Graphene Oxide Nanoribbons from the Oxidative Opening of Carbon Nanotubes Retain Electrochemically Active Metallic Impurities
Correction(s) for this article
-
Corrigendum: Graphene Oxide Nanoribbons from the Oxidative Opening of Carbon Nanotubes Retain Electrochemically Active Metallic Impurities
- Volume 53Issue 21Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- pages: 5233-5233
- First Published online: May 14, 2014
Colin Hong An Wong
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorChun Kiang Chua
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorBahareh Khezri
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorRichard D. Webster
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Martin Pumera
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorColin Hong An Wong
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorChun Kiang Chua
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorBahareh Khezri
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorRichard D. Webster
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Martin Pumera
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry & Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
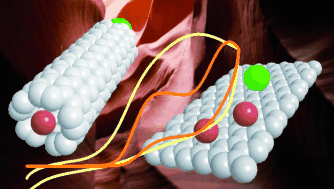
Metallic impurities: Graphene oxide nanoribbons (GONRs) are commonly synthesized using carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as a precursor (see picture). The CNTs contain significant amounts of metallic impurities even after purification. These impurities persist after oxidative opening of the CNTS to GONRs and heavily influence the electrochemical behavior of the resulting material.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201303837_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf195.6 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. K. Geim, K. S. Novoselov, Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191.
- 2M. Pumera, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4146–4157.
- 3Y. Shao, J. Wang, H. Wu, J. Liu, I. A. Aksay, H. Lin, Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036.
- 4M. Pumera, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 668–674.
- 5S. Stankovich, D. A. Dikin, G. J. B. Dommett, K. M. Kohlhaas, E. J. Zimney, E. A. Stach, R. D. Piner, S. T. Nguyen, R. S. Ruoff, Nature 2006, 442, 282–286.
- 6J. A. Rogers, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 254–255.
- 7S. Park, R. S. Ruoff, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 217–224.
- 8M. J. McAllister, J.-L. Li, D. H. Adamson, H. C. Schniepp, A. A. Abdala, J. Liu, M. Herrera-Alonso, D. L. Milius, R. Car, R. K. Prud’homme, I. A. Aksay, Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4396–4404.
- 9S. R. C. Vivekchand, C. S. Rout, K. S. Subrahmanyam, A. Govindaraj, C. N. R. Rao, J. Chem. Sci. 2008, 120, 9–13.
- 10G. X. Wang, J. Yang, J. Park, X. L. Gou, B. Wang, H. Liu, J. Yao, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8192–8195.
- 11V. C. Tung, M. J. Allen, Y. Yang, R. B. Kaner, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 25–29.
- 12H. L. Guo, X. F. Wang, Q. Y. Qian, F. B. Wang, X. H. Xia, ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2653–2659.
- 13M. Zhou, Y. Wang, Y. Zhai, J. Zhai, W. Ren, F. Wang, S. Dong, Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6116–6120.
- 14IUPAC in Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. ) [Online] (Eds.: A. D. McNaught, A. Wilkinson), Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1997. DOI: (accessed Feb 23, 2013).
- 15M. Y. Han, B. Özyilmaz, Y. Zhang, P. Kim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805.
- 16K. Nakada, M. Fujita, G. Dresselhaus, M. S. Dresselhaus, Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 17954–17961.
- 17Y.-W. Son, M. L. Cohen, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803.
- 18L. Jiao, L. Zhang, X. Wang, G. Diankov, H. Dai, Nature 2009, 458, 877–880.
- 19A. G. Cano-Márquez, F. J. Rodríguez-Macías, J. Campos-Delgado, C. G. Espinosa-González, F. Tristán-López, D. Ramírez-González, D. A. Cullen, D. J. Smith, M. Terrones, Y. I. Vega-Cantú, Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1527–1533.
- 20D. V. Kosynkin, W. Lu, A. Sinitskii, G. Pera, Z. Sun, J. M. Tour, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 968–974.
- 21A. V. Talyzin, S. Luzan, I. V. Anoshkin, A. G. Nasibulin, H. Jiang, E. I. Kauppinen, V. M. Mikoushkin, V. V. Shnitov, D. E. Marchenko, D. Noreus, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5132–5140.
- 22A. L. Elías, A. R. Botello-Méndez, D. Meneses-Rodríguez, V. J. González, D. Ramírez-González, L. Ci, E. Muñoz-Sandoval, P. M. Ajayan, H. Terrones, M. Terrones, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 366–372.
- 23D. V. Kosynkin, A. L. Higginbotham, A. Sinitskii, J. R. Lomeda, A. Dimiev, B. K. Price, J. M. Tour, Nature 2009, 458, 872–876.
- 24L. Jiao, X. Wang, G. Diankov, H. Wang, H. Dai, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 321–325.
- 25A. L. Higginbotham, D. V. Kosynkin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, J. M. Tour, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2059–2069.
- 26M. Pumera, Langmuir 2007, 23, 6453–6458.
- 27T. Kolodiazhnyi, M. Pumera, Small 2008, 4, 1476–1484.
- 28P.-X. Hou, C. Liu, H.-M. Cheng, Carbon 2008, 46, 2003–2005.
- 29X. Liu, L. Guo, D. Morris, A. B. Kane, R. H. Hurt, Carbon 2008, 46, 489–500.
- 30C. E. Banks, A. Crossley, C. Salter, S. J. Wilkins, R. G. Compton, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 2595–2599;
10.1002/ange.200600033 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2533–2537.
- 31B. Šljukić, C. E. Banks, R. G. Compton, Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1556–1558.
- 32X. Dai, G. G. Wildgoose, R. G. Compton, Analyst 2006, 131, 901–906.
- 33C. Batchelor-McAuley, G. G. Wildgoose, R. G. Compton, L. Shao, M. L. H. Green, Sens. Actuators B 2008, 132, 356–360.
- 34
- 34aA. Ambrosi, M. Pumera, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 1786–1792;
- 34bM. Pumera, A. Ambrosi, E. L. K. Chng, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 3347–3355.
- 35S.-J. Choi, J.-M. Oh, J.-H. Choy, J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 615–620.
- 36S. Koyama, Y. A. Kim, T. Hayashi, K. Takeuchi, C. Fujii, N. Kuroiwa, H. Koyama, T. Tsukahara, M. Endo, Carbon 2009, 47, 1365–1372.
- 37S. Azevedo, C. Chesman, J. R. Kaschny, Eur. Phys. J. B 2010, 74, 123–128.
- 38A. Ambrosi, C. K. Chua, B. Khezri, Z. Sofer, R. D. Webster, M. Pumera, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12899–12904.
- 39E. J. E. Stuart, M. Pumera, J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21296–21298.
- 40E. L. K. Chng, M. Pumera, Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 2304–2307.
- 41T. J. Davies, M. E. Hyde, R. G. Compton, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 5251–5256;
10.1002/ange.200462750 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5121–5126.
- 42M. Pumera, H. Iwai, J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4401–4405.