Enhanced Infrared Neural Stimulation using Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanorods
Kyungsik Eom
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, 151–744 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJinhyung Kim
Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine Yonsei University, Seoul, 120–752 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJong Min Choi
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, 446–701 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorTaekyeong Kang
Department of Electronics Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJin Woo Chang
Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine Yonsei University, Seoul, 120–752 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kyung Min Byun
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, 446–701 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sang Beom Jun
Department of Electronics Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sung June Kim
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, 151–744 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorKyungsik Eom
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, 151–744 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJinhyung Kim
Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine Yonsei University, Seoul, 120–752 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJong Min Choi
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, 446–701 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorTaekyeong Kang
Department of Electronics Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorJin Woo Chang
Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine Yonsei University, Seoul, 120–752 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kyung Min Byun
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Kyung Hee University, Yongin, 446–701 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sang Beom Jun
Department of Electronics Engineering, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 120–750 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sung June Kim
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, 151–744 Republic of Korea
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
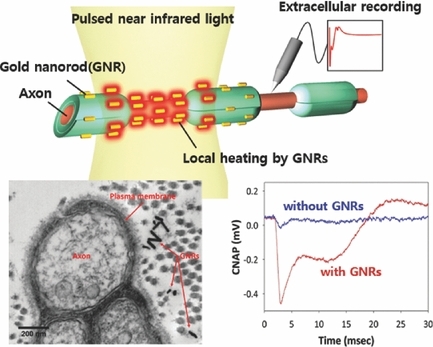
An advanced optical activation of neural tissues is demonstrated using pulsed infrared light and plasmonic gold nanorods. Photothermal effect localized in plasma membrane triggers action potentials of in vivo neural tissues. Compared with conventional infrared stimulation, the suggested method can increase a neural responsivity and lower a threshold stimulation level significantly, thereby reducing a requisite radiant exposure and the concern of tissue damage.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| smll201400599-sup-0001-S1.pdf187.1 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. Franze, J. Guck, Rep. Prog. Phys. 2010, 73, 094601.
- 2J. Wells, C. Kao, E. D. Jansen, P. Konrad, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 064003.
- 3Y. Hu, W. Zhong, J. M. F. Wan, A. C. H. Yu, Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013, 39, 915.
- 4M. Kobayashi, A. Pascual-Leone, Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 145.
- 5E. S. Boyden, F. Zhang, E. Bamberg, G. Nagel, K. Deisseroth, Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1263.
- 6M. G. Shapiro, K. Homma, S. Villarreal, C.-P. Richter, F. Bezanilla, Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 736.
- 7A. R. Duke, M. W. Jenkins, H. Lu, J. M. McManus, H. J. Chiel, E. D. Jansen, Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2600.
- 8J. Wells, C. Kao, K. Mariappan, J. Albea, E. D. Jansen, P. Konrad, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 504.
- 9J. Wells, P. Konrad, C. Kao, E. D. Jansen, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 163, 326.
- 10A. D. Izzo, E. Suh, J. Pathria, J. T. Walsh, D. S. Whitlon, C. P. Richter, J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 021008.
- 11C. P. Richter, R. Bayon, A. D. Izzo, M. Otting, E. Suh, S. Goyal, J. Hotaling, J. T. Walsh Jr., Hear. Res. 2008, 242, 42.
- 12C. P. Richter, A. I. Matic, J. D. Wells, E. D. Jansen, J. T. Walsh, Laser Photonics Rev. 2011, 5, 68.
- 13J. Wells, C. Kao, P. Konrad, T. Milner, J. Kim, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, E. D. Jansen, Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 2567.
- 14E. J. Katz, I. K. Ilev, V. Krauthamer, D. H. Kim, D. Weinreich, NeuroReport 2010, 21, 662.
- 15E. Hutter, J. H. Fendler, Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1685.
- 16M. E. Stewart, C. R. Anderton, L. B. Thompson, J. Maria, S. K. Gray, J. A. Rogers, R. G. Nuzzo, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 494.
- 17G. Baffou, R. Quidant, Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 171.
- 18C. Paviolo, J. W. Haycock, J. Yong, A. Yu, P. R. Stoddart, S. L. McArthur, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 2277.
- 19C. F. Bohren, Am. J. Phys. 1983, 51, 323.
- 20L. R. Hirsch, R. J. Stafford, J. A. Bankson, S. R. Sershen, R. E. Price, J. D. Hazle, N. J. Halas, J. L. West, Proc. Second Joint EMBS/BMES Conf., Houston, TX, USA 2002.
- 21G. Fischer, S. Kostic, H. Nakai, F. Park, D. Sapunar, H. Yu, Q. Hogan, J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 199, 43.
- 22J. D. Wells, S. Thomsen, P. Whitaker, E. D. Jansen, C. C. Kao, P. E. Konrad, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 513.