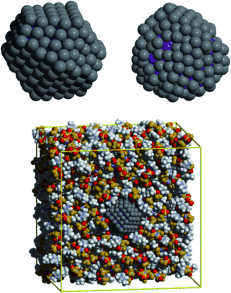
Solvation and Stabilization of Metallic Nanoparticles in Ionic Liquids†
Alfonso S. Pensado
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Agílio A. H. Pádua
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)Search for more papers by this authorAlfonso S. Pensado
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Agílio A. H. Pádua
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)
Laboratoire Thermodynamique et Interactions Moléculaires, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand & CNRS, BP 80026, 63171 Aubière (France)Search for more papers by this authorWe thank Dr. Ekaterina Izgorodina (Monash University, Australia), Dr. Patricia Hunt (Imperial College London (UK)), and Dr. Bruno Chaudret (LCC CNRS Toulouse, France) for fruitful discussions and advice. This work was supported by the Agence National de la Recherche, France (CALIST) and by the supercomputing centers IDRIS (France) and CESGA (Galicia, Spain). A.S.P. was a recipient of an Ánxeles Alvariño fellowship from Xunta de Galicia, Spain.
Graphical Abstract
Dünnhäutig: Die Solvatisierung eines metallischen Nanopartikels in der ionischen Flüssigkeit [C4C1im][Ntf2] wurde in einer Molekülsimulation mit einem spezifischen Wechselwirkungspotential untersucht. Die Grenzflächenschicht der ionischen Flüssigkeit hat eine Dicke von nur einem Ion, wodurch Stabilisierungsmechanismen auf Basis einer elektrostatischen Doppelschicht ausgeschlossen sind.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201103096_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.4 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Dupont, J. D. Scholten, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1780–1804.
- 2G. Fonseca, G. Machado, S. Teixeira, G. Fecher, J. Morais, M. C. M. Alves, J. Dupont, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 193–204.
- 3L. S. Ott, M. L. Cline, M. Deetlefs, K. R. Seddon, R. G. Finke, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5758–5759.
- 4H. S. Schrekker, M. A. Gelesky, M. P. Stracke, C. M. L. Schrekker, G. Machado, S. R. Teixeira, J. C. Rubim, J. Dupont, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 189–195.
- 5
- 5aE. Redel, R. Thomann, C. Janiak, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 14–16;
- 5bE. Redel, R. Thomann, C. Janiak, Chem. Commun. 2008, 1789–1791.
- 6
- 6aJ. N. Canongia Lopes, A. A. H. Pádua, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3330–3335;
- 6bA. Triolo, O. Russina, H.-J. Bleif, E. Di Cola, J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4641–4644.
- 7T. Gutel, C. C. Santini, K. Philippot, A. Padua, K. Pelzer, B. Chaudret, Y. Chauvin, J.-M. Basset, J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3624–3631.
- 8R. Atkin, G. G. Warr, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 5162–5168.
- 9S. Baldelli, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 421–431.
- 10
- 10aJ. Dupont, G. Fonseca, A. Umpierre, P. Fichtner, S. Teixeira, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4228–4229;
- 10bT. Welton, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2459–2477;
- 10cP. Migowski, J. Dupont, Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 32–39.
- 11J. N. C. Canongia Lopes, M. F. Costa Gomes, A. Pádua, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16816–16818.
- 12
- 12aJ. N. Canongia Lopes, J. Deschamps, A. Pádua, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2038–2047;
- 12bJ. N. Canongia Lopes, A. Pádua, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16893–16898.
- 13M. W. Finnis, J. E. Sinclair, Philos. Mag. A 1984, 50, 45–55.
- 14J. Li, L. Kong, B. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16071–16076.
- 15
- 15aK. Lee, Y. Morikawa, D. C. Langreth, Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 155461;
- 15bP. R. Schreiner, A. A. Fokin, R. A. Pascal, A. de Meijere, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3635–3638.
- 16S. Grimme, J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799.
- 17Y. Zhao, D. G. Truhlar, J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194101.
- 18Gaussian 09 (Revision A02), M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J. L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J. Montgomery, J. A., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, N. Rega, N. J. Millam, M. Klene, J. E. Knox, J. B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R. E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A. J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, V. G. Zakrzewski, G. A. Voth, P. Salvador, J. J. Dannenberg, S. Dapprich, A. D. Daniels, Ö. Farkas, J. B. Foresman, J. V. Ortiz, J. Cioslowski, D. J. Fox, , Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, USA, 2009.
- 19
- 19aA. Schaefer, H. Horn, R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577;
- 19bA. Schaefer, C. Huber, R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5829–5835.
- 20D. Andrae, U. Haeussermann, M. Dolg, H. Stoll, H. Preuss, Theor. Chem. Acc. 1990, 77, 123–141.
- 21S. F. Boys, F. Bernardi, Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566.
- 22T. A. Jachimowski, W. H. Weinberg, Surf. Sci. 1997, 372, 145–154.
- 23C. J. Hagedorn, M. J. Weiss, C.-H. Chung, P. J. Mikesell, R. D. Little, W. H. Weinberg, J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 1745–1753.
- 24F. Iori, S. Corni, J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1656–1666.
- 25
- 25aC. Pan, K. Pelzer, K. Philippot, B. Chaudret, F. Dassenoy, P. Lecante, M.-J. Casanove, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7584–7593;
- 25bS. Jansat, D. Picurelli, K. Pelzer, K. Philippot, M. Gomez, G. Muller, P. Lecante, B. Chaudret, New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 115–122.
- 26W. Smith, T. R. Forester, DL POLY 2.20, Daresbury Laboratory, UK, 2007.
- 27T. Pery, K. Pelzer, G. Buntkowsky, K. Philippot, H.-H. Limbach, B. Chaudret, ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 605–607.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.