Pathological features of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease in transbronchial cryobiopsies
Abstract
Aim
Transbronchial cryobiopsies are increasingly used for the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD), but there is a lack of published information on the features of specific ILD in cryobiopsies. Here we attempt to provide pathological guidelines for separating usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (FHP) and connective tissue disease-associated ILD (CTD–ILD) in cryobiopsies.
Methods
We examined 120 cryobiopsies from patients with multidisciplinary discussion (MDD)-established CTD–ILD and compared them to a prior series of 121 biopsies from patients with MDD-established IPF or FHP.
Results
A non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) pattern alone was seen in 36 of 120 (30%) CTD–ILD, three of 83 (3.6%) FHP and two of 38 (5.2%) IPF cases, statistically favouring a diagnosis of CTD–ILD. The combination of NSIP + OP was present in 29 of 120 (24%) CTD–ILD, two of 83 (2.4%) FHP and none of 38 (0%) IPF cases, favouring a diagnosis of CTD–ILD. A UIP pattern, defined as fibroblast foci plus any of patchy old fibrosis/fibrosis with architectural distortion/honeycombing, was identified in 28 of 120 (23%) CTD–ILD, 45 of 83 (54%) FHP and 27 of 38 (71%) IPF cases and supported a diagnosis of FHP or IPF. The number of lymphoid aggregates/mm2 and fibroblast foci/mm2 was not different in IPF, CTD–ILD or FHP cases with a UIP pattern. Interstitial giant cells supported a diagnosis of FHP or CTD–ILD over IPF, but were infrequent.
Conclusions
In the correct clinical/radiological context the pathological findings of NSIP, and particularly NSIP plus OP, favour a diagnosis of CTD–ILD in a cryobiopsy, but CTD–ILD with a UIP pattern, FHP with a UIP pattern and IPF generally cannot be distinguished.
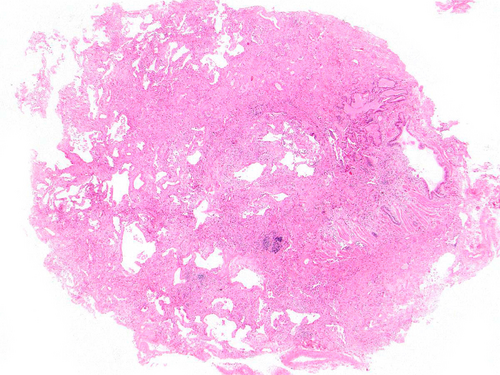
Graphical Abstract
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) in a transbronchial cryobiopsy from a patient with an underlying connective tissue disease (CTD). UIP is one of the patterns seen in cryobiopsies from CTD patients and usually is not separable from UIP in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in this type of biopsy.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.