Photocatalytic Au–Bi2S3 Heteronanostructures†
The DST Swarnajayanti (DST/SJF/CSA-01/2010-2012) project is acknowledged for funding. The research group of Prof. A. K. Nandi is acknowledged for helping with the photocurrent measurements.
Graphical Abstract
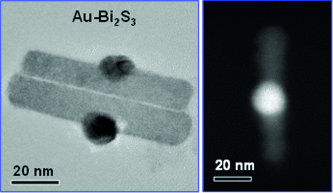
Promising returns of gold on the side: In a designed Au–Bi2S3 heteronanostructure photocatalyst, Au nanoparticles were located at the center of the semiconductor nanorods (see picture), rather than at the tip, as usually reported. These nanostructures were found to be efficient visible-light photocatalysts and to have excellent photocurrent and photoresponse properties.
Abstract
Au–Bi2S3 heteronanostructure photocatalysts were designed in which the coupling of a metal plasmon and a semiconductor exciton aids the absorption of solar light, enhances charge separation, and results in improved catalytic activity. Furthermore, these nanostructures show a unique pattern of structural combination, with Au nanoparticles positioned at the center of Bi2S3 nanorods. The chemistry of formation of these nanostructures, their epitaxy at the junction, and their photoconductance were studied, as well as their photoresponse properties.