Determination of MoCA Cutoff Score in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorders
Valérie Ewert
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Search for more papers by this authorStéphanie Pelletier
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Inserm U1018, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorRégis Alarcon
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bertrand Nalpas
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Département d'Information Scientifique et de Communication (DISC), Inserm, Paris, France
Reprint requests: Bertrand Nalpas, MD, PhD, Service d'Addictologie & Inserm DISC, CHU Caremeau, Place du Pr R. Debré, 30029 Nîmes, France; Tel.: +33 (0)4 66 68 72 14; Fax: 33 (0)4 66 68 69 46; E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHélène Donnadieu-Rigole
Service Addictologie, Hôpital Saint-Eloi, CHU Montpellier, Montpellier, France
Inserm, U1183, IRMB, Hôpital Saint-Eloi, CHU Montpellier, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorRaphaël Trouillet
Université Paul Valery-Montpellier3, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorPascal Perney
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Inserm U1018, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorValérie Ewert
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Search for more papers by this authorStéphanie Pelletier
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Inserm U1018, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorRégis Alarcon
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bertrand Nalpas
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Département d'Information Scientifique et de Communication (DISC), Inserm, Paris, France
Reprint requests: Bertrand Nalpas, MD, PhD, Service d'Addictologie & Inserm DISC, CHU Caremeau, Place du Pr R. Debré, 30029 Nîmes, France; Tel.: +33 (0)4 66 68 72 14; Fax: 33 (0)4 66 68 69 46; E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHélène Donnadieu-Rigole
Service Addictologie, Hôpital Saint-Eloi, CHU Montpellier, Montpellier, France
Inserm, U1183, IRMB, Hôpital Saint-Eloi, CHU Montpellier, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorRaphaël Trouillet
Université Paul Valery-Montpellier3, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorPascal Perney
Service Addictologie, Hôpital du Grau du Roi, CHU Caremeau, Nîmes, France
Inserm U1018, Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Background
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) score is a convenient and promising tool for estimating alcoholic patients’ global cognitive functioning, a major challenge for all specialized alcohol treatment centers. However, whether or not the score should be corrected for education level and whether the proposed cutoff is relevant in patients with alcohol use disorders (AUD) should be determined.
Methods
We compared the MoCA scores in patients hospitalized for AUD with and without cognitive impairment assessed by a battery of neuropsychological (NP) tests. Sensitivity, specificity, and cutoff of the MoCA score were analyzed using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
Results
Thirty-one patients with and 25 without cognitive impairment were included in the study. There were 40 men and 16 women, with a mean age of 49.5 years. The mean uncorrected MoCA score was 23.1 ± 3.3 in those with and 27.0 ± 1.9 in those without cognitive impairment. NP tests were significantly correlated with the MoCA score. Uncorrected MoCA scores identified more than 80% of the patients with a cutoff score equal to 26, to obtain similar accuracy with the corrected score required using a cutoff score equal to 27.
Conclusions
Our results confirm that the MoCA test is a convenient and reliable screening tool to measure cognition defects in alcoholic patients. As using the 1-point education adjustment increases the cutoff score by 1 point, it is suggested to use the noncorrected score and the usual cutoff, that is, 26. Being easy to administer and only moderately time-consuming, the MoCA score should be used extensively in addiction treatment centers.
Graphical Abstract
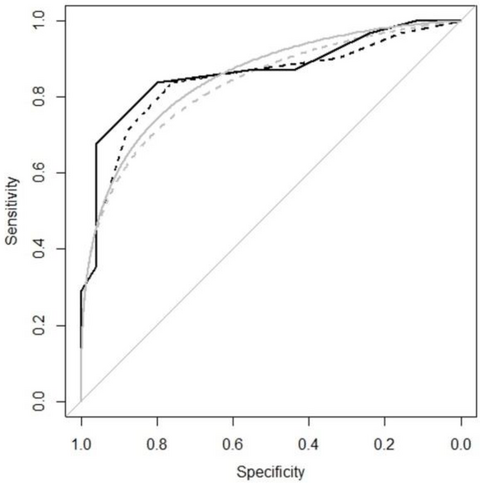
We determined the best cutoff of the MoCA screening tool of cognition defects in alcoholics. It can be used with or without correction for education level. However, as using the correction increases the cutoff score by one point, it is suggested that the uncorrected score be used with the usual cutoff, i.e. 26. [ROC analysis for the corrected (empirical and smoothed = black and gray dotted lines) (AUC = 0.84; p < 0.001) and the uncorrected MoCA scores (black and gray full lines) (AUC = 0.87; p < 0.001)].
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Alarcon R, Nalpas B, Pelletier S, Perney P (2015) MoCA as a screening tool of neuropsychological deficits in alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39: 1042–1048.
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington,VA.
10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 Google Scholar
- Ball J, Carrington MJ, Stewart S (2013) Mild cognitive impairment in high-risk patients with chronic atrial fibrillation: a forgotten component of clinical management? Heart 99: 542–547.
- Bates ME, Buckman JF, Nguyen TT (2013) A role for cognitive rehabilitation in increasing the effectiveness of treatment for alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychol Rev 23: 27–47.
- Brown DS, Bernstein IH, McClintock SM, Munro Cullum C, Dewey RB Jr, Husain M, Lacritz LH (2016) Use of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Alzheimer's disease-8 as cognitive screening measures in Parkinson's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 31: 264–272.
- Cameron J, Worral-Carter L, Page K, Stewart S, Ski CF (2013) Screening for mild cognitive impairment in patients with heart failure: Montreal Cognitive Assessment versus mini mental state exam. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 12: 252–260.
- Cardebat D, Doyon B, Puel M, Goulet P, Joanette Y (1990) Formal and semantic lexical evocation in normal subjects. Performance and dynamics of production as a function of sex, age and educational level. Acta Neurol Belg 90: 207–217.
- Chanraud S, Martelli C, Delain F, Kostogianni N, Douau G, Aubin HJ, Reynaud M, Martinot JL (2007) Brain morphometry and cognitive performance in detoxified alcohol-dependents with preserved psychosocial functioning. Neuropsychopharmacology 32: 429–438.
- Chen L, Yu C, Fu X, Liu W, Hua P, Zhang N, Kuo S (2013) Using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale to screen for dementia in Chinese patients with Parkinson's Disease. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry 25: 296–305.
- Chou KL, Lenhart A, Koeppe RA, Bohnen NI (2014) Abnormal MoCA and normal range MMSE scores in Parkinson disease without dementia: cognitive and neurochemical correlates. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20: 1076–1080.
- Copersino ML, Fals-Stewart W, Fitzmaurice G, Schretlen DJ, Sokoloff J, Weiss RD (2009) Rapid cognitive screening of patients with substance use disorders. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 17: 337–344.
- Copersino ML, Schretlen DJ, Fitzmaurice G, Lukas SE, Faberman J, Sokoloff J, Weiss RD (2012) Effects of cognitive impairment on substance abuse treatment attendance: predictive validation of a brief cognitive screening measure. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 38: 246–250.
- Dalrymple-Alford JC, MacAskill MR, Nakas CT, Livingston LL, Graham CC, Crucian GP, Melzer TR, Kirwan J, Keenan R, Wells S, Porter RJ, Watts R, Anderson TJ (2010) The MoCA: well-suited screen for cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 75: 1717–1725.
- Davies SJ, Pandit SA, Feeney A, Stevenson BJ, Kerwin RW, Nutt DJ, Marshall EJ, Boddington S, Lingford-Huhes A (2005) Is there cognitive impairment in clinically ‘healthy’ abstinent alcohol dependence? Alcohol Alcohol 40: 498–503.
- Delis DC, Freeland J, Kramer JH, Kaplan E (1988) Integrating clinical assessment with cognitive neuroscience: construct validation of the California Verbal Learning Test. J Consult Clin Psychol 56: 123–130.
- Fagerström KO (1978) Measuring degree of physical dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of treatment. Addict Behav 3: 235–241.
- Fama R, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV (2004) Perceptual learning in detoxified alcoholic men: contributions from explicit memory, executive function, and age. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28: 1657–1665.
- Fein G, Bachman L, Fisher S, Davenport L (1990) Cognitive impairments in abstinent alcohol dependent patients. West J Med 152: 531–537.
- Fengler S, Kessler J, Timmermann L, Zapf A, Elben S, Wojtecki L, Tucha O, Kalbe E (2016) Screening for cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: improving the diagnostic utility of the MoCA through subtest weighting. PLoS One 11: e0159318.
- Fitzpatrick LE, Crowe SF (2013) Cognitive and emotional deficits in chronic alcoholics: a role for the cerebellum? Cerebellum 12: 520–533.
- Goldstein RZ, Leskovjan AC, Hoff AL, Hitzemann R, Bashan F, Khalsa SS, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Volkow ND (2004) Severity of neuropsychological impairment in cocaine and alcohol addiction: association with metabolism in the prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychologia 42: 1447–1458.
- Green A, Garrick T, Sheedy D, Blake H, Shores EA, Harper C (2010) The effect of moderate to heavy alcohol consumption on neuropsychological performance as measured by the repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34: 443–450.
- Groupe de Réflexion sur l'Evaluation des Fonctions Exécutives (2001) L’évaluation des fonctions exécutives en pratique clinique. Rev Neuropsychol 11: 383–434.
- Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6: 65–70.
- Ihara H, Berrios GE (2000) Group and case study of the dysexecutive syndrome in alcoholism without amnesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68: 731–737.
- Le Berre AP, Pinon K, Vabret F, Pitel AL, Allain P, Eustache F, Beaunieux H (2010) Study of metamemory in patients with chronic alcoholism using a feeling-of-knowing episodic memory task. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34: 1888–1898.
- Lezak MD, Howison DB, Bigler ED, Tranel D (2012) Neuropsychological Assessment. 5th ed. Oxford University Press, New York, NY.
- Likhitsathian S, Uttawichai K, Booncharoen H, Wittayanookulluk A, Angkurawaranon C, Srisurapanont M (2013) Topiramate treatment for alcohol dependent outpatients recently receiving residential treatment programs: a 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Alcohol Depend 133: 440–446.
- Lusins J, Zimberg S, Smokler H, Gurley K (1980) Alcoholism and cerebral atrophy: a study of 50 patients with CT scan and psychologic testing. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 4: 406–411.
- Martin PR, Adinoff B, Weingartner H, Mukherjee AB, Eckardt MJ (1986) Alcohol dependent patients organic brain disease: nosology and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 10: 147–164.
- Mechtcheriakov S, Brenneis C, Egger K, Koppelstaetter F, Schocke M, Marksteiner J (2007) A widespread distinct pattern of cerebral atrophy in patients with alcohol addiction revealed by voxel-based morphometry. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78: 610–614.
- Monnig MA, Tonigan JS, Yeo RA, Thoma RJ, McCrady BS (2013) White matter volume in alcohol use disorders: a meta-analysis. Addict Biol 18: 581–592.
- Nalpas B, Combescure C, Pierre B, Ledent T, Gillet C, Playoust D, Danel T, Bozonnat MC, Martin S, Balmes JL, Daures JP (2003) Financial costs of alcoholism treatment programs: a longitudinal and comparative evaluation between four specialised centres. Alcoholism Clin Exp Res 27: 51–56.
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, Cummings JL, Chertkow H (2005) The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatric Soc 53: 695–699.
- Nixon SJ, Lawton-Craddock A, Tivis R, Ceballos N (2007) Nicotine's effects on attentional efficiency in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31: 2083–2091.
- Noël X, Paternot J, van der Linden M, Sferrazza R, Verhas M, Hanak C, Kornreich C, Martin P, de Mol J, Pelc I, Verbanck P (2001) Correlation between inhibition, working memory and delimited frontal area blood flow measured by 99MTc-bicisate spect in alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Alcohol 36: 556–563.
- Noël X, Sferrazza R, van der Linden M, Paternot J, Verhas M, Hanak C, Pelc I, Verbranck P (2002) Contribution of frontal cerebral blood flow measured by 99MTc-bicisate spect and executive function deficits to predicting treatment outcome in alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 347–354.
- Osterrieth PA (1944) Le test de copie d'une figure complexe; contribution à l’étude de la perception et de la mémoire. Arch Psychol 30: 206–356.
- Pelletier S, Nalpas B, Régis Alarcon R, Hélène Rigole R, Perney P (2016) Investigation of Cognitive Improvement in alcohol-dependent inpatients using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Score. J Addict 2016: 1539096.
- Pelletier S, Vaucher E, Aider R, Martin S, Perney P, Balmes Jl, Nalpas B (2002) Wine consumption is not associated with a decreased risk of alcoholic cirrhosis in heavy drinkers. Alcohol Alcohol 37: 618–621.
- Pitel AL, Beaunieux H, Witkowski T, Vabret F, de la Sayette V, Viader F, Desgranges B, Eustache F (2008) Episodic and working memory deficits in alcohol dependent patients Korsakoff patients: the continuity theory revisited. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32: 1229–1241.
- R Core Team (2013) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (URL http://www.R-project.org/).
- Rando K, Hong KI, Bhagwagar Z, Ray Li CS, Bergquist K, Guarnaccia J, Sinha R (2011) Association of frontal and posterior cortical gray matter volume with time to alcohol relapse: a prospective study. Am J Psychiatry 168: 183–192.
- Reitan RM (1958) The validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 8: 271–276.
10.2466/pms.1958.8.3.271 Google Scholar
- Revelle W (2015) Procedures for psychological, psychometric, and personality research (R package “Psych” version 1.5–8). Available at: http://personality-project.org/r/psych. Accessed September 4, 2017.
- Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, Müller M (2016) Display and analyze ROC curves (R package pROC version 1.8). Available at: http://expasy.org/tools/pROC/. Accessed September 4, 2017.
- Rodriguez-Alvarez MX, Roca-Pardinas J (2017) Kernel-based nonparametric roc regression modelling (R package npROCRegression version 1.0-5). Available at: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=npROCRegression. Accessed September 4, 2017.
- Rossetti HC, Lacritz LH, Cullum CM, Weiner MF (2011) Normative date for the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in the population-based sample. Neurology 77: 1272–1275.
- Rupp CI, Beck JK, Heinz A, Kemmler G, Manz S, Tempel K, Fleischhacker WW (2016) Impulsivity and alcohol dependence treatment completion: Is there a neurocognitive risk factor at treatment entry? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40: 152–160.
- Sanhueza C, Garcia-Moreno LM, Exposito J (2011) Weekend alcoholism in youth and neurocognitive aging. Psicothema 23: 209–214.
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB (1973) A self feedback technique to monitor drinking behavior in alcoholics. Behav Res Therapy 11: 237–238.
- Sorg SF, Taylor MJ, Alhassoon OM, Gongvatana A, Theilmann RJ, Frank LR, Grant I (2012) Frontal white matter integrity predictors of adult alcohol treatment outcome. Biol Psychiatry 71: 262–268.
- Stavro K, Pelletier J, Potvin S (2013) Widespread and sustained cognitive deficits in alcoholism: a meta-analysis. Addict Biol 18: 203–213.
- Stroop J (1935) Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18: 643–662.
- Tan JP, Li N, Gao J, Wang LN, Zhao YM, Yu BC, Du W, Zhang WJ, Cui LQ, Wang QS, Li JJ, Yang JS, Yu JM, Xia XN, Zhou PY (2015) Optimal cutoff scores for dementia and mild cognitive impairment of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment among elderly and oldest-old Chinese population. J Alzheimers Dis 43: 1403–1412.
- Tombaugh TN (2004) Trail Making Test A and B: normative data stratified by age and education. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 19: 203–214.
- Wechsler D (2011) WAIS-IV Echelle d'intelligence de Wechsler pour adultes-quatrième édition. Centre de psychologie appliquée, Paris, France.
- Wester AJ, Westhoff J, Kessels RP, Egger JI (2013) The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) as a measure of severity of amnesia in patients with alcohol-related cognitive impairments and Korsakoff syndrome. Clin Neuropsychiatry 10: 134–141.
- Youden J (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3: 32–35.
10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<32::AID-CNCR2820030106>3.0.CO;2-3 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Zinn S, Stein R, Swartzwelder HS (2004) Executive functioning early in abstinence from alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28: 1338–1346.
- Zorumski CF, Mennerick S, Izumi Y (2014) Acute and chronic effects of ethanol on learning-related synaptic plasticity. Alcohol 48: 1–17.
- Zuo L, Dong Y, Zhu R, Jin Z, Li Z, Wang Y, Zhao X, Sachdev P, Zhang W, Wang Y (2016) Screening for cognitive impairment with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in Chinese patients with acute mild stroke and transient ischemic attack: a validation study. BMJ Open 6: e011310.