN bond formation proceeds with high chemoselectivity. A series of acetophenone derivatives as well as more challenging aryl ketones with long-chain alkyl groups could be cleaved efficiently to give the corresponding amides, which are frequently found in biologically active compounds and pharmaceuticals.
Abstract
A novel copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative C(CO)C(alkyl) bond cleavage reaction of aryl alkyl ketones for CN bond formation is described. A series of acetophenone derivatives as well as more challenging aryl ketones with long-chain alkyl substituents could be selectively cleaved and converted into the corresponding amides, which are frequently found in biologically active compounds and pharmaceuticals.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201403528_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf902.9 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For reviews on CC bond cleavage, see:
- 1aR. H. Crabtree, Chem. Rev. 1985, 85, 245;
- 1bM. Murakami, Y. Ito, Top. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 3, 97;
- 1cB. Rybtchinski, D. Milstein, Angew. Chem. 1999, 111, 918;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19990401)111:7<918::AID-ANGE918>3.0.CO;2-X Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 870;10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990401)38:7<870::AID-ANIE870>3.0.CO;2-3 PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 1dC.-H. Jun, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 610;
- 1eC.-H. Jun, J.-W. Park, Top. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 24, 117;
- 1fY. J. Park, J.-W. Park, C.-H. Jun, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 222;
- 1gM. Tobisu, N. Chatani, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 300;
- 1hA. Masarwa, I. Marek, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 9712;
- 1iM. Murakami, T. Matsuda, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1100.
- 2
- 2aO. G. Kulinkovich, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2597;
- 2bM. Rubin, M. Rubina, V. Gevorgyan, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3117;
- 2cT. Seisera, N. Cramer, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2835;
- 2dC. A. Carson, M. A. Kerr, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3051;
- 2eT. Seiser, T. Saget, D. N. Tran, N. Cramer, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 7884;
10.1002/ange.201101053 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7740;
- 2fT. Seiser, N. Cramer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5340;
- 2gS. C. Bart, P. J. Chirik, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 886;
- 2hP. A. Wender, A. G. Correa, Y. Sato, R. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7815;
- 2iM. Murakami, H. Amii, K. Shigeto, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8285.
- 3
- 3aJ. W. Suggs, C.-H. Jun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 3054;
- 3bC.-H. Jun, H. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 880;
- 3cM. Gandelman, D. Milstein, Chem. Commun. 2000, 1603;
- 3dC.-H. Jun, D.-Y. Lee, H. Lee, J.-B. Hong, Angew. Chem. 2000, 112, 3214;
10.1002/1521-3757(20000901)112:17<3214::AID-ANGE3214>3.0.CO;2-T Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3070;10.1002/1521-3773(20000901)39:17<3070::AID-ANIE3070>3.0.CO;2-G CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 3eA. M. Dreis, C. J. Douglas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 412;
- 3fN. Chatani, Y. Ie, F. Kakiuchi, S. Murai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8645;
- 3gJ. Wang, W. Chen, S. Zuo, L. Liu, X. Zhang, J. Wang, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 12500; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12334;
- 3hF. D. Lewis, J. G. Magyar, J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 2102;
- 3iN. Zhang, J. Vozzolo, J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 1703;
- 3jZ.-Q. Lei, H. Li, Y. Li, X.-S. Zhang, K. Chen, X. Wang, J. Sun, Z.-J. Shi, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 2744; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2690.
- 4For reviews on aerobic oxidative reactions, see:
- 4aS. S. Stahl, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3480;
10.1002/ange.200300630 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3400;
- 4bB. M. Stoltz, Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 362;
- 4cT. Punniyamurthy, S. Velusamy, J. Iqbal, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2329;
- 4dK. M. Gligorich, M. S. Sigman, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 6764;
10.1002/ange.200602138 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6612;
- 4eM. S. Sigman, D. R. Jensen, Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 221;
- 4fJ. Muzart, Chem. Asian J. 2006, 1, 508;
- 4gE. M. Beccalli, G. Broggini, M. Martinelli, S. Sottocornola, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5318;
- 4hJ. Piera, J. E. Bäckvall, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3558;
10.1002/ange.200700604 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3506;
- 4iS. S. Stahl, Science 2005, 309, 1824;
- 4jM. J. Schultz, M. S. Sigman, Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 8227;
- 4kW. Wu, H. Jiang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1736;
- 4lZ. Shi, C. Zhang, C. Tang, N. Jiao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3381;
- 4mA. N. Campbell, S. S. Stahl, Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 851.
- 5For examples of aerobic oxidative CC and CC bond cleavage reactions, see:
- 5aT. Wang, N. Jiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11692;
- 5bR. Lin, F. Chen, N. Jiao, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4158;
- 5cM. Tokunaga, Y. Shirogane, H. Aoyama, Y. Obora, Y. Tsuji, J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5378;
- 5dY. Hayashi, M. Takeda, Y. Miyamoto, M. Shoji, Chem. Lett. 2002, 414;
- 5eC.-X. Miao, B. Yu, L.-N. He, Green Chem. 2011, 13, 541;
- 5fS.-i. Hirashima, Y. Kudo, T. Nobuta, N. Tada, A. Itoh, Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4328;
- 5gT. Yamaguchi, T. Nobuta, Y. Kudo, S.-i. Hirashima, N. Tada, T. Miura, A. Itoh, Synlett 2013, 607;
- 5hA. Wang, H. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5030;
- 5iY. Liu, F. Song, S. Guo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11332;
- 5jA. Das, R. Chaudhuri, R.-S. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2009, 4046.
- 6For examples of aerobic oxidative decarboxylation or decarbonylation reactions, see:
- 6aC. Zhang, Z. Xu, T. Shen, G. Wu, L. Zhang, N. Jiao, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2362;
- 6bB. Tiwari, J. Zhang, Y. R. Chi, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 1947; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1911;
- 6cQ. Feng, Q. Song, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 1867;
- 6dQ. Song, Q. Feng, K. Yang, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 624;
- 6eJ. Liu, Q. Liu, H. Yi, C. Qin, R. Bai, X. Qi, Y. Lan, A. Lei, Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 512; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 502;
- 6fB. Wen, Y. Li, C. Chen, W. Ma, J. Zhao, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 11859.
- 7H. Liu, C. Dong, Z. Zhang, P. Wu, X. Jiang, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 12738; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12570.
- 8L. Zhang, X. Bi, X. Guan, X. Li, Q. Liu, B.-D. Barry, P. Liao, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 11513; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11303.
- 9For recently reported examples of copper-catalyzed CC bond cleavage reactions, see:
- 9aT. Sugiishi, A. Kimura, H. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5332;
- 9bC. He, S. Guo, L. Huang, A. Lei, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8273;
- 9cS. Chiba, L. Zhang, G. Y. Ang, B. W.-Q. Hui, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2052;
- 9dM. Sai, H. Yorimitsu, K. Oshima, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 3352; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3294;
- 9eF. Chen, C. Qin, Y. Cui, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11689; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11487;
- 9fW. Zhou, Y. Yang, Y. Liu, G.-J. Deng, Green Chem. 2013, 15, 76.
- 10For previous reports on the C(CO)C(α) bond cleavage of ketones to give amides, see:
- 10aJ. Y. Becker, L. L. Miller, T. M. Siege, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 849;
- 10bK. Ishihara, T. Yano, Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1983;
- 10cY. Kuninobu, T. Uesugi, A. Kawata, K. Takai, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10590;
10.1002/ange.201104704 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10406.
- 11For recent examples of copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative reactions, see:
- 11aS. Chiba, L. Zhang, J.-Y. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7266;
- 11bH. Wang, Y. Wang, D. Liang, L. Liu, J. Zhang, Q. Zhu, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 5796; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5678;
- 11cQ. Liu, P. Wu, Y. Yang, Z. Zeng, J. Liu, H. Yi, A. Lei, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 4744; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4666;
- 11dL. Zhang, G. Y. Ang, S. Chiba, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1622;
- 11eC. Zhang, Z. Xu, L. Zhang, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11284; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11088; for mechanistic studies, see:
- 11fA. E. King, L. M. Huffman, A. Casitas, M. Costas, X. Ribas, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12068;
- 11gY.-H. Zhang, J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14654;
- 11hN. Decharin, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5732;
- 11iE. Boess, D. Sureshkumar, A. Sud, C. Wirtz, C. Fares, M. Klussmann, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8106;
- 11jK. Schröder, B. Join, A. J. Amali, K. Junge, X. Ribas, M. Costas, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 1461; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1425.
- 12
- 12aC. Tang, N. Jiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18924;
- 12bW. Zhou, L. Zhang, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 7228; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7094;
- 12cC. Qin, T. Shen, C. Tang, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 7077; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6971;
- 12dC. Tang, Y. Yuan, Y. Cui, N. Jiao, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 7480;
- 12eT. Shen, T. Wang, C. Qin, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 6809; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6677;
- 12fF. Chen, X. Huang, Y. Cui, N. Jiao, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11199;
- 12gY. Yuan, T. Shen, K. Wang, N. Jiao, Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 2932.
- 13
- 13aW. Zhu, D. Ma, Chem. Commun. 2004, 888;
- 13bJ. Andersen, U. Madsen, F. Björkling, X. Liang, Synlett 2005, 2209.
- 14
- 14aK. F. Z. Schmidt, Angew. Chem. 1923, 36, 511;
- 14bS. Lang, J. A. Murphy, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 146.
- 15
- 15aC. Zhang, C. Tang, N. Jiao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3464;
- 15bM. Gómez-Gallego, M. A. Sierra, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 4857.
- 16
- 16aH. R. Lucas, L. Li, A. A. N. Sarjeant, M. A. Vance, E. I. Solomon, K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3230;
- 16bC. Wurtele, O. Sander, V. Lutz, T. Waitz, F. Tuczek, S. Schindler, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7544;
- 16cI. Garcia-Bosch, A. Company, J. R. Frisch, M. Torrent-Sucarrat, M. Cardellach, I. Gamaba, M. Guell, L. Casella, L. Que, Jr., X. Ribas, J. M. Luis, M. Costas, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 2456;
10.1002/ange.200906749 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2406.
- 17When 1-phenylhexan-1-one was used as the substrate, pentanal was detected as a side product by mass spectrometry; the mass spectrum was carefully compared with standard MS spectra from http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry. For C(CO)C(alkyl) bond cleavage reactions of ketones with an alkyl fragment leaving as a carbonyl moiety, see: H. S. Fung, B. Z. Li, K. S. Chan, Organometallics 2012, 31, 570.