Measurement Error in Epidemiologic Studies
5
Raymond J. Carroll,
Raymond J. Carroll
Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorRaymond J. Carroll,
Raymond J. Carroll
Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
This article concerns measurement error in epidemilogic studies, often called errors-in-variables. I discuss what measurement error is, its impact on parameter estimates and hypothesis tests, and how to perform statistical analyses that account for the measurement error.
References
- 1 Amemiya, Y. (1985). Instrumental variable estimator for the nonlinear errors in variables model, Journal of Econometrics 28, 273–289.
- 2 Amemiya, Y. (1990). Instrumental variable estimation of the nonlinear measurement error model, in Statistical Analysis of Measurement Error Models and Application, P. J. Brown & W. A. Fuller, eds. American Mathematics Society, Providence.
- 3 Amemiya, Y. & Fuller, W. A. (1988). Estimation for the nonlinear functional relationship, Annals of Statistics 16, 147–160.
- 4 Armstrong, B. (1985). Measurement error in generalized linear models, Communications in Statistics, Part B—Simulation and Computation 14, 529–544.
- 5 Armstrong, B. G., Whittemore, A. S. & Howe, G. R. (1989). Analysis of case-control data with covariate measurement error: application to diet and colon cancer, Statistics in Medicine 8, 1151–1163.
- 6 Berkson, J. (1950). Are there two regressions?, Journal of the American Statistical Association 45, 164–180.
- 7 Breslow, N. E. & Cain, K. C. (1988). Logistic regression for two-stage case-control data, Biometrika 75, 11–20.
- 8 Buonaccorsi, J. P. (1988). Errors in variables with systematic biases, Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 18, 1001–1021.
- 9 Buonaccorsi, J. P. (1990). Double sampling for exact values in some multivariate measurement error problems, Journal of the American Statistical Association 85, 1075–1082.
- 10 Buonaccorsi, J. P. (1990). Double sampling for exact values in the normal discriminant model with application to binary regression, Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 19, 4569–4586.
- 11 Buonaccorsi, J. P. (1991). Measurement error, linear calibration and inferences for means, Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 11, 239–257.
- 12 Buonaccorsi, J. P. & Tosteson, T. (1993). Correcting for nonlinear measurement error in the dependent variable in the general linear model, Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 22, 2687–2702.
- 13 Buzas, J. S. & Stefanski, L. A. (1995). A note on corrected score estimation, Statistics and Probability Letters 28, 1–8.
- 14 Carroll, R. J. & Ruppert, D. (1988). Transformation and Weighting in Regression. Chapman & Hall, London.
- 15 Carroll, R. J. & Ruppert, D. (1996). The use and misuse of orthogonal regression in measurement error models, American Statistician 50, 1–6.
- 16 Carroll, R. J. & Stefanski, L. A. (1990). Approximate quasilikelihood estimation in models with surrogate predictors, Journal of the American Statistical Association 85, 652–663.
- 17 Carroll, R. J. & Stefanski, L. A. (1994). Measurement error, instrumental variables and corrections for attenuation with applications to meta-analyses, Statistics in Medicine 13, 1265–1282.
- 18 Carroll, R. J., Gail, M. H. & Lubin, J. H. (1993). Case-control studies with errors in predictors, Journal of the American Statistical Association 88, 177–191.
- 19 Carroll, R. J., Gallo, P. P. & Gleser, L. J. (1985). Comparison of least squares and errors-in-variables regression, with special reference to randomized analysis of covariance, Journal of the American Statistical Association 80, 929–932.
- 20
Carroll, R. J.,
Ruppert, D. &
Stefanski, L. A.
(1995).
Measurement Error in Nonlinear Models.
Chapman & Hall,
London.
10.1007/978-1-4899-4477-1 Google Scholar
- 21 Carroll, R. J., Wang, S. & Wang, C. Y. (1995). Asymptotics for prospective analysis of stratified logistic case-control studies, Journal of the American Statistical Association 90, 157–169.
- 22 Carroll, R. J., Küchenhoff, H., Lombard, F. & Stefanski, L. A. (1996). Asymptotics for the SIMEX estimator in structural measurement error models, Journal of the American Statistical Association 91, 242–250.
- 23 Carroll, R. J., Spiegelman, C., Lan, K. K., Bailey, K. T. & Abbott, R. D. (1984). On errors-in-variables for binary regression models, Biometrika 71, 19–26.
- 24 Casella, G. & George, E. I. (1992). Explaining the Gibbs sampler, American Statistician 46, 167–174.
- 25 Clayton, D. G. (1991). Models for the analysis of cohort and case-control studies with inaccurately measured exposures, in Statistical Models for Longitudinal Studies of Health, J. H. Dwyer, M. Feinleib, P. Lipsert et al., eds. Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 301–331.
- 26 Cook, J. & Stefanski, L. A. (1995). A simulation extrapolation method for parametric measurement error models, Journal of the American Statistical Association 89, 1314–1328.
- 27
Crouch, E. A. &
Spiegelman, D.
(1990).
The evaluation of integrals of the form
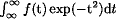 : applications to logistic-normal models,
Journal of the American Statistical Association
85,
464–467.
: applications to logistic-normal models,
Journal of the American Statistical Association
85,
464–467.
- 28 Dosemeci, M., Wacholder, S. & Lubin, J. H. (1990). Does non-differential misclassification of exposure always bias a true effect towards the null value?, American Journal of Epidemiology 132, 746–748.
- 29
Freedman, L. S.,
Carroll, R. J. &
Wax, Y.
(1991).
Estimating the relationship between dietary intake obtained from a food frequency questionnaire and true average intake,
American Journal of Epidemiology
134,
510–520.
10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116086 Google Scholar
- 30
Fuller, W. A.
(1987).
Measurement Error Models.
Wiley,
New York.
10.1002/9780470316665 Google Scholar
- 31 Ganse, R. A., Amemiya, Y. & Fuller, W. A. (1983). Prediction when both variables are subject to error, with application to earthquake magnitude, Journal of the American Statistical Association 78, 761–765.
- 32 Gleser, L. J. (1981). Estimation in multivariate errors in variables regression model: large sample results, Annals of Statistics 9, 24–44.
- 33
Gleser, L. J.
(1990).
Improvements of the naive approach to estimation in nonlinear errors-in-variables regression models, in
Statistical Analysis of Measurement Error Models and Application,
P. J. Brown &
W. A. Fuller, eds.
American Mathematical Society,
Providence.
10.1090/conm/112/1087101 Google Scholar
- 34 Greenland, S. (1980). The effect of misclassification in the presence of covariates, American Journal of Epidemiology 112, 564–569.
- 35 Greenland, S. & Robins, J. M. (1985). Confounding and misclassification, American Journal of Epidemiology 122, 495–506.
- 36 Hughes, M. D. (1993). Regression dilution in the proportional hazards model, Biometrics 49, 1056–1066.
- 37 Hunter, D. J., Spiegelman, D., Adami, H.-O., Beeson, L., van der Brandt, P. A., Folsom, A. R., Fraser, G. E., Goldbohm, A., Graham, S., Howe, G. R., Kushi, L. H., Marshall, J. R., McDermott, A., Miller, A. B., Speizer, F. E., Wolk, A., Yaun, S. S. & Willett, W. (1996). Cohort studies of fat intake and the risk of breast cancer-a pooled analysis, New England Journal of Medicine 334, 356–361.
- 38
Küchenhoff, H. &
Carroll, R. J.
(1997).
Segmented regression with errors in predictors: semiparametric and parametric methods,
Statistics in Medicine
16,
169–188.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970130)16:2<169::AID-SIM478>3.0.CO;2-M CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 39 Kuha, J. (1994). Corrections for exposure measurement error in logistic regression models with an application to nutritional data, Statistics in Medicine 13, 1135–1148.
- 40
Kuha, J.
(1997).
Estimation by data augmentation in regression models with continuous and discrete covariates measured with error,
Statistics in Medicine
16,
189–201.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970130)16:2<189::AID-SIM479>3.0.CO;2-H CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 41 Li, L., Freedman, L., Kipnis, V. & Carroll, R. J. (1997). Effects of bias and correlated measurement errors in the validation of food frequency questionnaires. Preprint.
- 42 Little, R. J. A. & Rubin, D. B. (1987). Statistical Analysis with Missing Data. Wiley, New York.
- 43 Liu, X. & Liang, K. Y. (1992). Efficacy of repeated measures in regression models with measurement error, Biometrics 48, 645–654.
- 44 MacMahon, S., Peto, R., Cutler, J., Collins, R., Sorlie, P., Neaton, J., Abbott, R., Godwin, J., Dyer, A. & Stamler, J. (1990). Blood pressure, stroke and coronary heart disease: Part 1, prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias, Lancet 335, 765–774.
- 45 Mallick, B. K. & Gelfand, A. E. (1996). Semiparametric errors-in-variables models: a Bayesian approach, Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 52, 307–322.
- 46 Michalek, J. E. & Tripathi, R. C. (1980). The effect of errors in diagnosis and measurement on the probability of an event, Journal of the American Statistical Association 75, 713–721.
- 47 Müller, P. & Roeder, K. (1997). A Bayesian semiparametric model for case-control studies with errors in variables, Biometrika 84, 523–537.
- 48 Nakamura, T. (1990). Corrected score functions for errors-in-variables models: methodology and application to generalized linear models, Biometrika 77, 127–137.
- 49 Nakamura, T. (1992). Proportional hazards models with covariates subject to measurement error, Biometrics 48, 829–838.
- 50 Pepe, M. S., Self, S. G. & Prentice, R. L. (1989). Further results in covariate measurement errors in cohort studies with time to response data, Statistics in Medicine 8, 1167–1178.
- 51 Pierce, D. A., Stram, D. O., Vaeth, M. & Schafer, D. (1992). Some insights into the errors in variables problem provided by consideration of radiation dose-response analyses for the A-bomb survivors, Journal of the American Statistical Association 87, 351–359.
- 52 Prentice, R. L. (1982). Covariate measurement errors and parameter estimation in a failure time regression model, Biometrika 69, 331–342.
- 53 Prentice, R. L. (1989). Surrogate endpoints in clinical trials: definition and operational criteria, Statistics in Medicine 8, 431–440.
- 54 Prentice, R. L. (1996). Dietary fat and breast cancer: measurement error and results from analytic epidemiology, Journal of the National Cancer Institute 88, 1738–1747.
- 55 Prentice, R. L. & Pyke, R. (1979). Logistic disease incidence models and case-control studies, Biometrika 66, 403–411.
- 56 Racine-Poon, A., Weihs, C. & Smith, A. F. M. (1991). Estimation of relative potency with sequential dilution errors in radioimmunoassay, Biometrics 47, 1235–1246.
- 57 Richardson, S. & Gilks, W. R. (1993). A Bayesian approach to measurement error problems in epidemiology using conditional independence models, American Journal of Epidemiology 138, 430–442.
- 58 Roeder, K., Carroll, R. J. & Lindsay, B. G. (1996). A nonparametric mixture approach to case-control studies with errors in covariables, Journal of the American Statistical Association 91, 722–732.
- 59 Rosner, B., Spiegelman, D. & Willett, W. C. (1990). Correction of logistic regression relative risk estimates and confidence intervals for measurement error: the case of multiple covariates measured with error, American Journal of Epidemiology 132, 734–745.
- 60 Rosner, B., Willett, W. C. & Spiegelman, D. (1989). Correction of logistic regression relative risk estimates and confidence intervals for systematic within-person measurement error, Statistics in Medicine 8, 1051–1070.
- 61 Rudemo, M., Ruppert, D. & Streibig, J. C. (1989). Random effect models in nonlinear regression with applications to bioassay, Biometrics 45, 349–362.
- 62 Satten, G. A. & Kupper, L. L. (1993). Inferences about exposure-disease association using probability of exposure information, Journal of the American Statistical Association 88, 200–208.
- 63 Schafer, D. (1987). Covariate measurement error in generalized linear models, Biometrika 74, 385–391.
- 64 Schafer, D. (1993). Likelihood analysis for probit regression with measurement errors, Biometrika 80, 899–904.
- 65 Schmid, C. H. & Rosner, B. (1993). A Bayesian approach to logistic regression models having measurement error following a mixture distribution, Statistics in Medicine 12, 1141–1153.
- 66 Smith, A. F. M. & Gelfand, A. E. (1992). Bayesian statistics without tears: a sampling-resampling perspective, American Statistician 46, 84–88.
- 67 Stefanski, L. A. (1985). The effects of measurement error on parameter estimation, Biometrika 72, 583–592.
- 68 Stefanski, L. A. (1989). Unbiased estimation of a nonlinear function of a normal mean with application to measurement error models, Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 18, 4335–4358.
- 69 Stefanski, L. A. & Buzas, J. S. (1995). Instrumental variable estimation in binary regression measurement error models, Journal of the American Statistical Association 90, 541–549.
- 70 Stefanski, L. A. & Carroll, R. J. (1985). Covariate measurement error in logistic regression, Annals of Statistics 13, 1335–1351.
- 71 Stefanski, L. A. & Carroll, R. J. (1987). Conditional scores and optimal scores in generalized linear measurement error models, Biometrika 74, 703–716.
- 72 Stefanski, L. A. & Carroll, R. J. (1990). Structural logistic regression measurement error models, in Proceedings of the Conference on Measurement Error Models, P. J. Brown & W. A. Fuller, eds. Wiley, New York.
- 73 Stefanski, L. A. & Cook, J. (1995). Simulation extrapolation: the measurement error jackknife, Journal of the American Statistical Association 90, 1247–1256.
- 74 Stephens, D. A. & Dellaportas, P. (1992). Bayesian analysis of generalized linear models with covariate measurement error, in Bayesian Statistics 4, J. M. Bernado, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid & A. F. M. Smith, eds. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 813–820.
- 75
Tanner, M. A.
(1993).
Tools for Statistical Inference: Methods for the Exploration of Posterior Distributions and Likelihood Functions,
2nd Ed.
Springer-Verlag,
New York.
10.1007/978-1-4684-0192-9 Google Scholar
- 76 Thomas, D., Stram, D. & Dwyer, J. (1993). Exposure measurement error: influence on exposure-disease relationships and methods of correction, Annual Review of Public Health 14, 69–93.
- 77 Titterington, D. M., Smith, A. F. M. & Makov, U. E. (1985). Statistical Analysis of Finite Mixture Distributions. Wiley, New York.
- 78 Tosteson, T., Stefanski, L. A. & Schafer D. W. (1989). A measurement error model for binary and ordinal regression, Statistics in Medicine 8, 1139–1147.
- 79 Tosteson, T. & Tsiatis, A. (1988). The asymptotic relative efficiency of score tests in a generalized linear model with surrogate covariates, Biometrika 75, 507–514.
- 80 Tosteson, T. D. & Ware, J. H. (1990). Designing a logistic regression study using surrogate measures of exposure and outcome, Biometrika 77, 11–20.
- 81 Wang, N., Carroll, R. J. & Liang, K. Y. (1996). Quasilikelihood and variance functions in measurement error models with replicates, Biometrics 52, 401–411.
- 82 Weinberg, C. R. & Wacholder, S. (1993). Prospective analysis of case-control data under general multiplicative-intercept models, Biometrika 80, 461–465.
- 83 Whittemore, A. S. (1989). Errors in variables regression using Stein estimates, American Statistician 43, 226–228.
- 84 Whittemore, A. S. & Gong, G. (1991). Poisson regression with misclassified counts: application to cervical cancer mortality rates, Applied Statistics 40, 81–93.
- 85 Whittemore, A. S. & Keller, J. B. (1988). Approximations for regression with covariate measurement error, Journal of the American Statistical Association 83, 1057–1066.
- 86 Wittes, J., Lakatos, E. & Probstfield, J. (1989). Surrogate endpoints in clinical trials: cardiovascular trials, Statistics in Medicine 8, 415–425.
- 87 Zhao, L. P. & Lipsitz, S. (1992). Designs and analysis of two-stage studies, Statistics in Medicine 11, 769–782.



