Actuator and sensor fault estimation based on a proportional multiple-integral sliding mode observer for linear parameter varying systems with inexact scheduling parameters
Samuel Gómez-Peñate
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Francisco-Ronay López-Estrada
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Mexico
Correspondence Francisco-Ronay López-Estrada, Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Chiapas, Mexico.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGuillermo Valencia-Palomo
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Hermosillo, Hermosillo, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorDamiano Rotondo
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IDE), University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
Search for more papers by this authorMaria-Eusebia Guerrero-Sánchez
Cátedras Conacyt - Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Hermosillo, Hermosillo, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorSamuel Gómez-Peñate
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Francisco-Ronay López-Estrada
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Mexico
Correspondence Francisco-Ronay López-Estrada, Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Tuxtla Gutiérrez, TURIX-Dynamics - Diagnosis and Control Group, Tuxtla Gutierrez, Chiapas, Mexico.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGuillermo Valencia-Palomo
Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Hermosillo, Hermosillo, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorDamiano Rotondo
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IDE), University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
Search for more papers by this authorMaria-Eusebia Guerrero-Sánchez
Cátedras Conacyt - Tecnológico Nacional de México/IT Hermosillo, Hermosillo, Mexico
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, 759736
Abstract
This article proposes an approach for the estimation of states, actuator, and sensor faults in nonlinear systems represented by a polytopic linear parameter varying (LPV) system with inexact scheduling parameters. In the traditional LPV approaches, the scheduling variables are considered to be perfectly known. However, in practical applications, their measurement may contain precision and calibration errors or noise that can affect the performance of the diagnostic systems. Therefore, this work proposes the design of a proportional multiple-integral sliding mode observer for fault diagnosis (FD) that copes with LPV systems with inexact scheduling parameters. Due to the introduction of some nonlinear functions, the proposed observer is a nonlinear parameter varying system for which stability and robustness performance are formulated using the Lyapunov technique and a H∞ performance criterion. It is shown that the design conditions boil down to a set of linear matrix inequalities whose solution allows computing the observer gain matrix along with the tunable parameters of the nonlinear functions. Results obtained using the simulator of an octocopter-type unmanned aerial vehicle are used to demonstrate the applicability and performance of the proposed FD scheme.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
References
- 1Chen L, Alwi H, Edwards C. Development and evaluation of an integral sliding mode fault-tolerant control scheme on the RECONFIGURE benchmark. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control. 2019; 29(16): 5314-5340.
- 2Gómez-Peñate S, Valencia-Palomo G, López-Estrada FR, Astorga-Zaragoza CM, Osornio-Rios RA, Santos-Ruiz I. Sensor fault diagnosis based on a sliding mode and unknown input observer for Takagi-Sugeno systems with uncertain premise variables. Asian J Control. 2019; 21(1): 339-353.
- 3Alwi H, Edwards C, Marcos A. Fault reconstruction using a LPV sliding mode observer for a class of LPV systems. J Frankl Inst. 2012; 349(2): 510-530.
- 4Henry D, Cieslak J, Zolghadri A, Efimov D. H∞/ H− LPV solutions for fault detection of aircraft actuator faults: bridging the gap between theory and practice. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control. 2015; 25(5): 649-672.
- 5Jia Q, Chen W, Zhang Y, Chen X. Robust fault reconstruction via learning observers in linear parameter-varying systems subject to loss of actuator effectiveness. IET Control Theory Appl. 2014; 8(1): 42-50.
- 6Guzmán-Rabasa JA, López-Estrada FR, González-Contreras BM, Valencia-Palomo G, Chadli M, Pérez-Patricio M. Actuator fault detection and isolation on a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle modeled as a linear parameter-varying system. Measur Control. 2019; 52(9-10): 1228-1239.
- 7Rotondo D, Cristofaro A, Johansen TA, Nejjari F, Puig V. Robust fault and icing diagnosis in unmanned aerial vehicles using LPV interval observers. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control. 2019; 29(16): 5456-5480.
- 8Li S, Wang H, Aitouche A, Christov N. Unknown input observer design for faults estimation using linear parameter varying model. application to wind turbine systems. Paper presented at: Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Systems and Control, Valencia, Spain; 2018:45-50.
- 9López-Estrada FR, Rotondo D, Valencia-Palomo G. A review of convex approaches for control, observation and safety of linear parameter varying and Takagi-Sugeno systems. Processes. 2019; 7(11): 814.
- 10López-Estrada FR, Santos-Estudillo O, Valencia-Palomo G, Gómez-Peñate S, Hernandez-Gutiérrez C. Robust qLPV tracking fault-tolerant control of a 3 DOF mechanical crane. Math Comput Appl. 2020; 25(3): 48.
- 11Bokor J, Balas G. Detection filter design for LPV systems − a geometric approach. Automatica. 2004; 40(3): 511-518.
- 12Ho LM. Robust residual generator synthesis for uncertain LPV systems applied to lateral vehicle dynamics. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol. 2018; 27(3): 1275-1283.
- 13Rodrigues M, Hamdi H, Theilliol D, Mechmeche C, BenHadj BN. Actuator fault estimation based adaptive polytopic observer for a class of LPV descriptor systems. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control. 2015; 25(5): 673-688.
- 14Bedioui N, Houimli R, Besbes M. Simultaneous sensor and actuator fault estimation for continuous-time polytopic LPV system. Int J Syst Sci. 2019; 50(6): 1290-1302.
- 15Brizuela Mendoza J, Sorcia Vázquez FDJ, Guzmán Valdivia C, Osorio Sánchez R, Martínez García M. Observer design for sensor and actuator fault estimation applied to polynomial LPV systems: a riderless bicycle study case. Int J Syst Sci. 2018; 49(14): 2996-3006.
- 16Li X, Zhu F. Simultaneous actuator and sensor fault estimation for descriptor LPV system based on
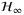 reduced-order observer. Opt Control Appl Methods. 2016; 37(6): 1122-1138.
reduced-order observer. Opt Control Appl Methods. 2016; 37(6): 1122-1138.
- 17Li X, Zhu F. Simultaneous time-varying actuator and sensor fault reconstruction based on PI observer for LPV systems. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process. 2015; 29(9): 1086-1098.
- 18Rotondo D, López-Estrada FR, Nejjari F, Ponsart JC, Theilliol D, Puig V. Actuator multiplicative fault estimation in discrete-time LPV systems using switched observers. J Frankl Inst. 2016; 353(13): 3176-3191.
- 19Zhang H, Zhang G, Wang J. H∞ observer design for LPV systems with uncertain measurements on scheduling variables: application to an electric ground vehicle. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron. 2016; 21(3): 1659-1670.
- 20Aouaouda S, Chadli M, Cocquempot V, Tarek Khadir M. Multi-objective ℋ−/ℋ∞ fault detection observer design for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with unmeasurable premise variables: descriptor approach. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process. 2013; 27(12): 1031-1047.
- 21López-Estrada FR, Ponsart JC, Astorga-Zaragoza C, Theilliol D. Fault estimation observer design for descriptor-LPV systems with unmeasurable gain scheduling functions. Paper presented at: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol 2013), Nice, France; 2013:269-274.
- 22Hassanabadi AH, Shafiee M, Puig V. Actuator fault diagnosis of singular delayed LPV systems with inexact measured parameters via PI unknown input observer. IET Control Theory Appl. 2017; 11(12): 1894-1903.
- 23Zhu K, Zhao J. Simultaneous fault detection and control for switched LPV systems with inexact parameters and its application. Int J Syst Sci. 2017; 48(14): 2909-2920.
- 24Gómez-Peñate S, López-Estrada FR, Valencia-Palomo G, Rotondo D, Enríquez-Zárate J. Actuator and sensor fault estimation based on a proportional-integral quasi-LPV observer with inexact scheduling parameters. IFAC-PapersOnLine. 2019; 52(28): 100-105.
10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.12.355 Google Scholar
- 25Cai X, Liu Y, Zhang W. Control design for a class of nonlinear parameter varying systems. Int J Syst Sci. 2015; 46(9): 1638-1647.
- 26Sala A, Ariño C, Robles R. Gain-scheduled control via convex nonlinear parameter varying models. IFAC-PapersOnLine. 2019; 52(28): 70-75.
10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.12.350 Google Scholar
- 27Chen F, Kang S, Ji L, Zhang X. Stability and stabilisation for time-varying polytopic quadratic systems. Int J Control. 2017; 90(2): 357-367.
- 28Kanarachos S, Dizqah AM, Chrysakis G, Fitzpatrick ME. Optimal design of a quadratic parameter varying vehicle suspension system using contrast-based fruit fly optimisation. Appl Soft Comput. 2018; 62: 463-477.
- 29Rotondo D, Johansen TA. Analysis and design of quadratic parameter varying (QPV) control systems with polytopic attractive region. J Frankl Inst. 2018; 355(8): 3488-3507.
- 30Yang R, Rotondo D, Puig V. D-stable controller design for lipschitz NLPV system. IFAC-PapersOnLine. 2019; 52(28): 88-93.
10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.12.353 Google Scholar
- 31Tan CP, Edwards C. An LMI approach for designing sliding mode observers. Int J Control. 2001; 74(16): 1559-1568.
- 32Utkin VI. Sliding Modes in Control and Optimization. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media; 2013.
- 33Edwards C, Spurgeon SK, Patton RJ. Sliding mode observers for fault detection and isolation. Automatica. 2000; 36(4): 541-553.
- 34Tan CP, Edwards C. Sliding mode observers for detection and reconstruction of sensor faults. Automatica. 2002; 38(10): 1815-1821.
- 35Brahim AB, Dhahri S, Hmida FB, Sellami A. An ℋ∞ sliding mode observer for Takagi–Sugeno nonlinear systems with simultaneous actuator and sensor faults. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci. 2015; 25(3): 547-559.
- 36Chen L, Edwards C, Alwi H. Sensor fault estimation using LPV sliding mode observers with erroneous scheduling parameters. Automatica. 2019; 101: 66-77.
- 37Rotondo D, Sanchez HS, Nejjari F, Puig V. Analysis and design of linear parameter varying systems using LMIs. RIAI Rev Iberoam Autom Inform Ind. 2019; 16: 1-14.
- 38Youssef T, Chadli M, Karimi HR, Wang R. Actuator and sensor faults estimation based on proportional integral observer for TS fuzzy model. J Frankl Inst. 2017; 354(6): 2524-2542.
- 39Ichalal D, Marx B, Ragot J, Maquin D. State estimation of Takagi–Sugeno systems with unmeasurable premise variables. IET Control Theory Appl. 2010; 4(5): 897-908.
- 40Elleuch I, Khedher A, Othman KB. Design of a proportional integral observer based on sliding mode principle for uncertain Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems: applications to a turbo-reactor. Int J Autom Control. 2018; 12(2): 179-194.
- 41Adir VG, Stoica AM. Integral LQR control of a star-shaped octorotor. Incas Bull. 2012; 4(2): 3.
10.13111/2066-8201.2012.4.2.1 Google Scholar
- 42Adir VG, Stoica AM, Whidborne JF. Sliding mode control of a 4Y octorotor. UPB Sci Bull Ser D. 2012; 74(4): 37-51.
- 43Li T, Zhang Y, Gordon BW. Passive and active nonlinear fault-tolerant control of a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle based on the sliding mode control technique. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part I J Syst Control Eng. 2013; 227(1): 12-23.
- 44Wang X, Sun S, van Kampen EJ, Chu Q. Quadrotor fault tolerant incremental sliding mode control driven by sliding mode disturbance observers. Aerosp Sci Technol. 2019; 87: 417-430.
- 45Saied M, Lussier B, Fantoni I, Shraim H, Francis C. Active versus passive fault-tolerant control of a redundant multirotor UAV. Aeronaut J. 2020; 124(1273): 385-408.
- 46Bertrand S, Guénard N, Hamel T, Piet-Lahanier H, Eck L. A hierarchical controller for miniature VTOL UAVs: design and stability analysis using singular perturbation theory. Control Eng Pract. 2011; 19(10): 1099-1108.
- 47Ortiz-Torres G, Castillo P, Sorcia-Vázquez FD, et al. Fault estimation and fault tolerant control strategies applied to vtol aerial vehicles with soft and aggressive actuator faults. IEEE Access. 2020; 8: 10649-10661.
- 48Avram RC, Zhang X, Muse J. Quadrotor actuator fault diagnosis and accommodation using nonlinear adaptive estimators. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol. 2017; 25(6): 2219-2226.
- 49Saied M, Lussier B, Fantoni I, Francis C, Shraim H, Sanahuja G. Fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy for rotor failure in an octorotor. Paper presented at: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2015, Seattle, Washington; May 26, 2015:5266-5271; IEEE.
- 50Alwi H, Edwards C. Sliding mode fault-tolerant control of an octorotor using linear parameter varying-based schemes. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015; 9(4): 618-636.
- 51Tanaka K, Wang HO. Fuzzy Control Systems Design and Analysis: A Linear Matrix Inequality Approach. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons; 2004.
- 52Isermann R. Model-based fault-detection and diagnosis–status and applications. Ann Rev Control. 2005; 29(1): 71-85.
- 53Saied M, Shraim H, Francis C, Fantoni I, Lussier B. Actuator fault diagnosis in an octorotor UAV using sliding modes technique: theory and experimentation. Paper presented at: 2015 European Control Conference (ECC) 2015 July 15, Linz, Austria; 2015:1639-1644.
Citing Literature
Special Issue:Emerging Approaches for Nonlinear Parameter Varying (NLPV) Systems
25 November 2021
Pages 8420-8441