Marginal screening of 2 × 2 tables in large-scale case-control studies
Summary
Assessing the statistical significance of risk factors when screening large numbers of 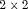 tables that cross-classify disease status with each type of exposure poses a challenging multiple testing problem. The problem is especially acute in large-scale genomic case-control studies. We develop a potentially more powerful and computationally efficient approach (compared with existing methods, including Bonferroni and permutation testing) by taking into account the presence of complex dependencies between the
tables that cross-classify disease status with each type of exposure poses a challenging multiple testing problem. The problem is especially acute in large-scale genomic case-control studies. We develop a potentially more powerful and computationally efficient approach (compared with existing methods, including Bonferroni and permutation testing) by taking into account the presence of complex dependencies between the 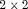 tables. Our approach gains its power by exploiting Monte Carlo simulation from the estimated null distribution of a maximally selected log-odds ratio. We apply the method to case-control data from a study of a large collection of genetic variants related to the risk of early onset stroke.
tables. Our approach gains its power by exploiting Monte Carlo simulation from the estimated null distribution of a maximally selected log-odds ratio. We apply the method to case-control data from a study of a large collection of genetic variants related to the risk of early onset stroke.



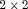 table with fixed margins
table with fixed margins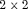 tables
tables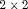 tables
tables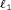 –penalized likelihood models
–penalized likelihood models
